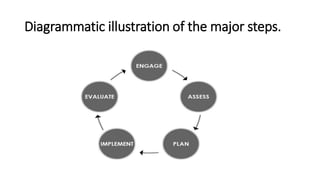
The document discusses the challenges involved in developing an infection prevention and control (IPC) protocol. It outlines the major steps as engaging stakeholders, assessing current IPC practices, planning IPC efforts, implementing the protocol, and evaluating progress. Some challenges discussed are lack of coordination with stakeholders, limited resources and data, gaps between planned and actual implementation, insufficient equipment and training, and poor monitoring and evaluation methods. The overall document provides an overview of the process for developing an IPC protocol and potential barriers that may be faced at each stage.