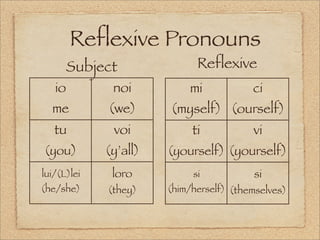
Il documento descrive le attività quotidiane di vari soggetti, fornendo vocaboli e frasi utili per la conversazione in italiano. Vengono anche introdotte le regole per esprimere l'ora e i verbi riflessivi. Inoltre, il testo include informazioni sulla regione Marche, evidenziando la sua storia e le sue industrie.