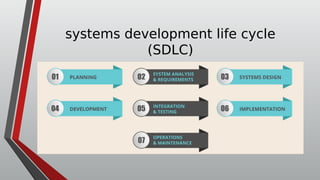
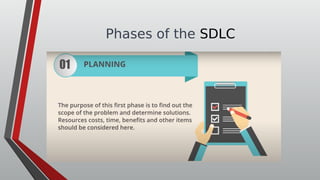
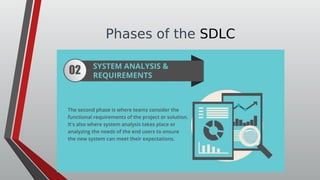
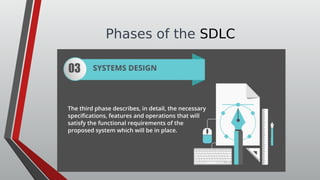
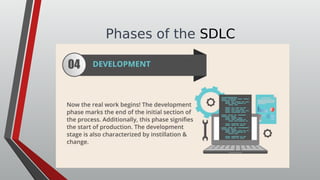
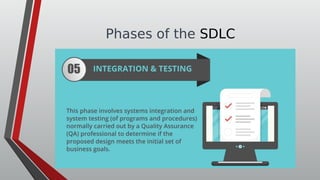
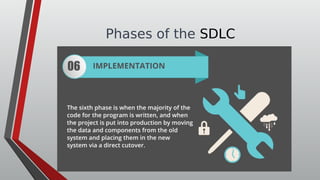
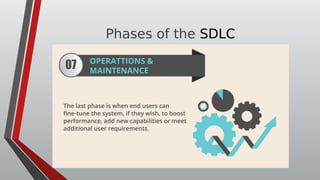
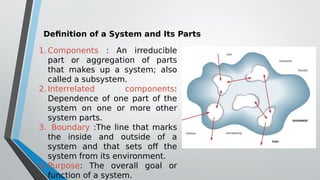
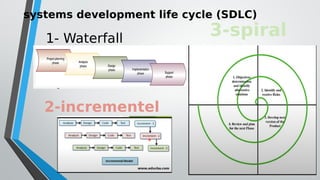
The document discusses information systems analysis and design (ISAD). It defines ISAD as the process of understanding, designing, and implementing an information system for an organization to improve efficiency and effectiveness. The document outlines the main steps in ISAD as system analysis, requirements gathering, system design, implementation, and maintenance. It also describes the systems development life cycle (SDLC) as a systematic approach consisting of planning, analysis, design, implementation, and maintenance phases.