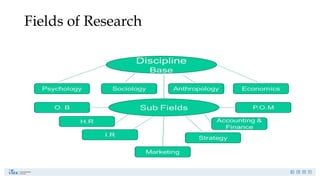
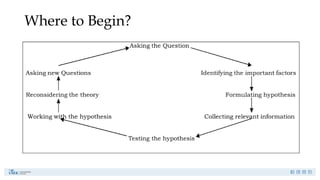
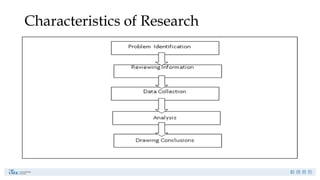
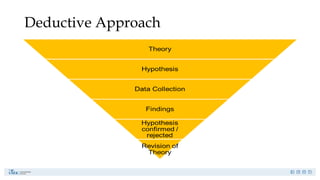
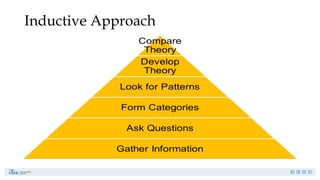
Research is a systematic investigation to gain knowledge about a particular phenomenon and typically begins with a question or problem. Its main purposes include exploration, description, causal explanation, and prediction, employing both quantitative and qualitative methods. The research process involves careful planning, data collection, and interpretation to address specific research problems.