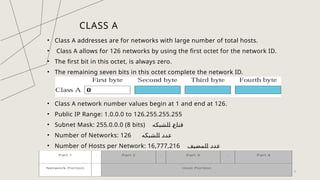
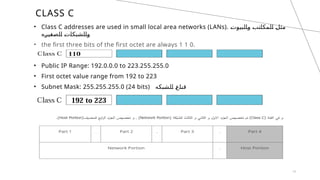
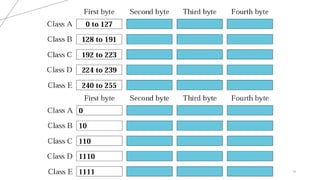
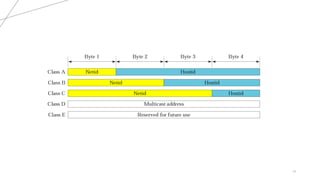
The document explains IP addresses, defining them as unique identifiers for devices on the internet structured in 32 bits divided into four octets. It categorizes IP addresses into classes A, B, C, D, and E, each with specific ranges and purposes, such as class A for large networks and class D for multicasting. It also provides examples of IP addresses and their corresponding classes based on the first octet values.