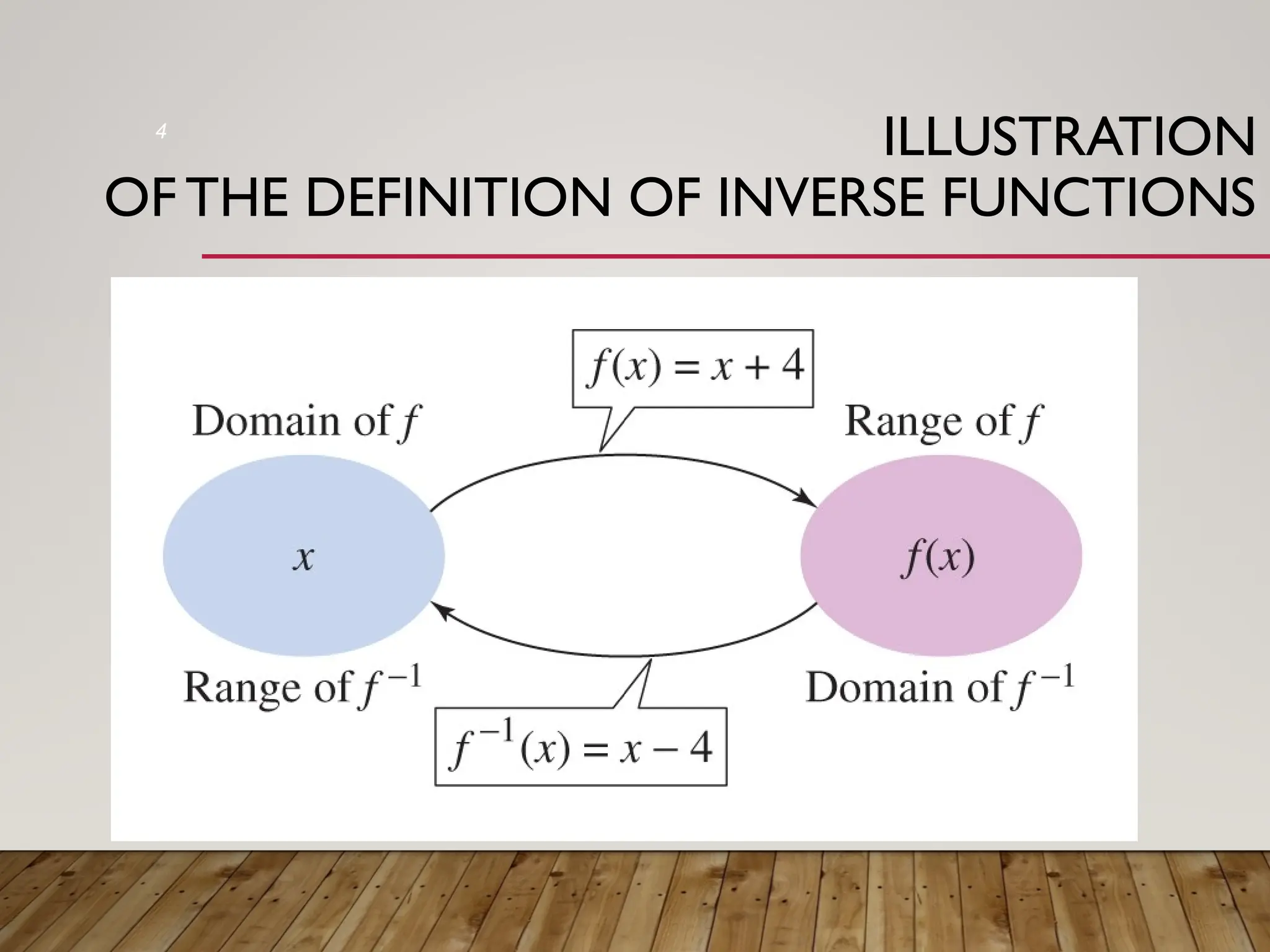
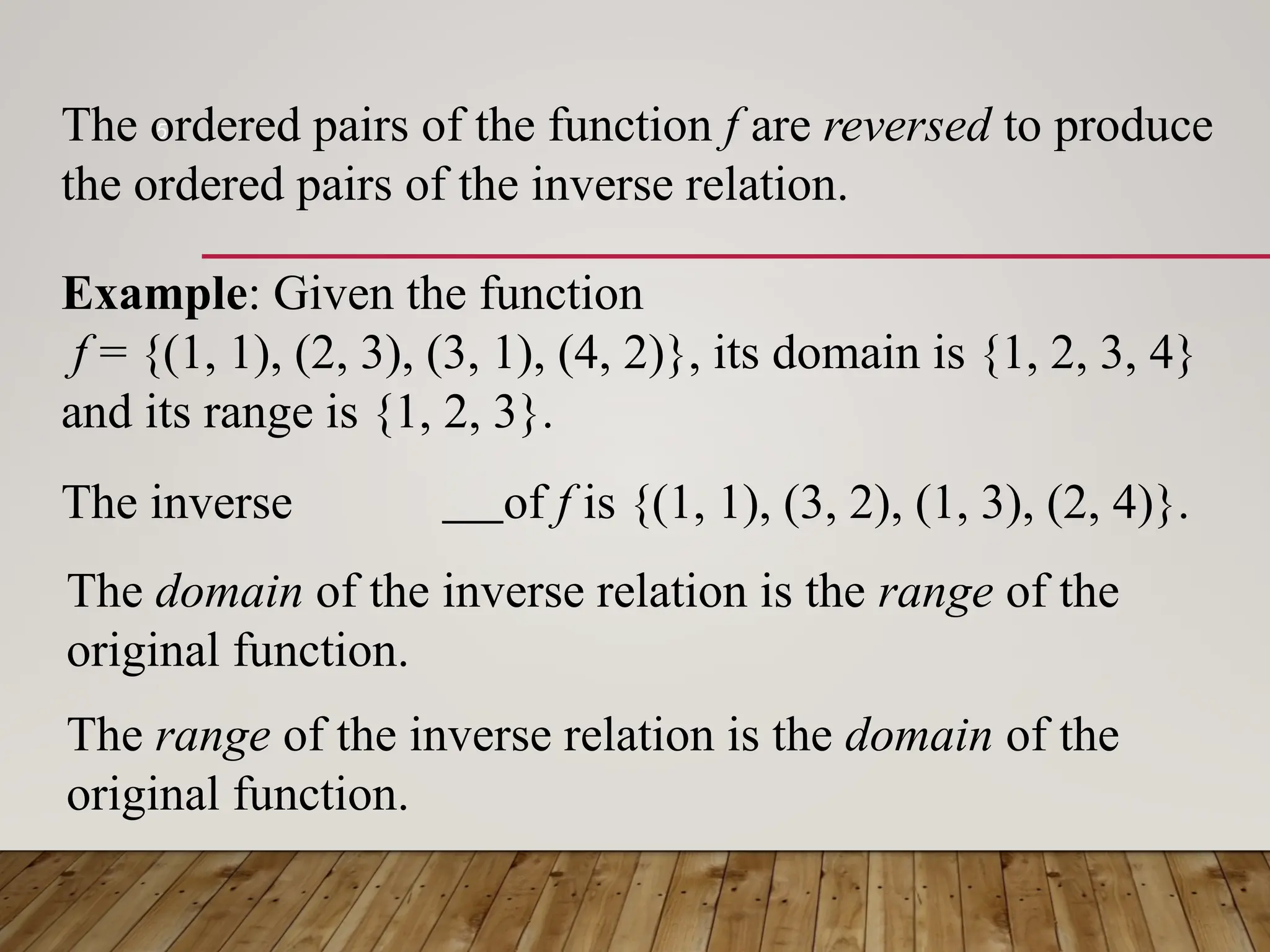
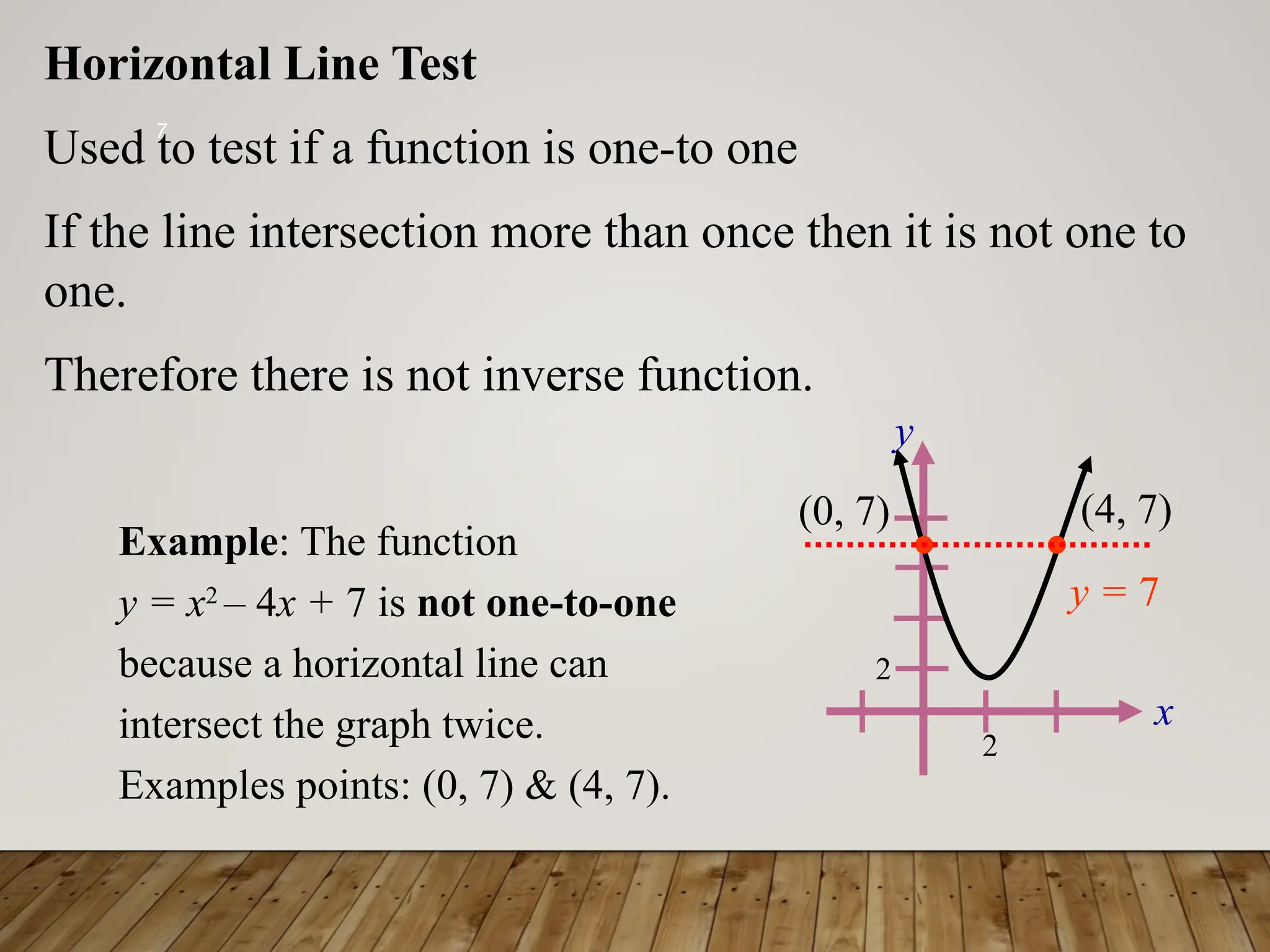
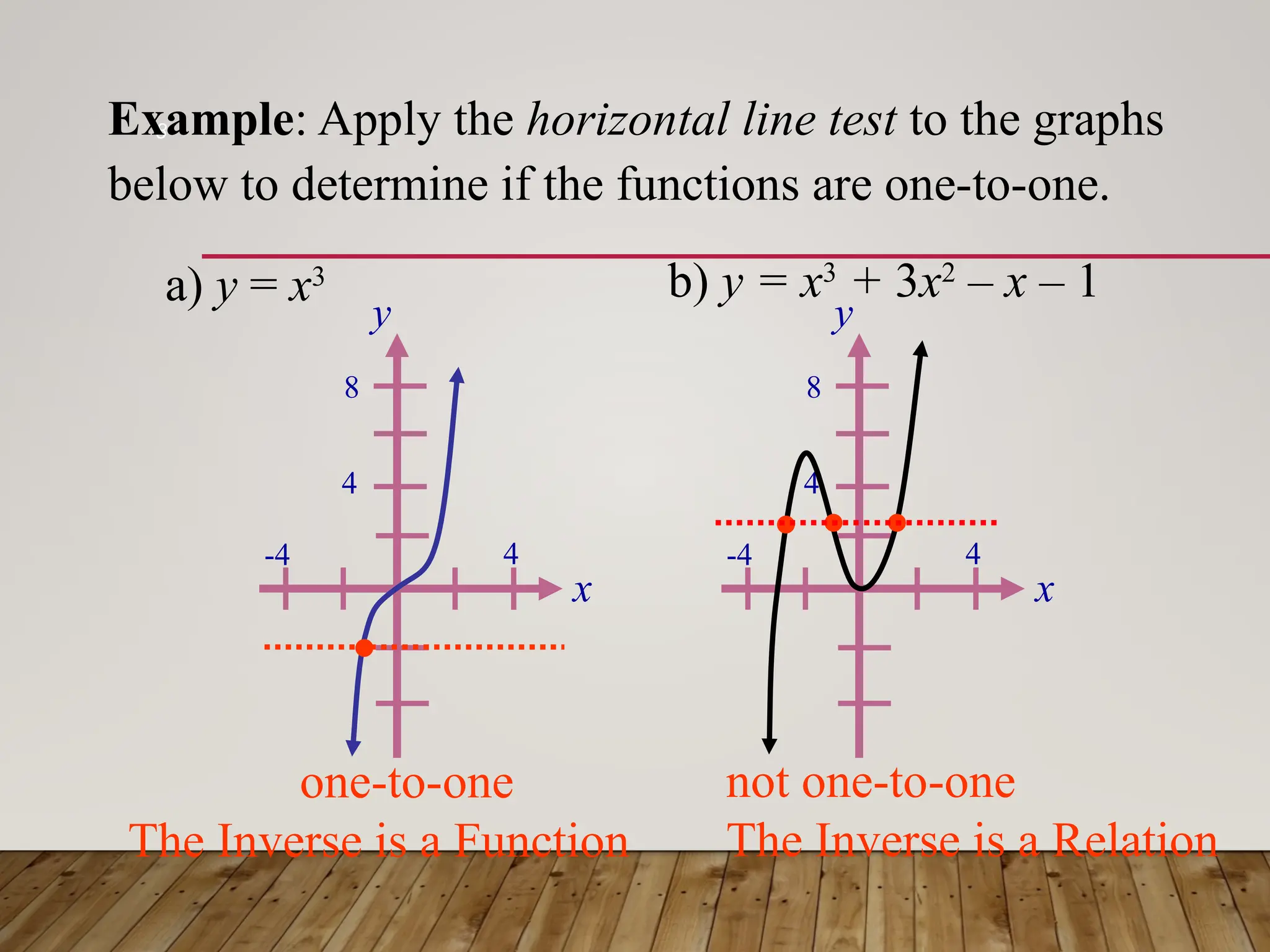
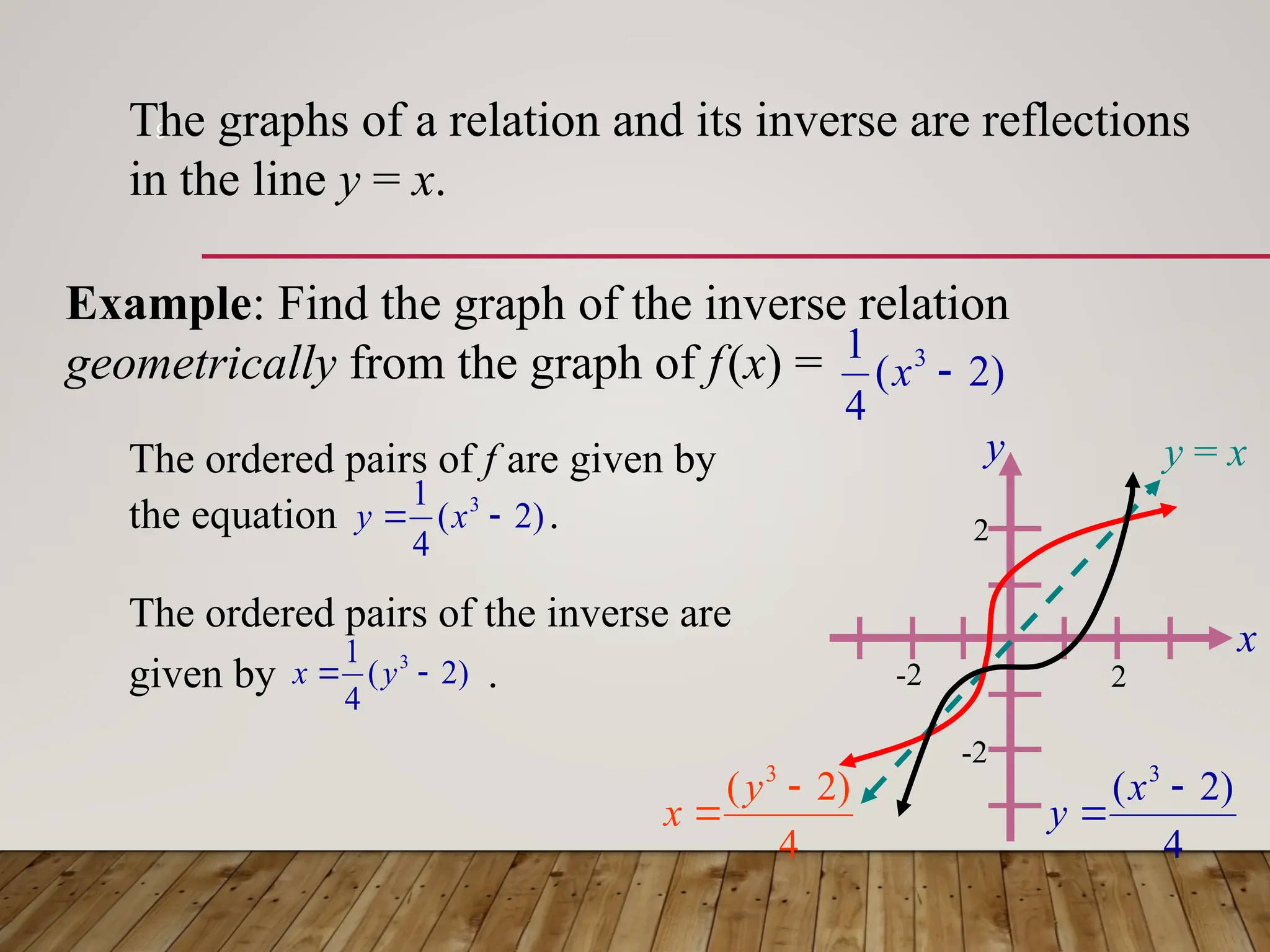
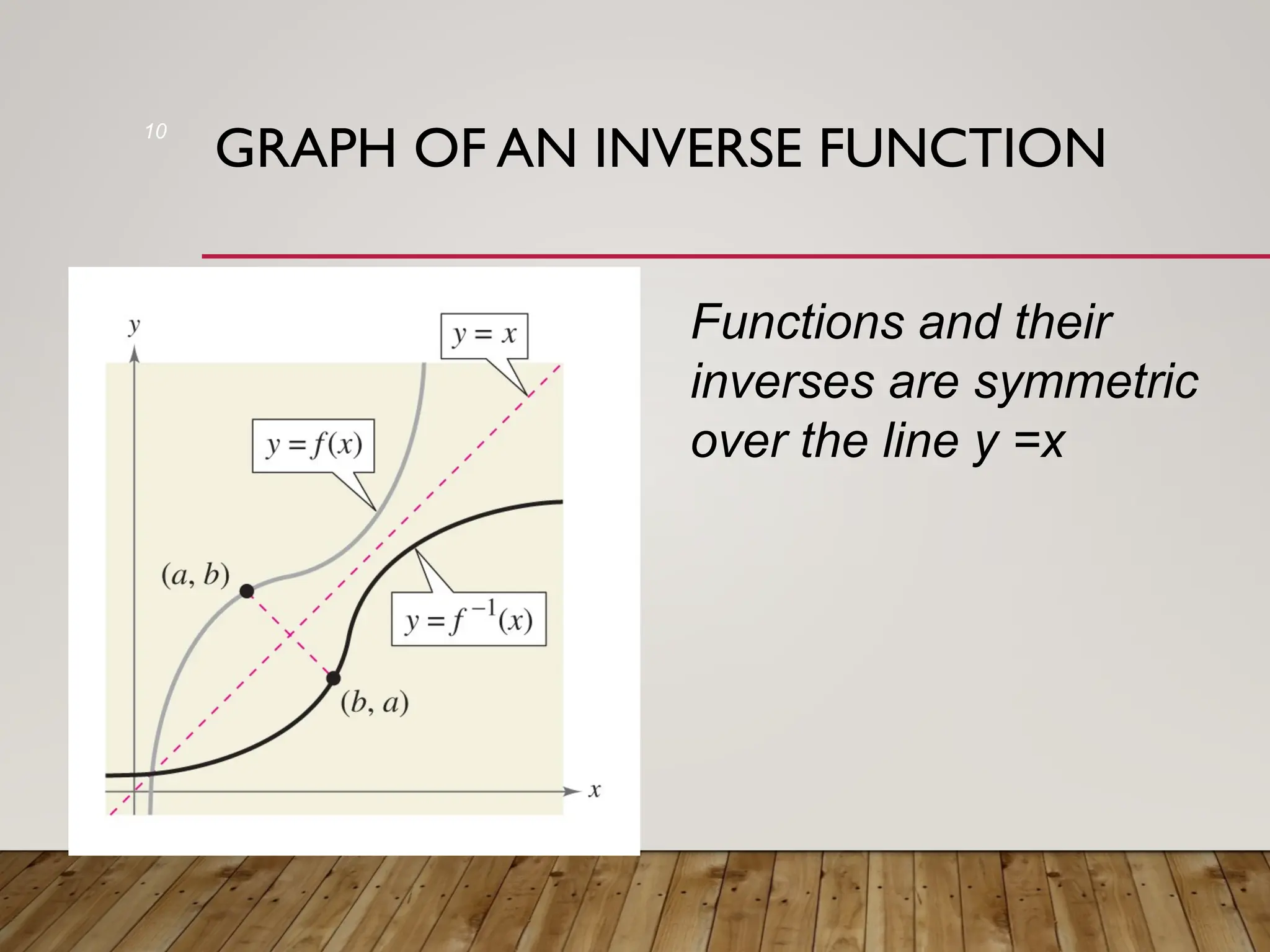
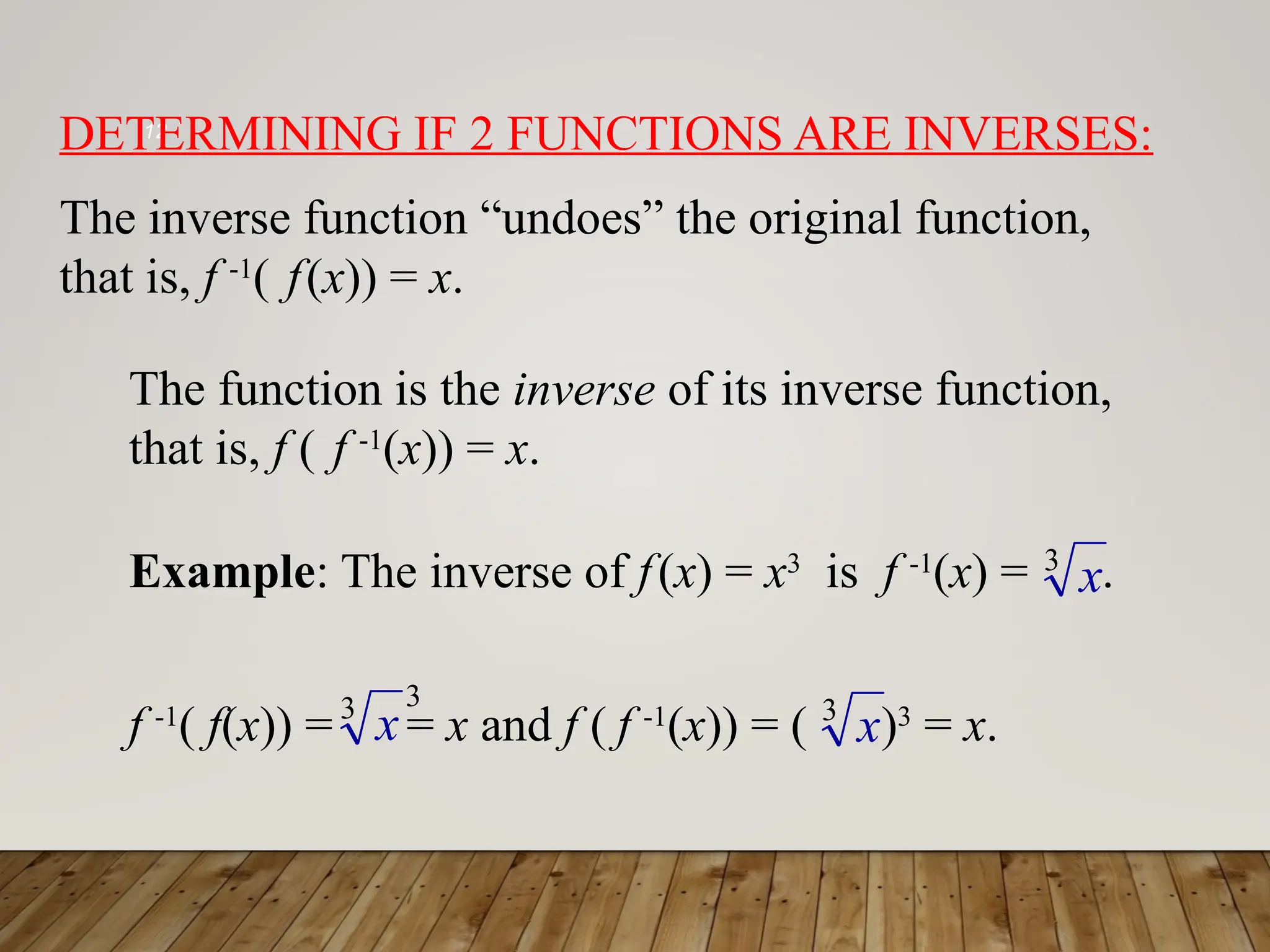
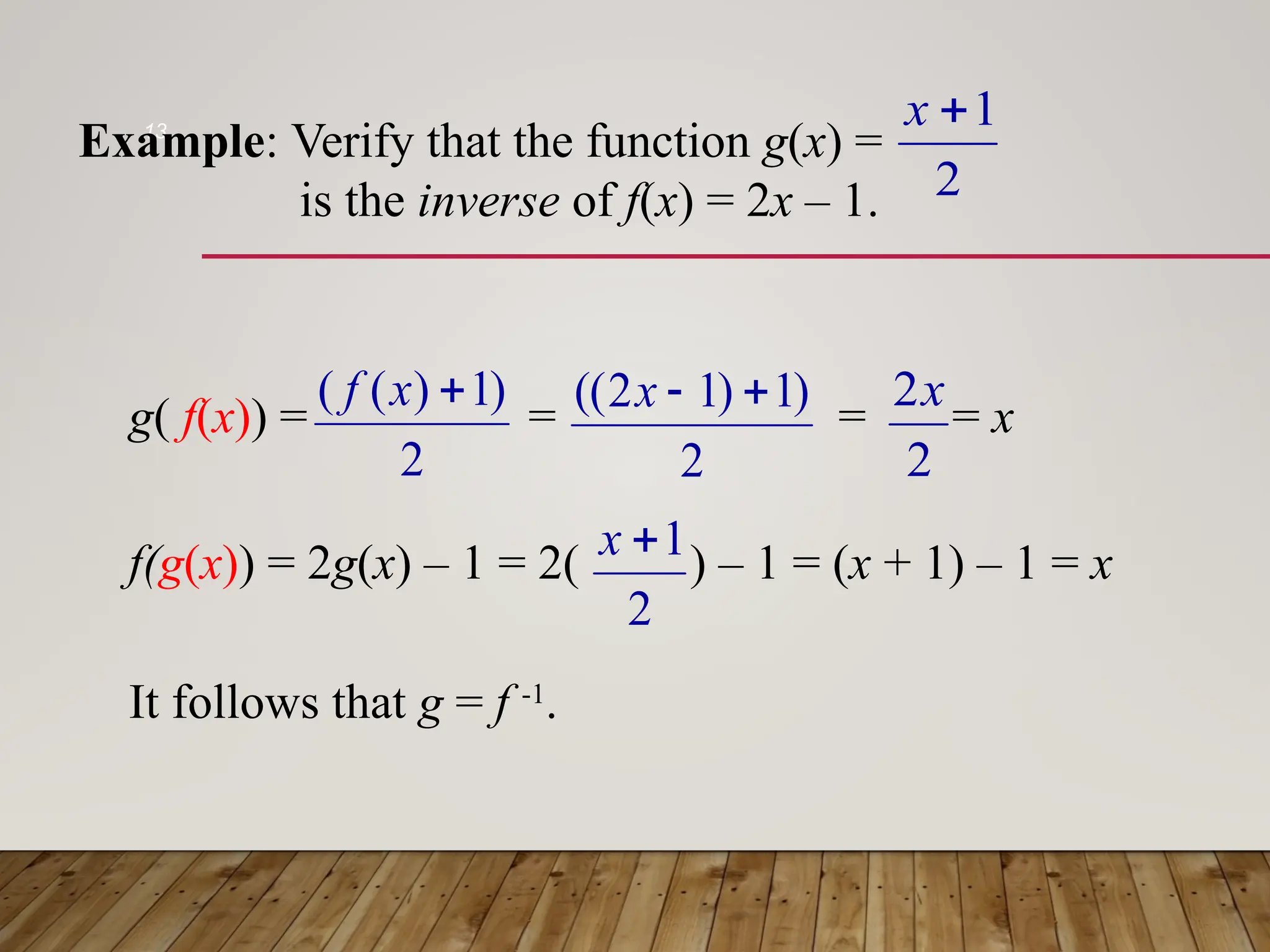
The document discusses one-to-one and inverse functions, noting that a function must have unique y-values to have an inverse. It explains how to determine if a function is one-to-one using the horizontal line test and provides examples of functions and their inverses. It also covers the algebraic process for finding inverses and tests for determining if two functions are inverses of each other.