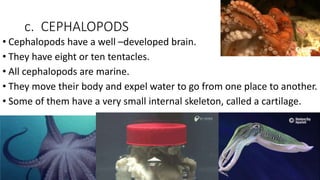
Invertebrates are animals without backbones or inner skeletons. They display a wide range of characteristics and live in various habitats around the world. The document categorizes invertebrates into six main groups - sponges, cnidarians, echinoderms, mollusks, worms, and arthropods. Each group contains different phyla of invertebrates that share similar anatomical features and life cycles.