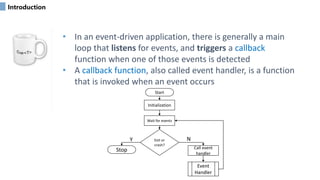
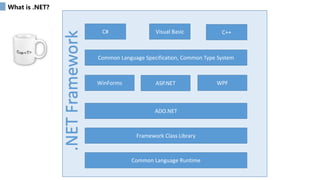
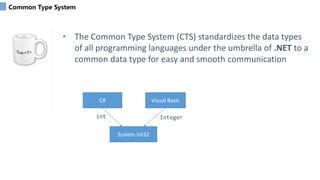
Event-driven programming is a programming paradigm where the flow of a program is determined by events. There are two main sources of events - users and other programs. An event-driven program contains a main loop that listens for events and triggers callback functions when events are detected. Callback functions are event handlers that are invoked in response to events. Graphical user interfaces predominantly use the event-driven paradigm.