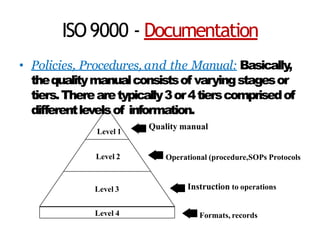
ISO 9000 provides quality management standards for organizations to implement quality assurance systems. It aims to facilitate international trade by providing commonly understood quality standards. Key aspects of ISO 9000 include establishing quality policies, documentation of processes, management commitment, and continual improvement. Organizations must demonstrate that their quality system meets the requirements of ISO 9001 through an external audit process. Implementing an ISO quality system involves investigating current practices, analyzing processes, designing new documentation, developing the quality system, implementing it, and ongoing maintenance.













![ISO9000 - The Philosophy
•
•
Basically,therearetwomindsetapproachestoISO 9000 registration.
First,toviewtheISO 9000seriesasasetof standardswhichneeds to
beaddressedsooneror later.
– Thisfirstapproachisinvariablyandprimarilymotivatedbya
commercial/marketing/businesssetofconvictions.]
TheotherapproachseestheISO 9000standardsassomethingmore
than justa model for quality assurance.
– ThisphilosophywillmoreoftenthannotseeinISO 9000an
opportunitytoimprovemanagerial style.
– Mostexpertsspeakof waysinwhichthevariousISO 9000models
canhelpacompanyreduceinternalcostand/orincreaseefficiency
.
•](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isointro1-231112071910-ed0b021c/85/ISO-Intro1-pptx-14-320.jpg)