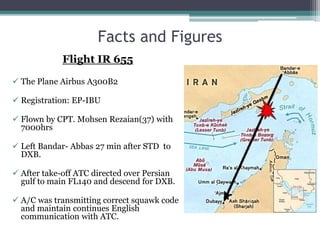
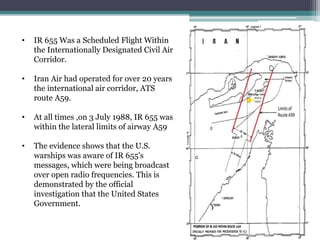
The document summarizes the shoot down of Iran Air Flight 655 by the USS Vincennes on July 3, 1988 which killed all 290 people on board. It provides background on the tensions between the US and Iran in the Persian Gulf due to the Iran-Iraq war. It describes the events, reactions, investigations and findings that the US Navy missile cruiser shot down the civilian airliner after mistakenly identifying it as a hostile fighter jet. It also examines the legal responsibilities and disputes between the US and Iranian governments over compensation.






















![The United States refused to accept liability
The United States refused to accept liability for the
destruction of IR 655
• Failed to offer any compensation to the Islamic Republic.
• Failed to take steps to guarantee the non-repetition of such an
incident.
• The offer made, took the form of an “”ex gratia”” [Latin for "by
favour“]. Payment was made to the victims but not to the Islamic
Republic.
**Either the shooting down of IR 655 was intentional or it was grossly
negligent. In either case, the United States actions still have the
character of an international crime and the United States bears full
responsibility.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ir655final-150610105959-lva1-app6892/85/Iran-air-flight-IR655-25-320.jpg)


