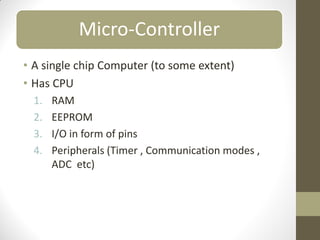
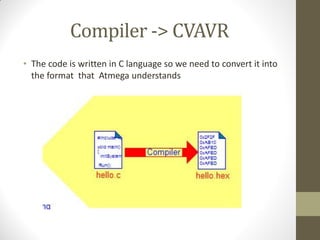
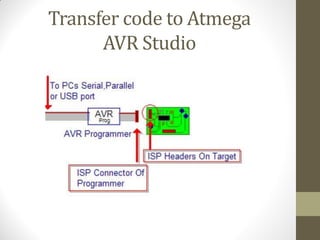
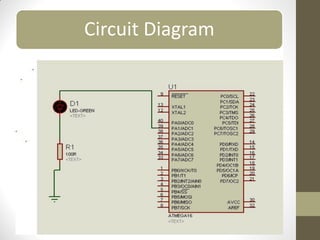
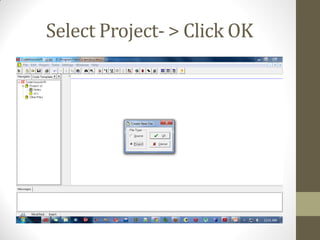
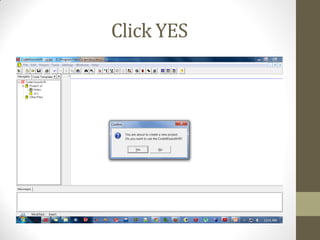
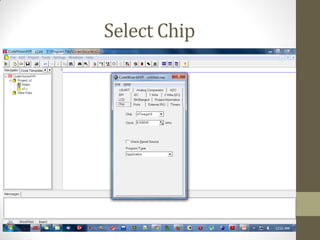
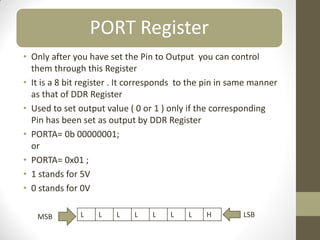
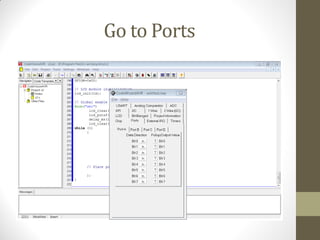
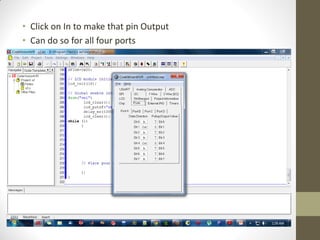
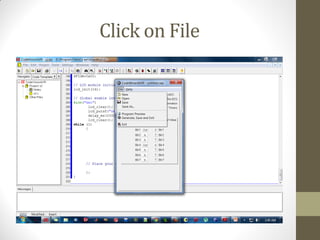
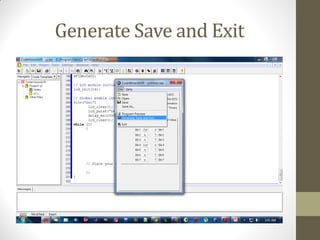
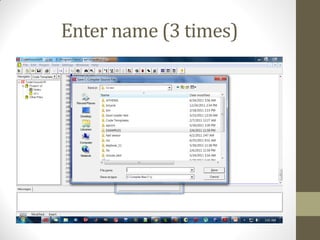
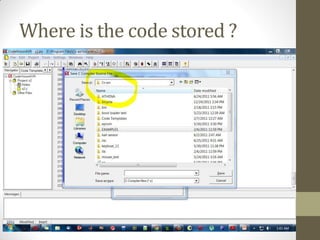
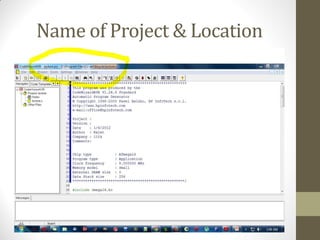
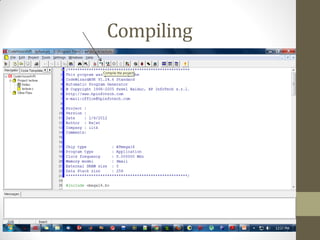
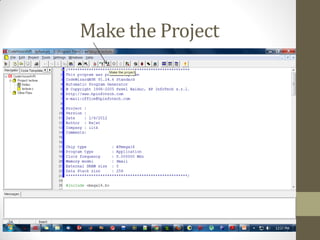
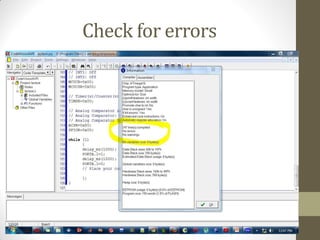
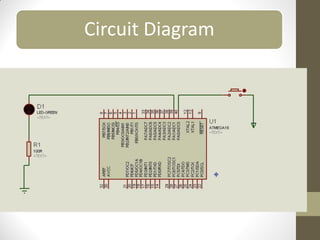
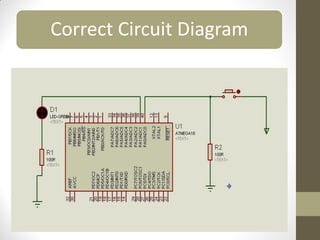
This document provides an introduction to microcontrollers. It discusses that microcontrollers are single-chip computers that contain a CPU, RAM, EEPROM, I/O pins, and peripherals. Examples of past projects using microcontrollers include line-following robots and wireless keyboards. Microcontrollers are preferable to general purpose computers for tasks like these due to their small size, low cost, efficiency, and ease of use. The document then discusses selecting microcontrollers from popular families like AVR and PIC, and using the AVR series for this introduction. It outlines the software tools like CVAVR for coding and compiling, as well as transferring the code to the Atmega microcontroller. Finally, it provides examples of blinking an LED