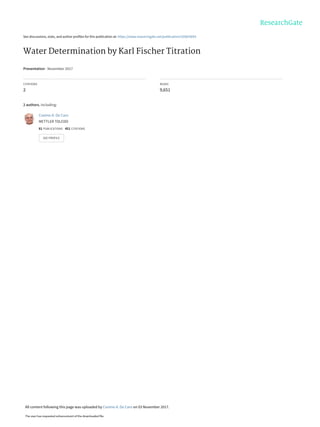
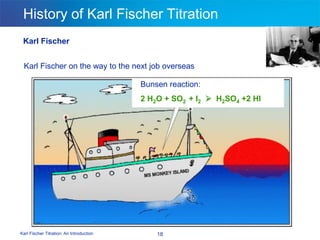
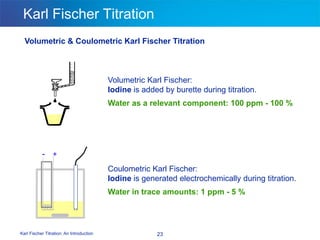
The document discusses the Karl Fischer titration technique for determining water content in samples. It describes the history of the technique developed by Karl Fischer in the 1930s. The technique is based on a chemical reaction between water and other reagents like iodine, sulfur dioxide, and a solvent. Depending on the water content, either volumetric or coulometric Karl Fischer methods are used to determine water over different concentration ranges. Now the technique is performed using automated Karl Fischer titration instruments.