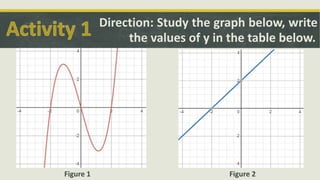
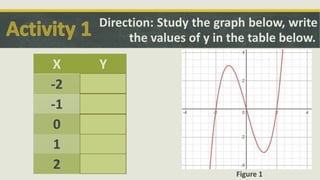
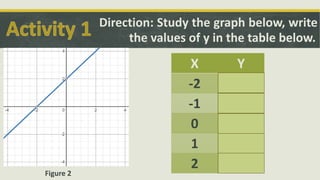
This document contains activities and lessons about functions, including:
1. Two activities that ask students to analyze graphs and tables to identify function properties like one-to-one and inverse functions.
2. A lesson explaining one-to-one functions, inverse functions, and how to determine if two functions are inverses. It provides examples of finding the inverse of different functions.
3. An activity that claims to be able to determine a number a student is thinking of through a series of math operations, linking it to the concept of inverse functions.