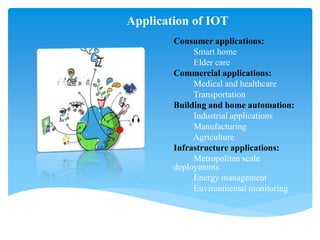
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that can communicate, interact, and exchange data, dating back to concepts introduced in the 1970s and named in 1999 by Kevin Ashton. IoT has various applications across consumer, commercial, and industrial sectors, enhancing areas like smart homes, healthcare, and smart cities through automation and improved monitoring. While there are advantages such as efficiency and improved quality of life, challenges related to privacy, complexity, and security also exist.