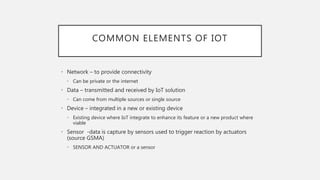
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) solution ColdTrace, which is used in Haiti to monitor vaccine temperatures in health clinics. ColdTrace uses wireless sensors in vaccine storage fridges that send SMS alerts to health workers if temperatures go outside the safe range. This helps ensure vaccines are not destroyed due to unreliable electricity infrastructure. While ColdTrace has potential to solve vaccination problems in Haiti, its use requires reliable 2G network coverage in remote areas and consideration of operational and policy issues like liability if the system fails.