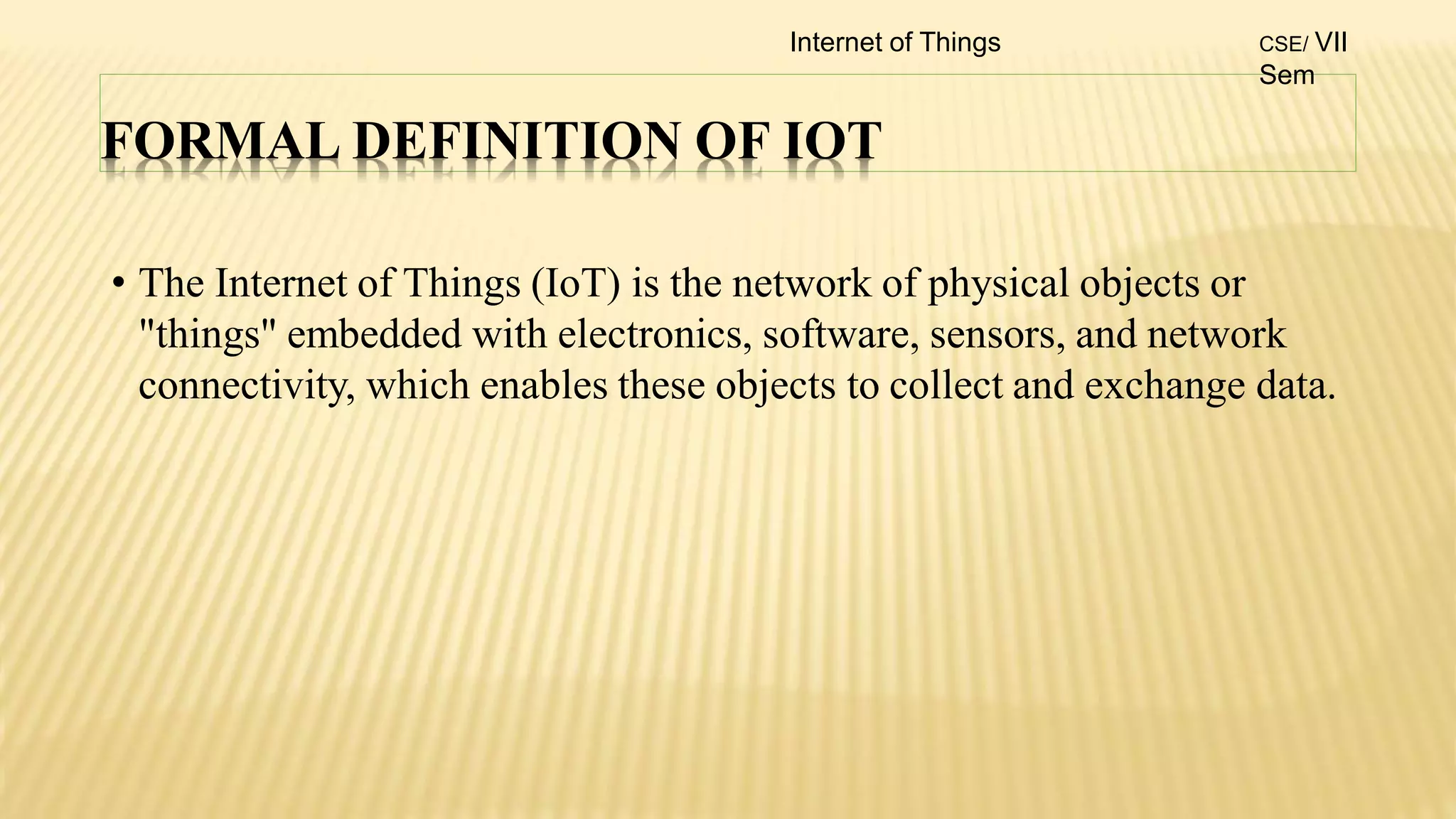
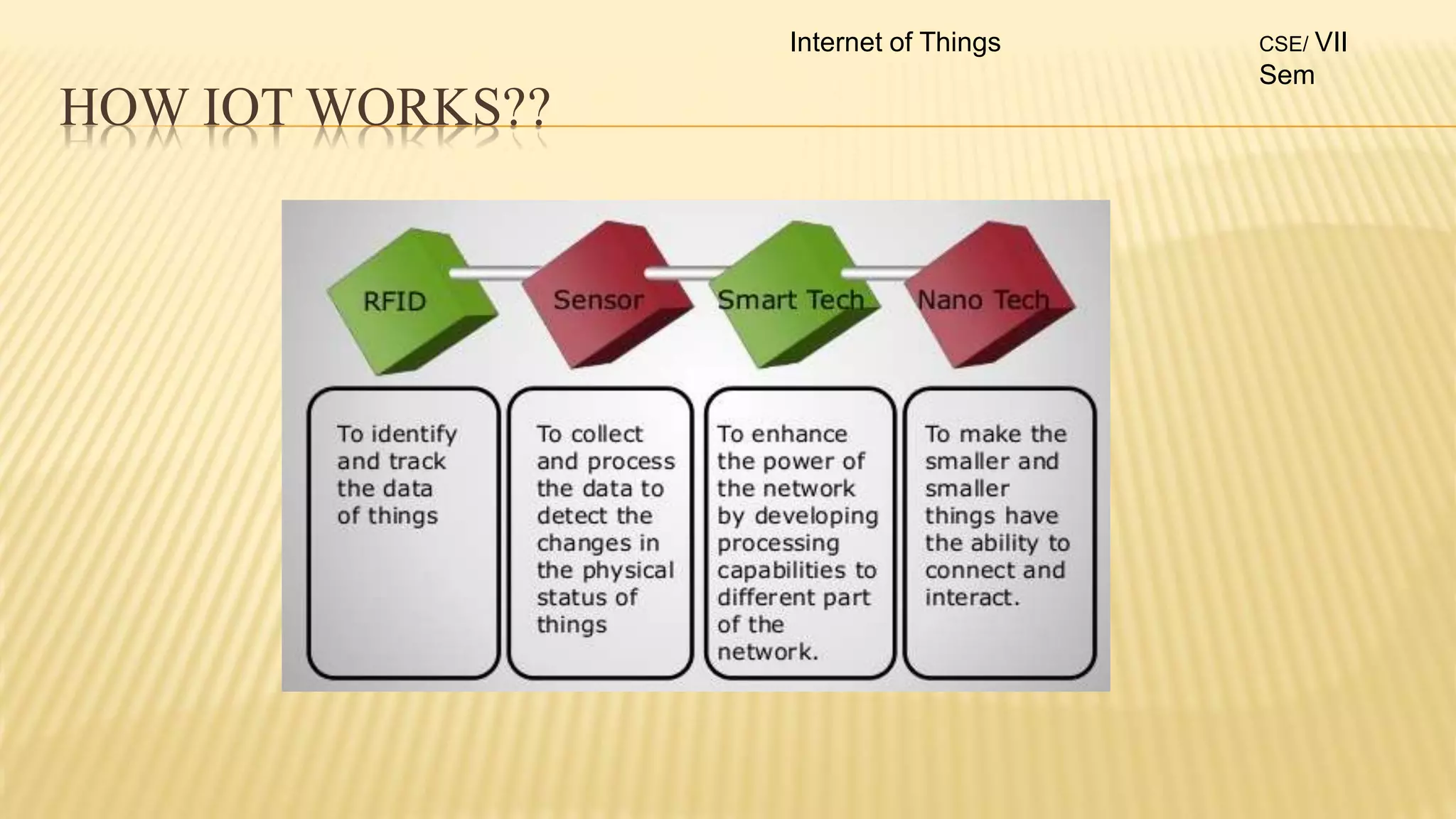
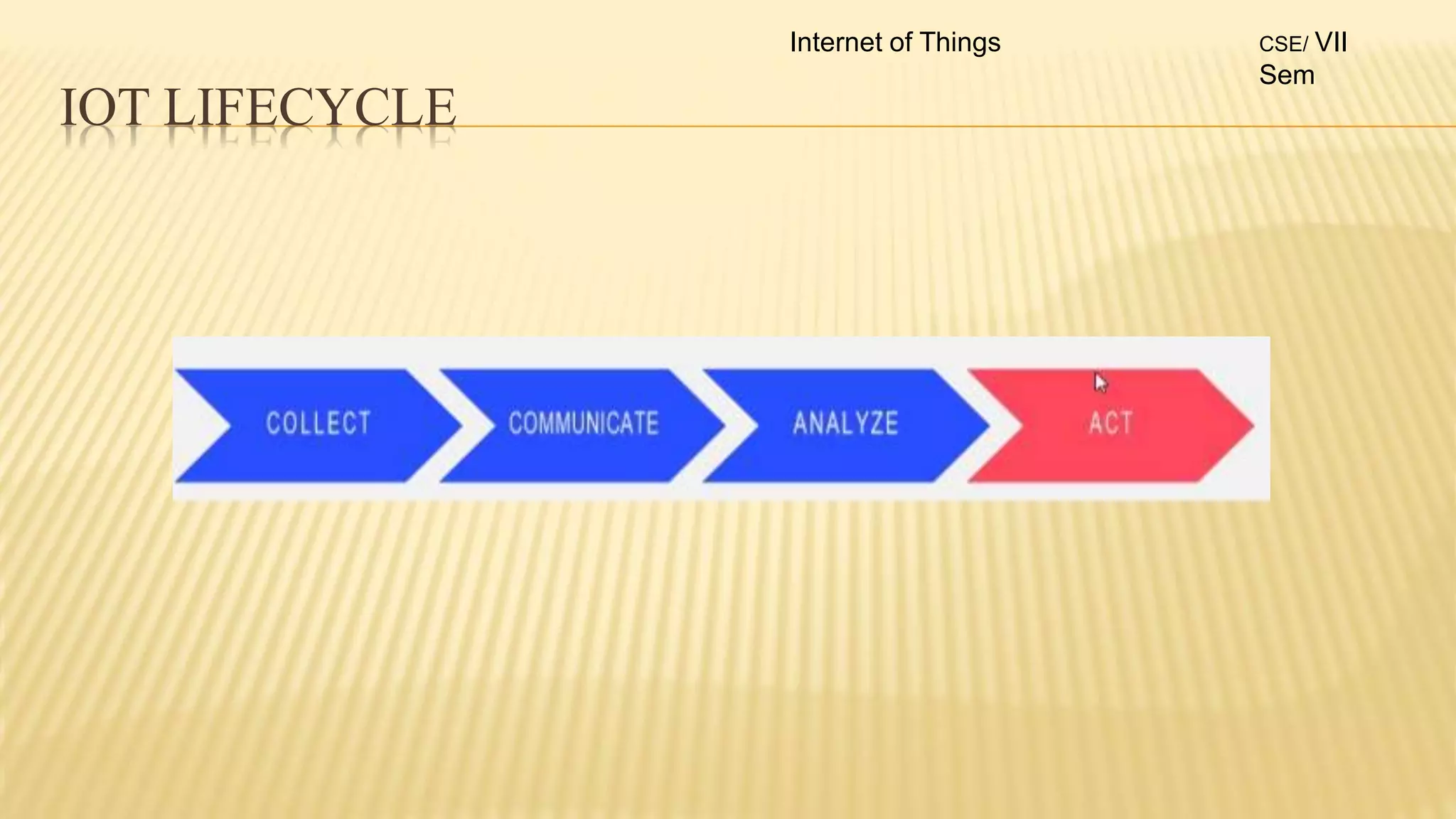
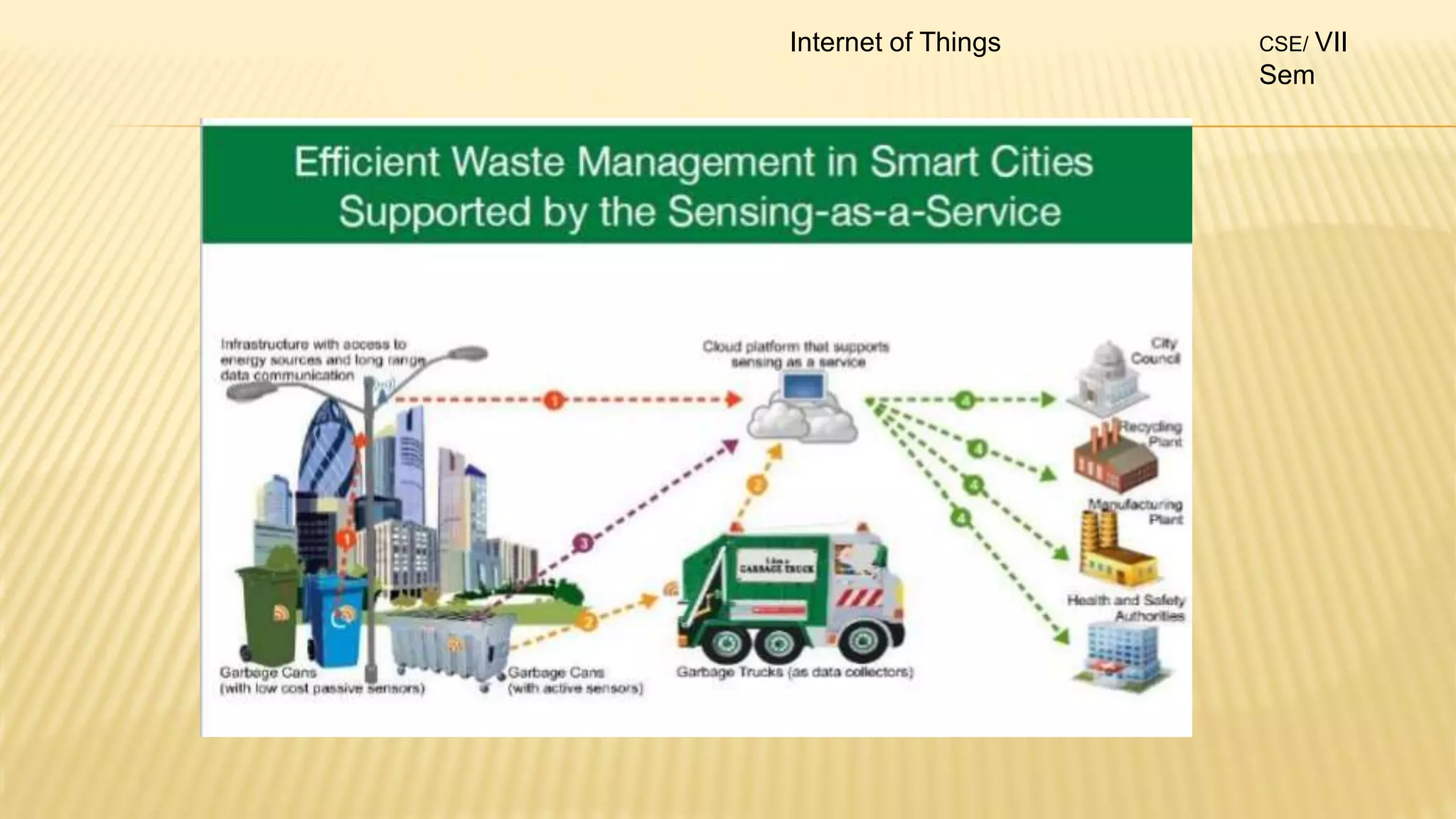
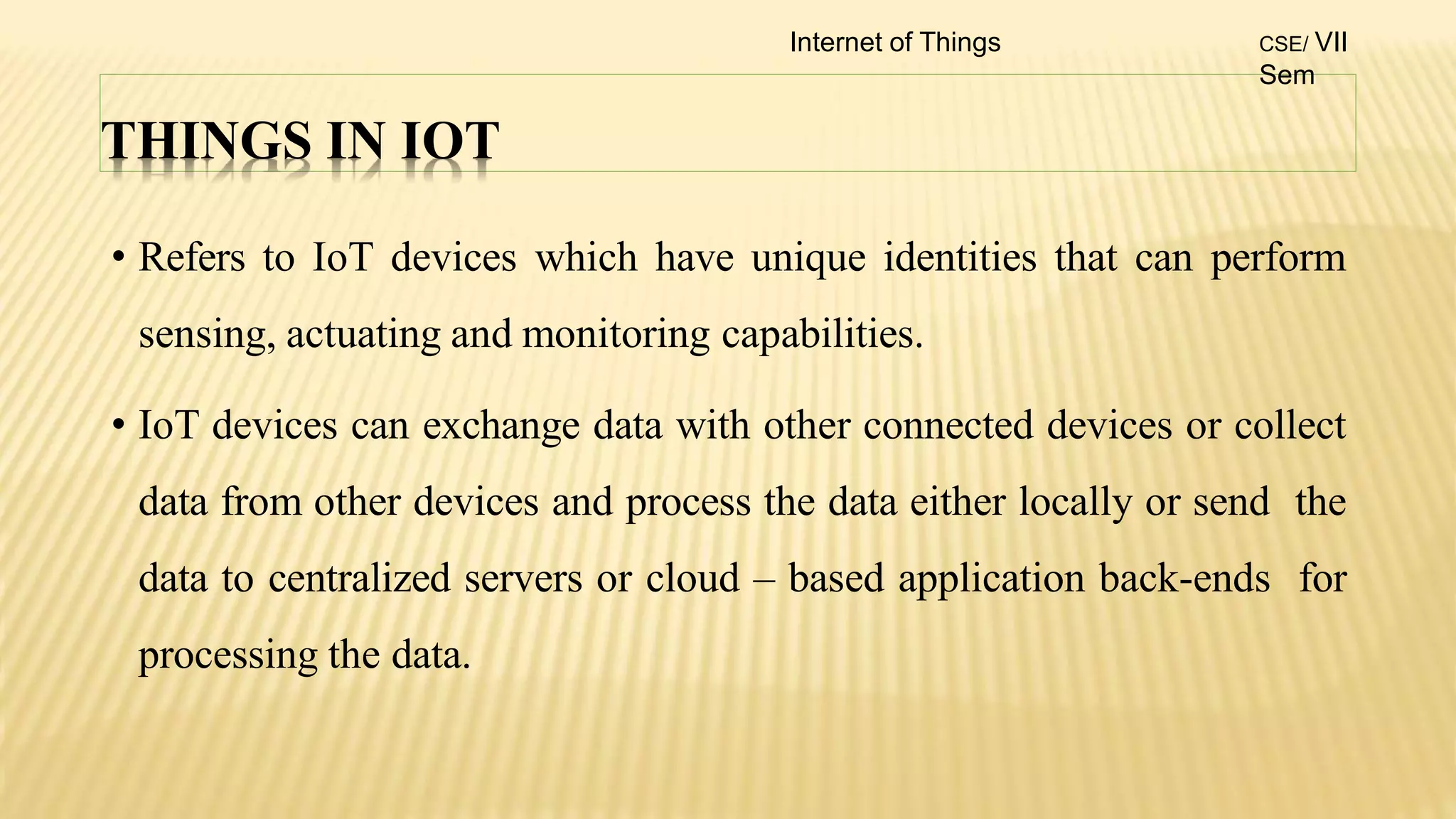
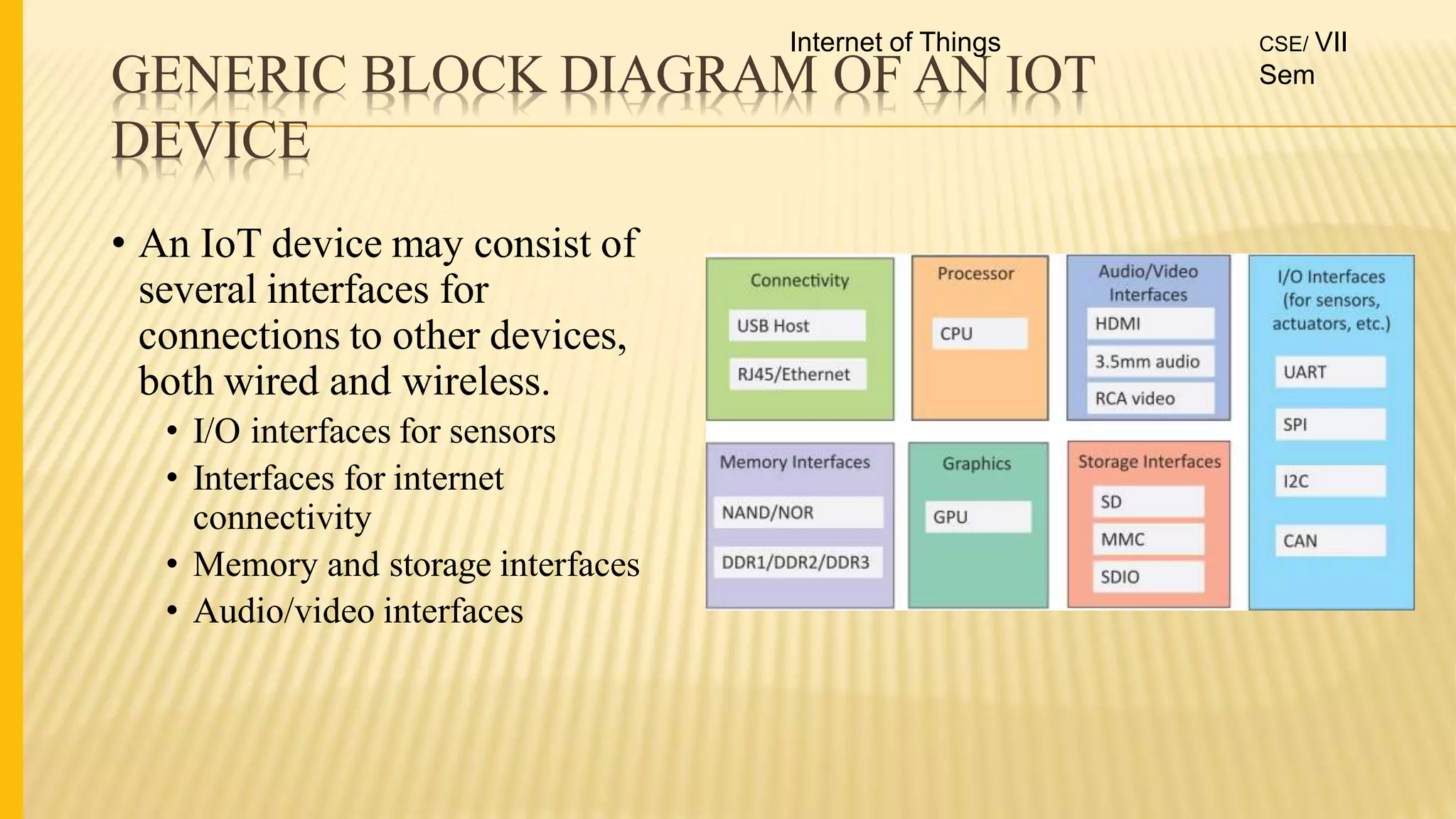
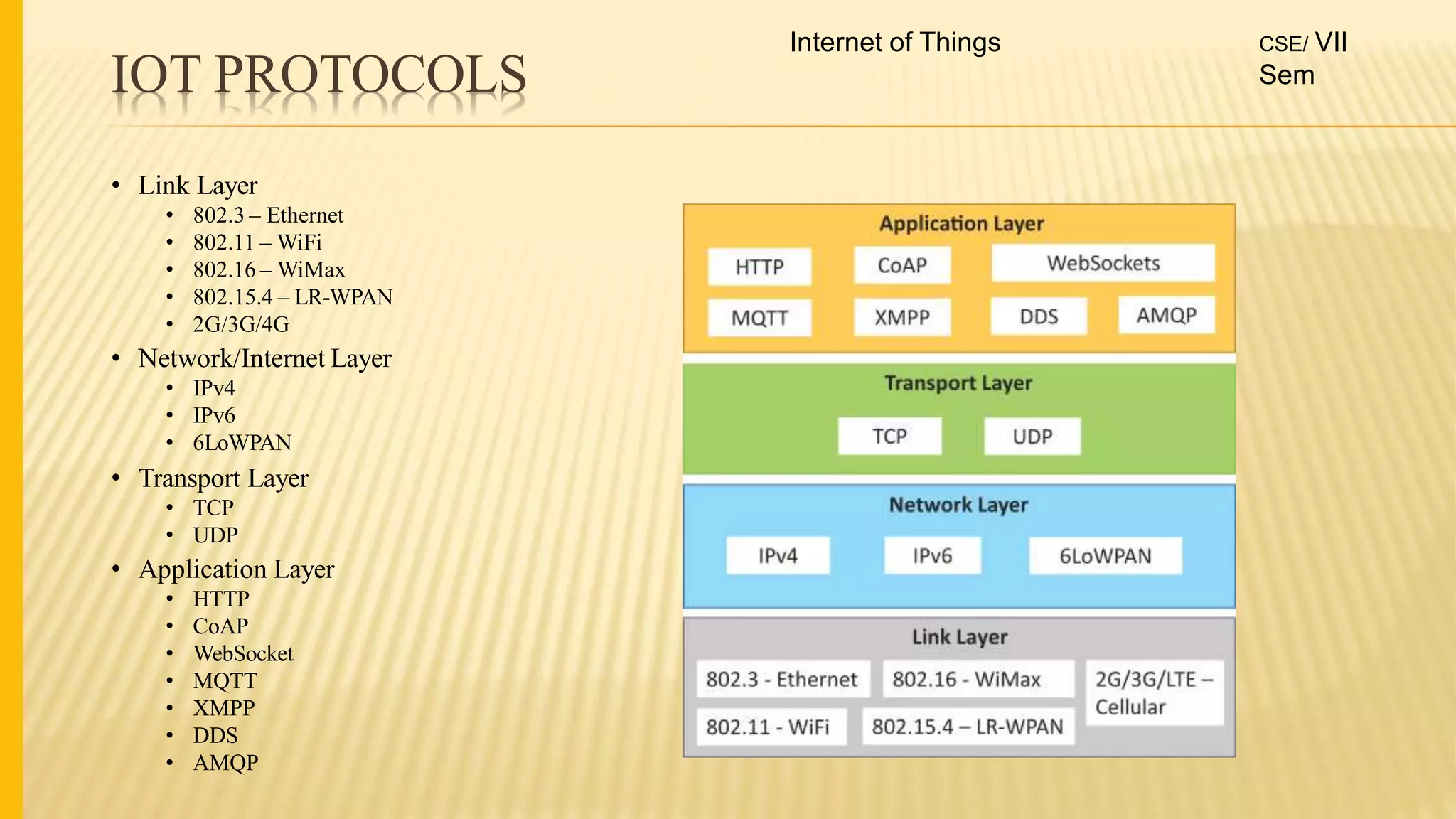
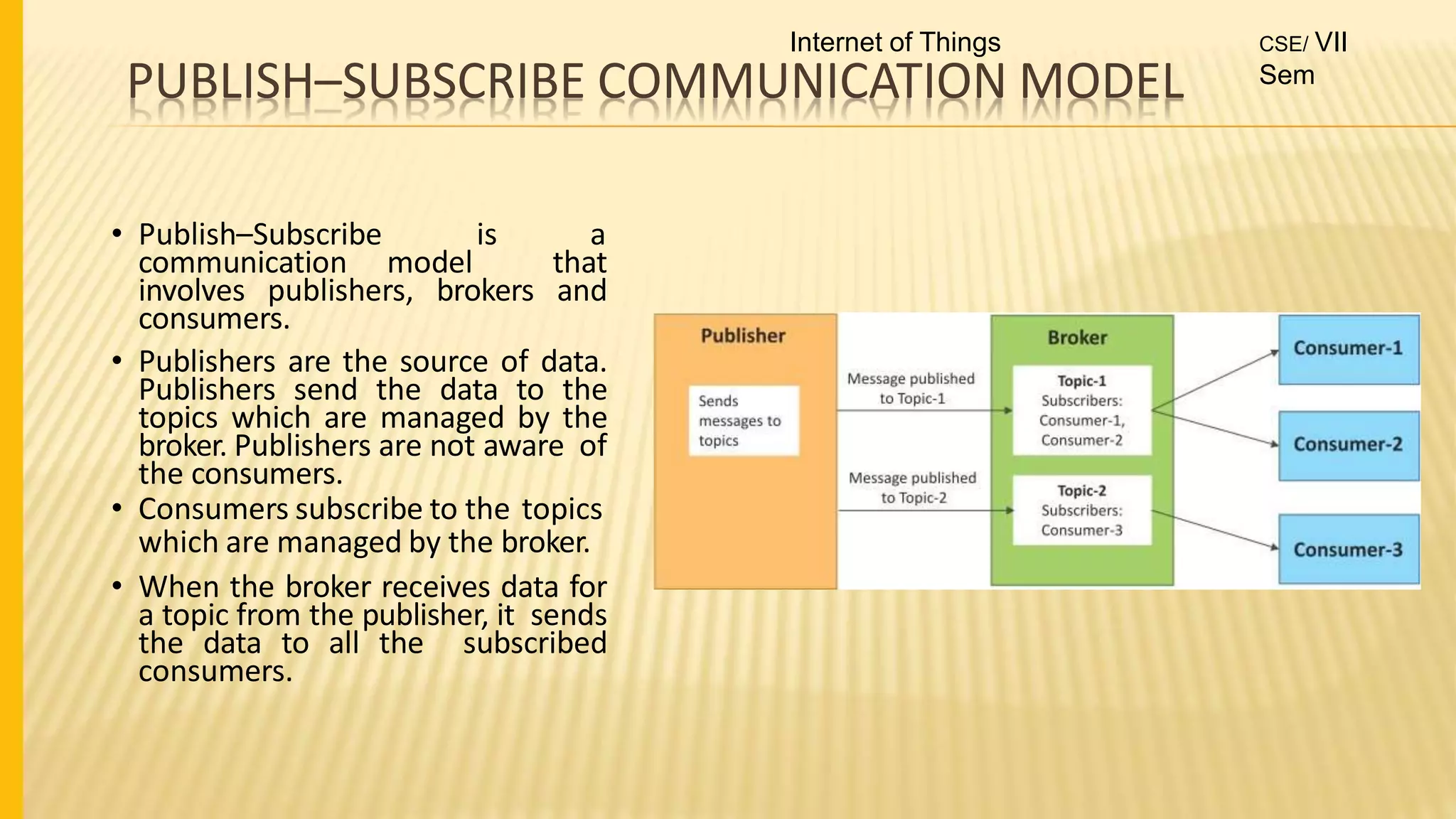
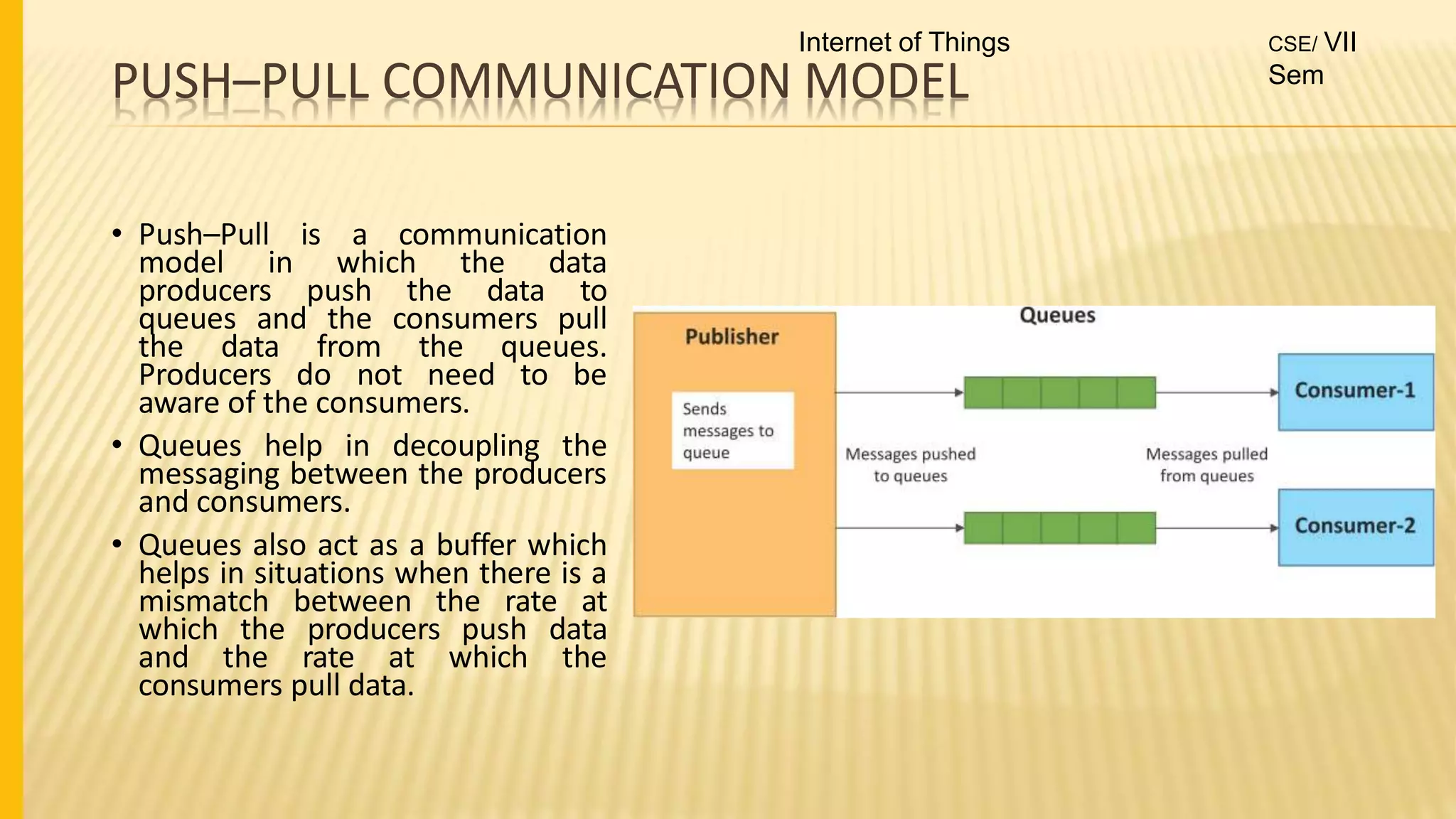
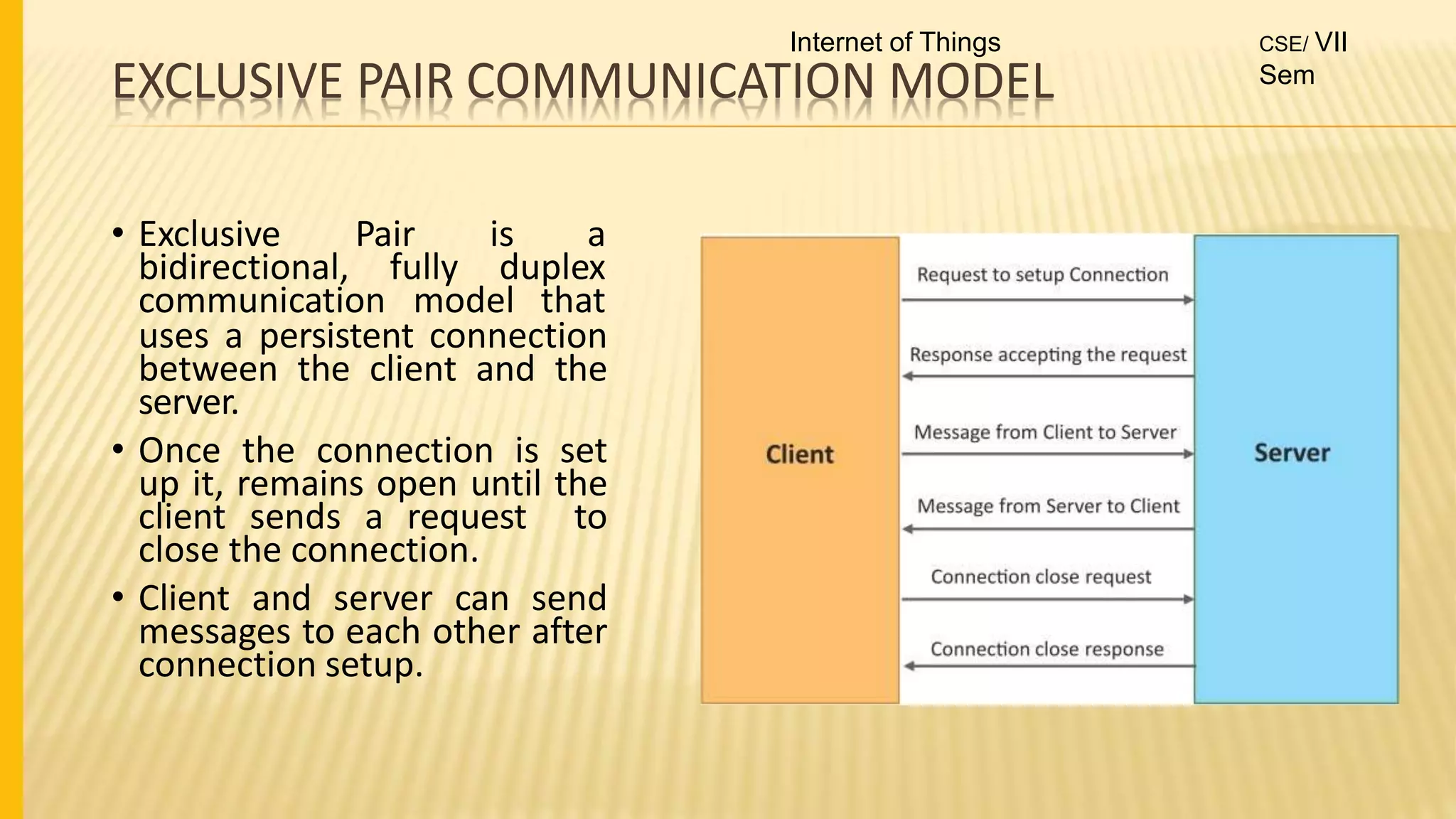
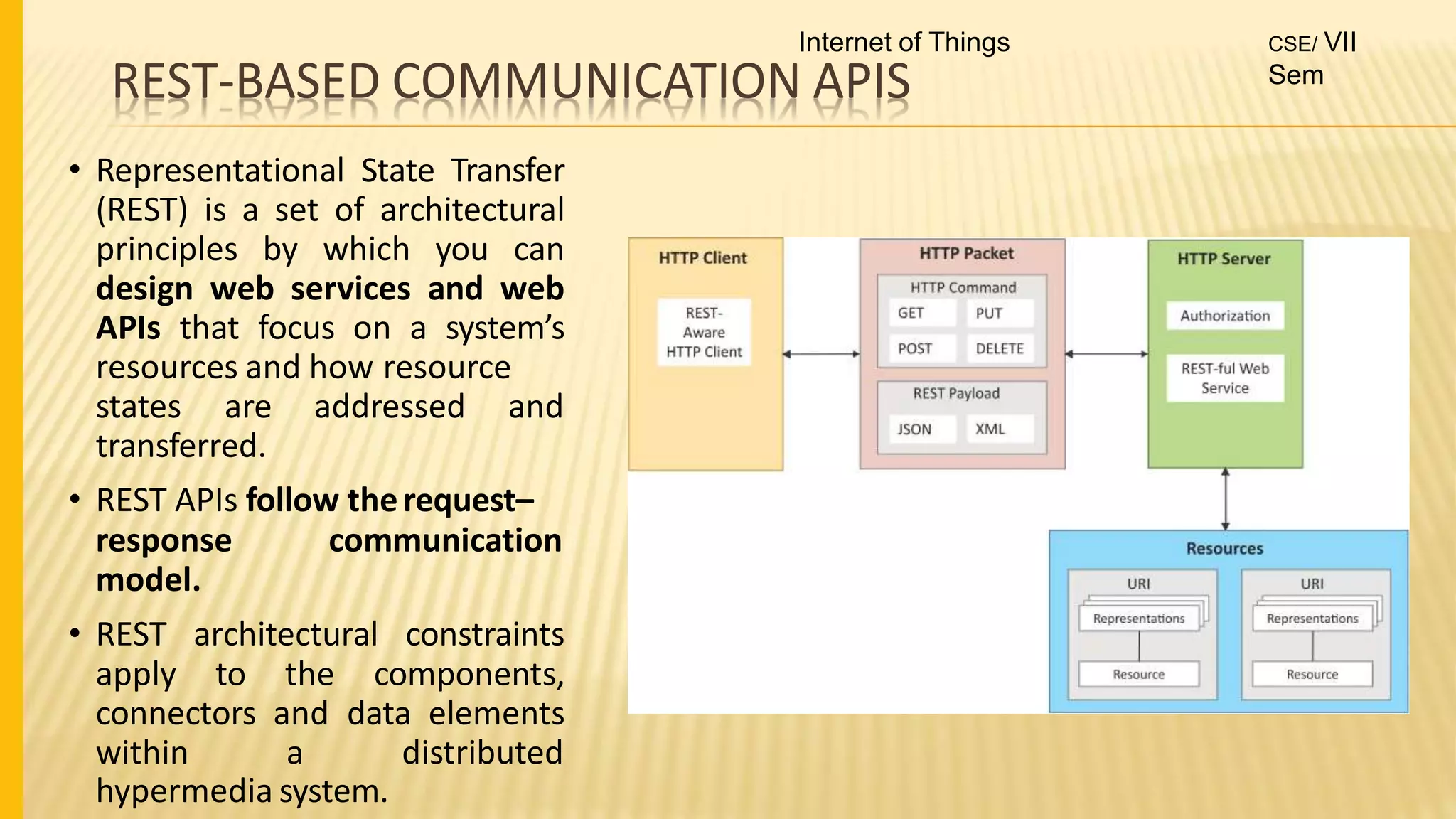
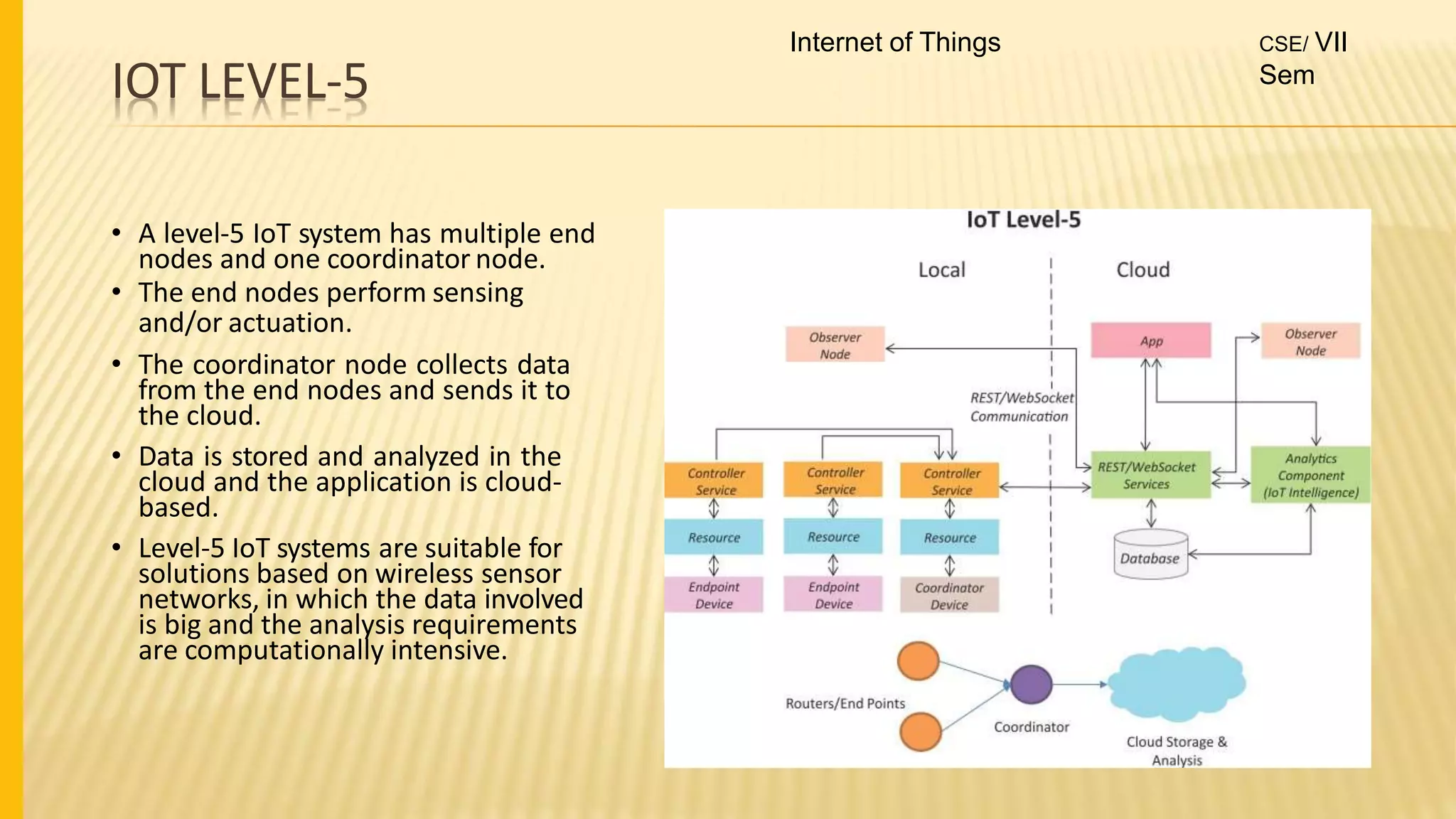
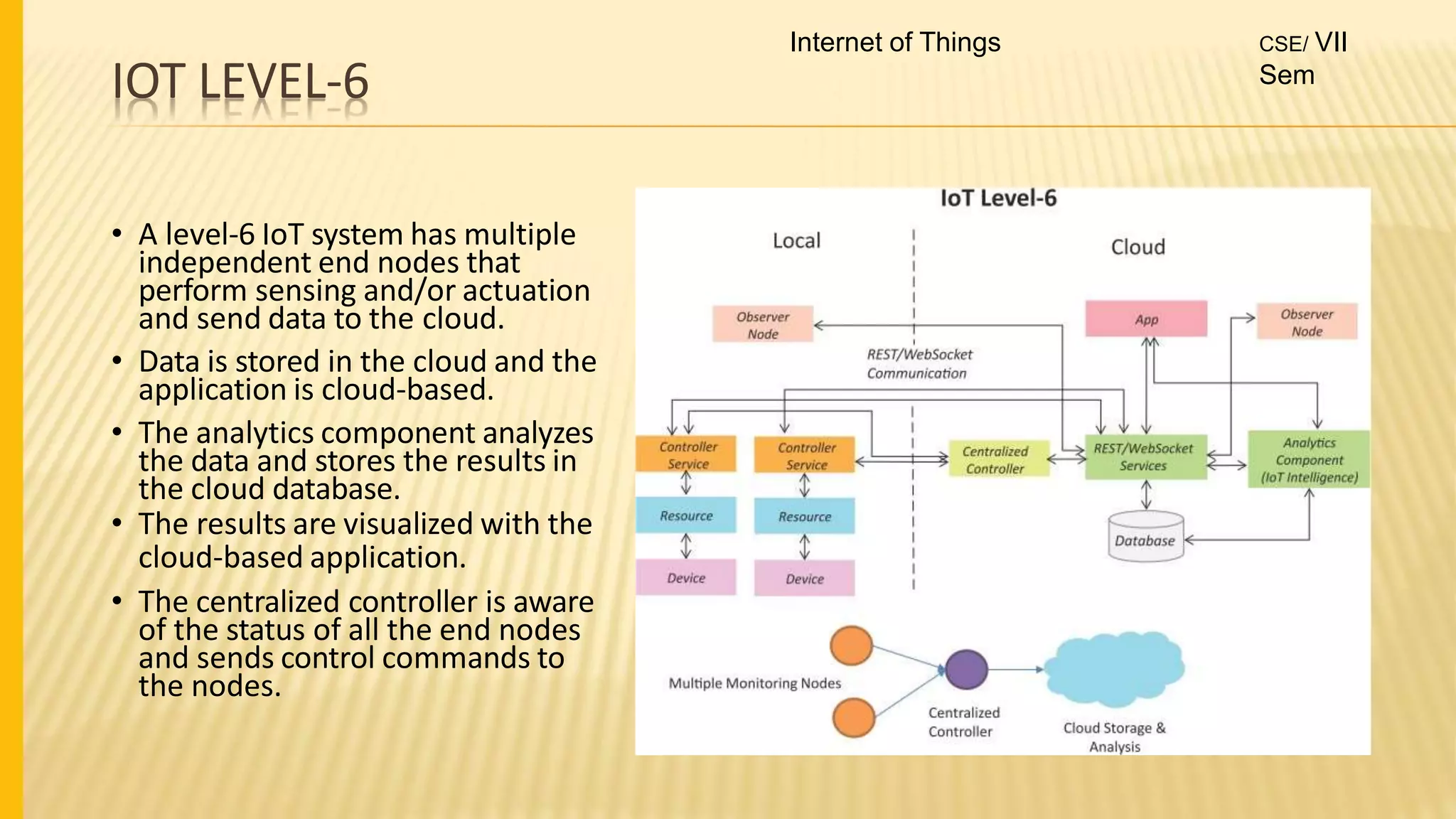
1. The document discusses the syllabus for the subject Internet of Things for the 4th year, 7th semester students. It includes the vision, mission and course outcomes of the Computer Science department.
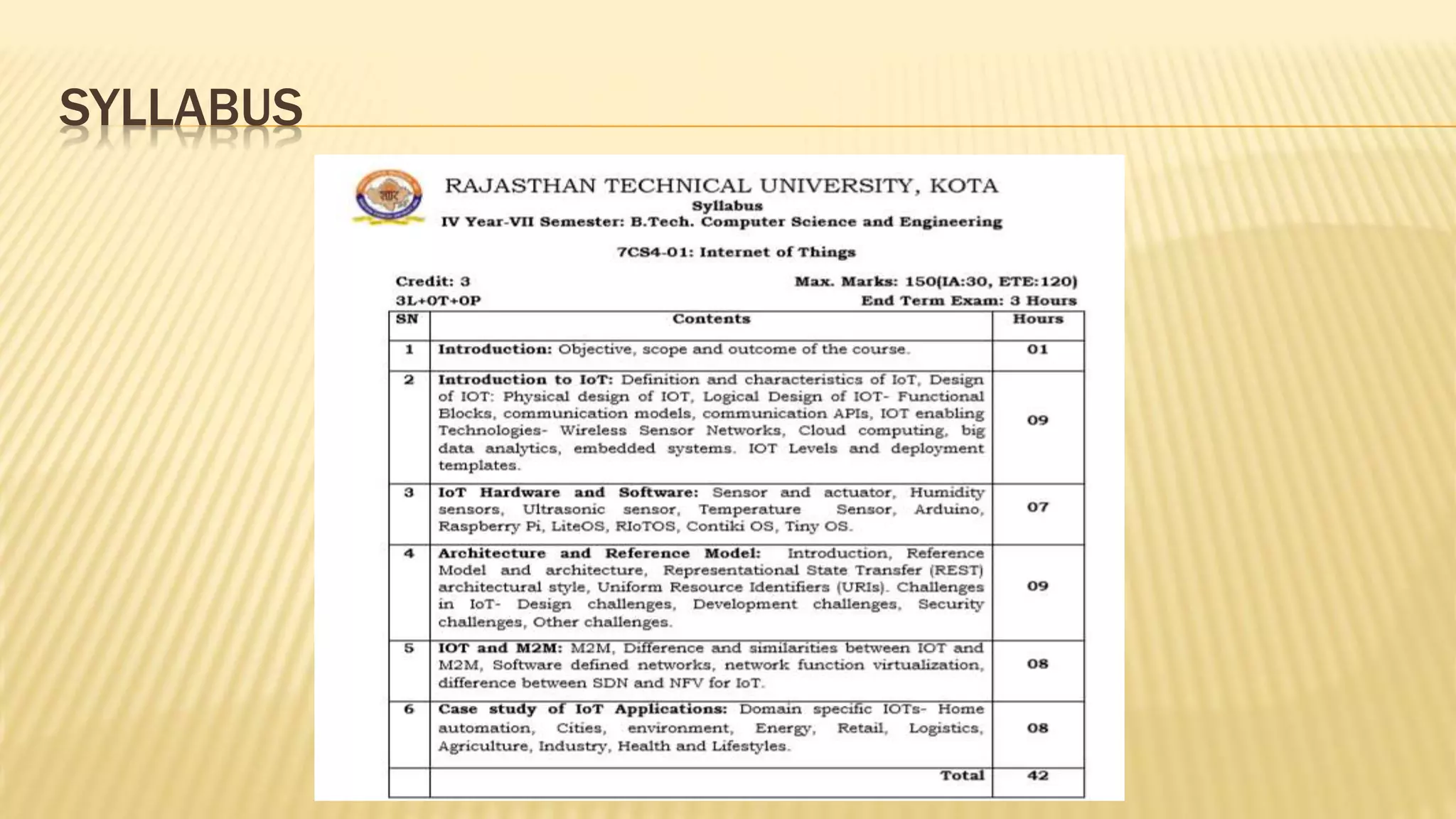
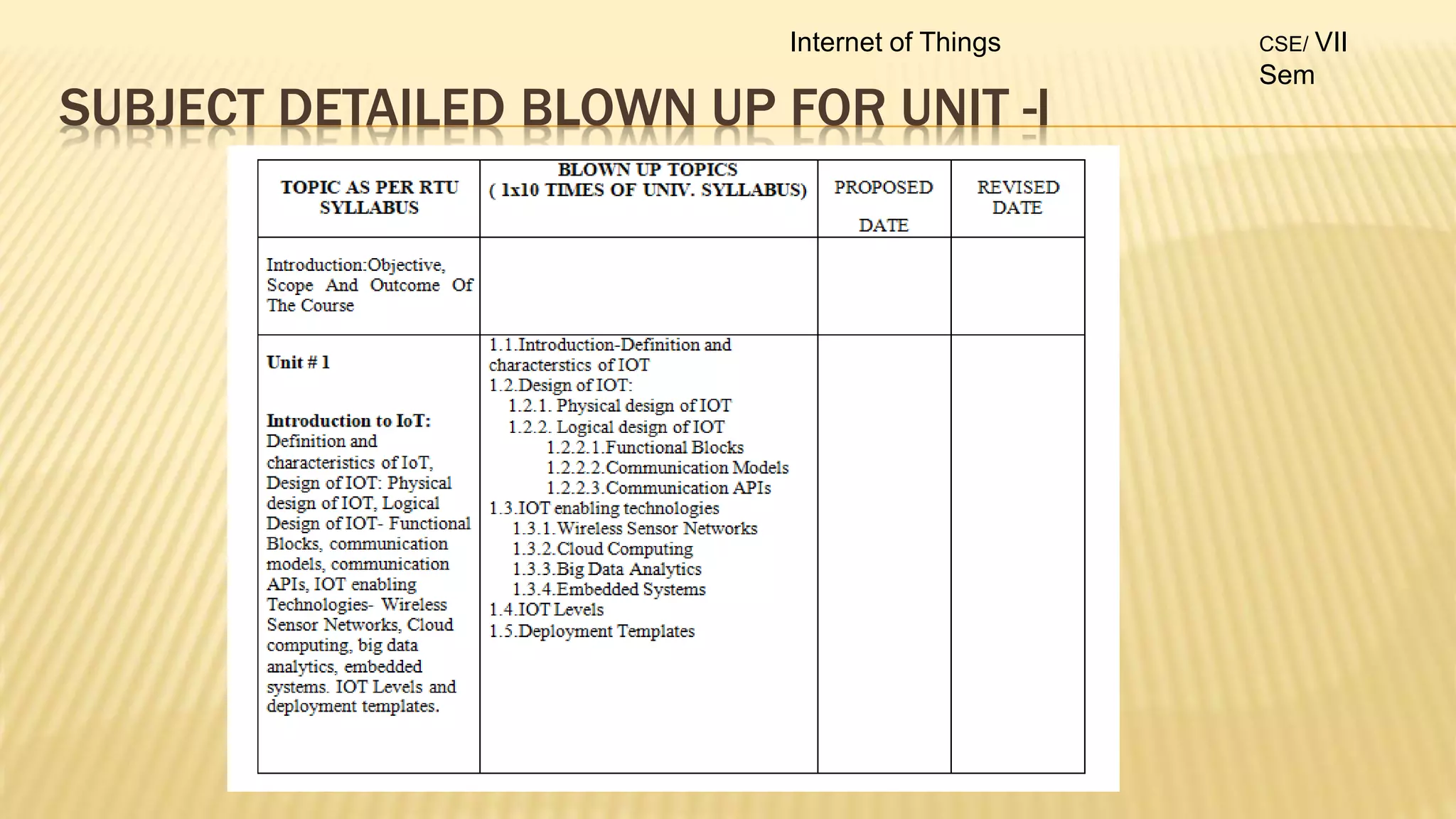
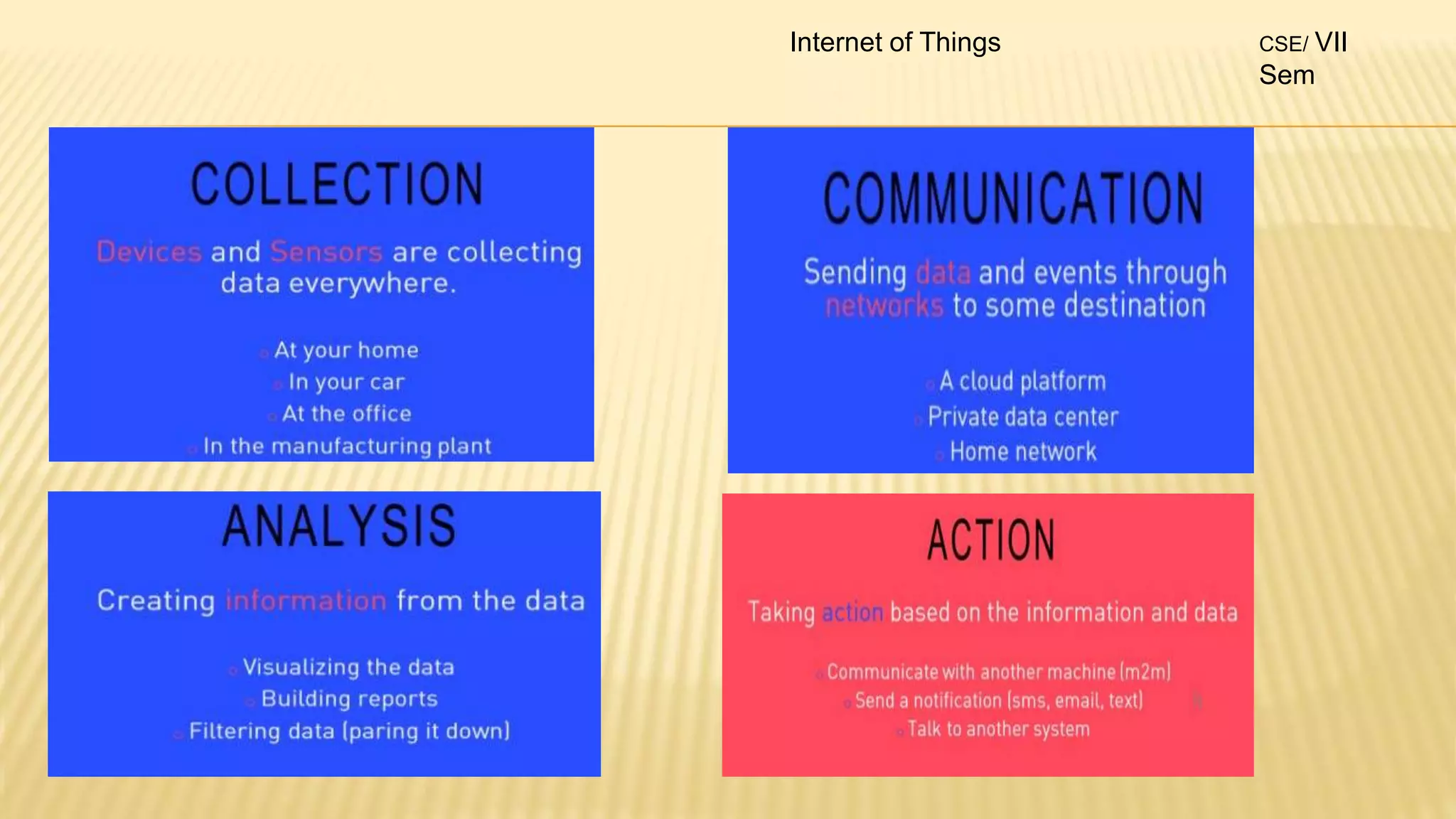
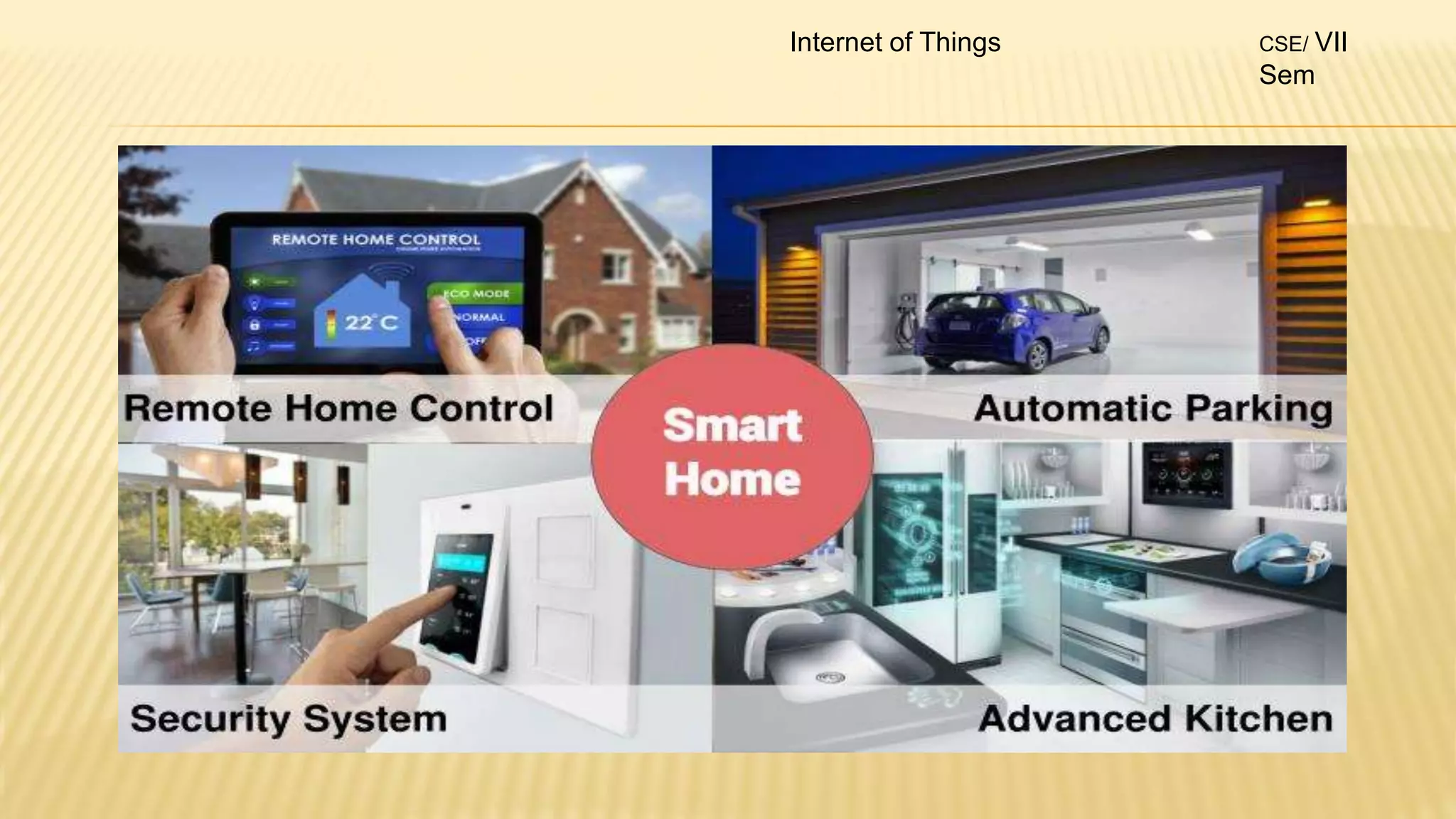
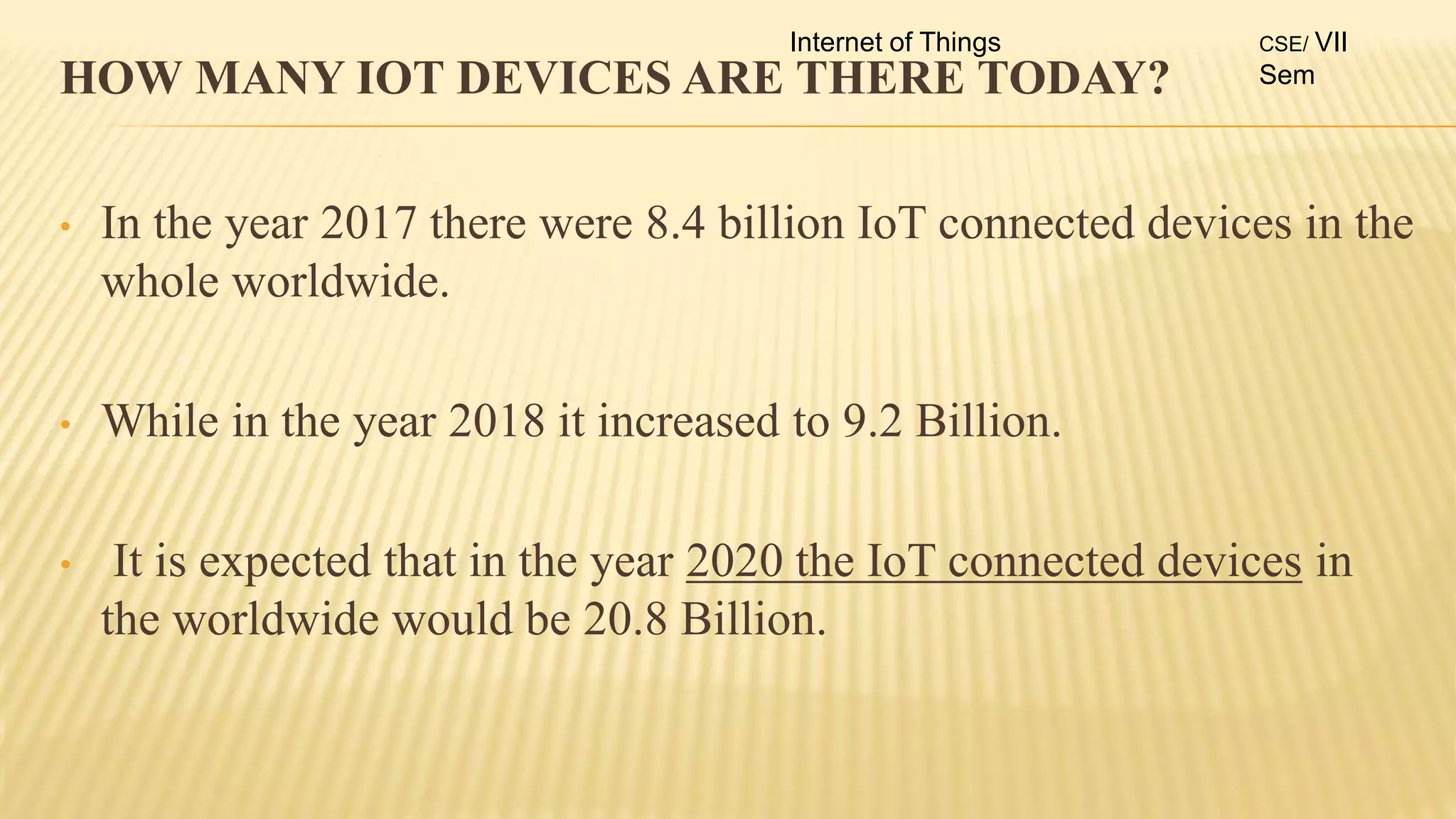
2. The syllabus is divided into 5 units - introduction to IoT, IoT sensors and devices, IoT architectures, comparison of IoT with other technologies, and applications of IoT.
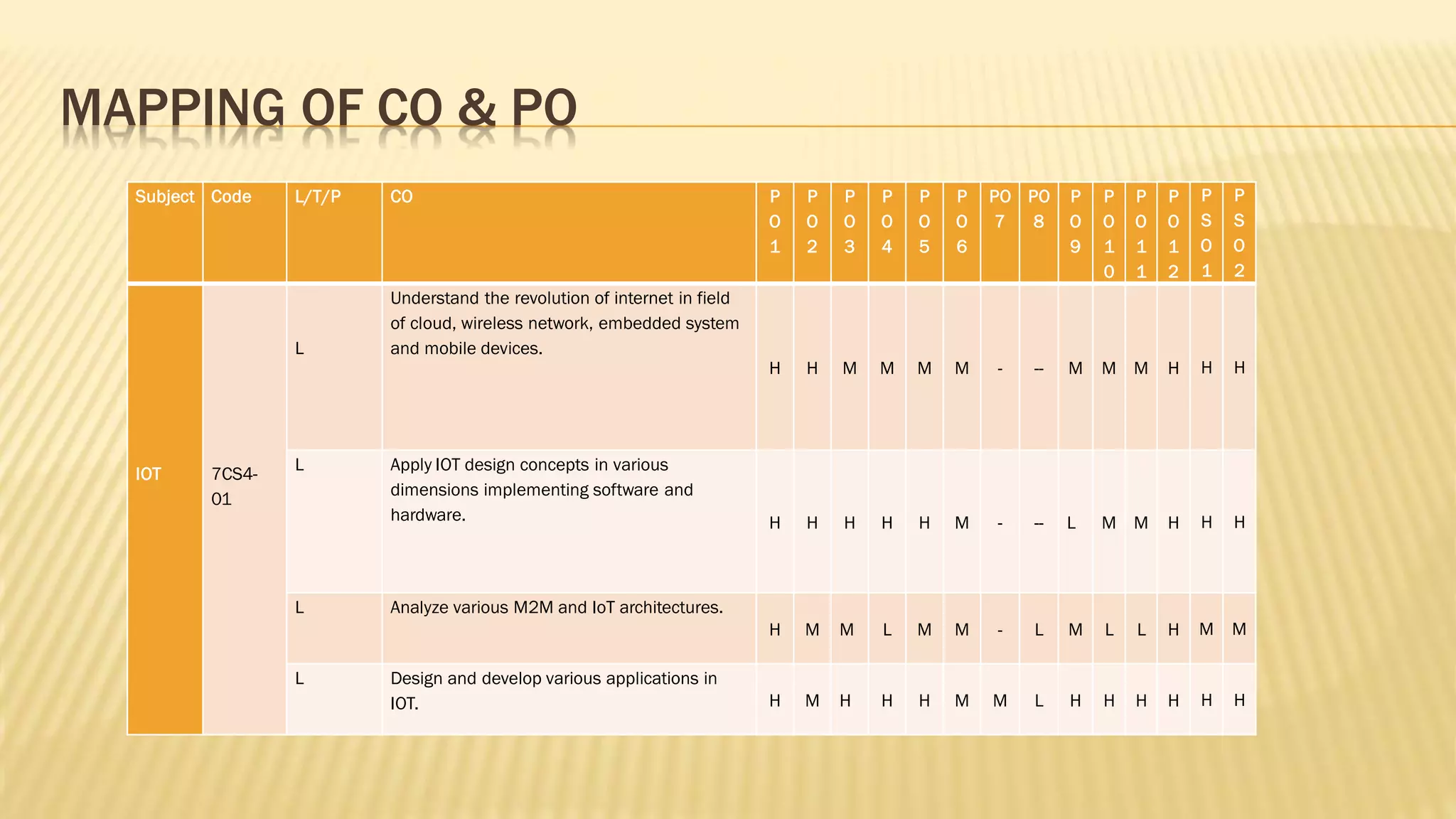
3. For each unit, the topics to be covered, number of lectures required and the lecture plan is provided along with the mapping of course outcomes to program outcomes.