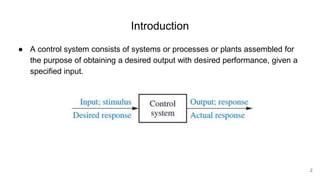
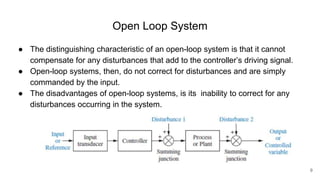
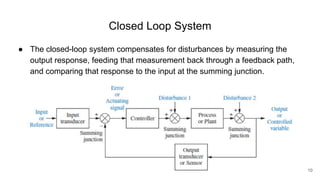
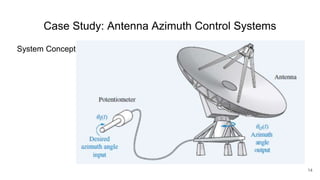
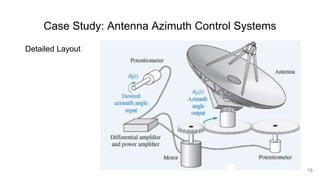
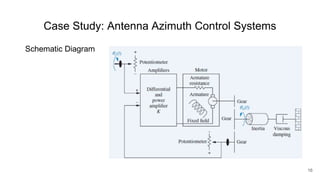
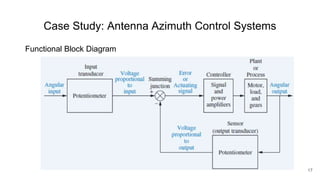
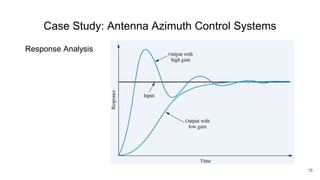
A control system consists of systems or processes assembled to obtain a desired output with specified performance given an input. An example is an elevator control system, which rises to the desired floor with speed and accuracy for passenger comfort. Control systems are integral to modern society and are found in applications like rockets, shuttles, manufacturing, and vehicles. Control systems in the body regulate processes like blood sugar, heart rate during fight or flight, eye movement, and grasping. The objectives of control systems are remote control, input convenience, disturbance compensation, and stability. Closed loop systems provide greater accuracy than open loop by measuring output, comparing to input, and correcting for disturbances through feedback.