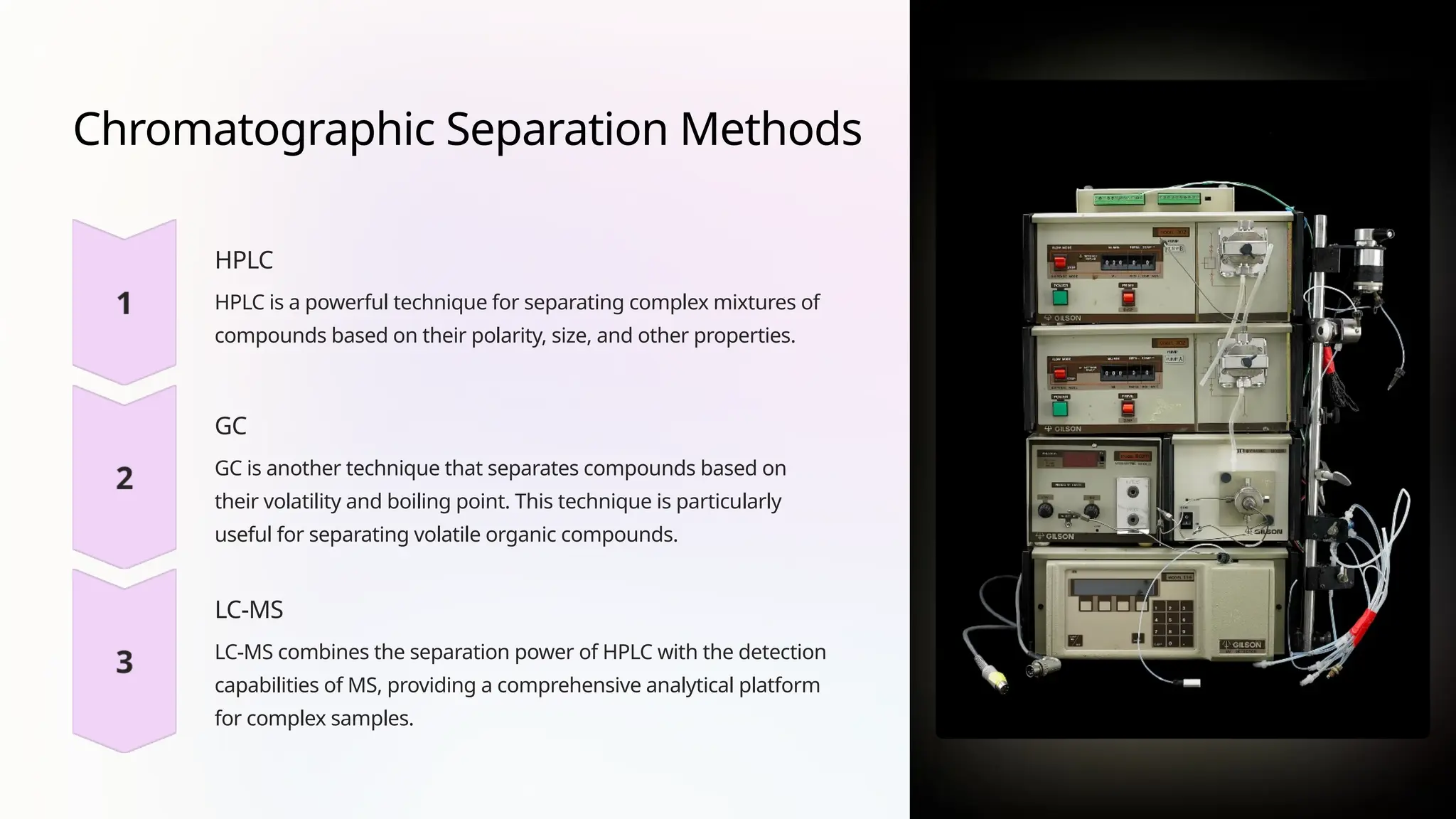
Ion suppression is a significant challenge in mass spectrometry, where certain compounds in a sample inhibit the ionization of analytes, affecting sensitivity and accuracy. Factors contributing to ion suppression include matrix effects, co-eluting compounds, and high concentrations of interfering substances. Strategies to mitigate ion suppression involve appropriate sample preparation, chromatographic separation, optimizing MS parameters, and using internal standards.