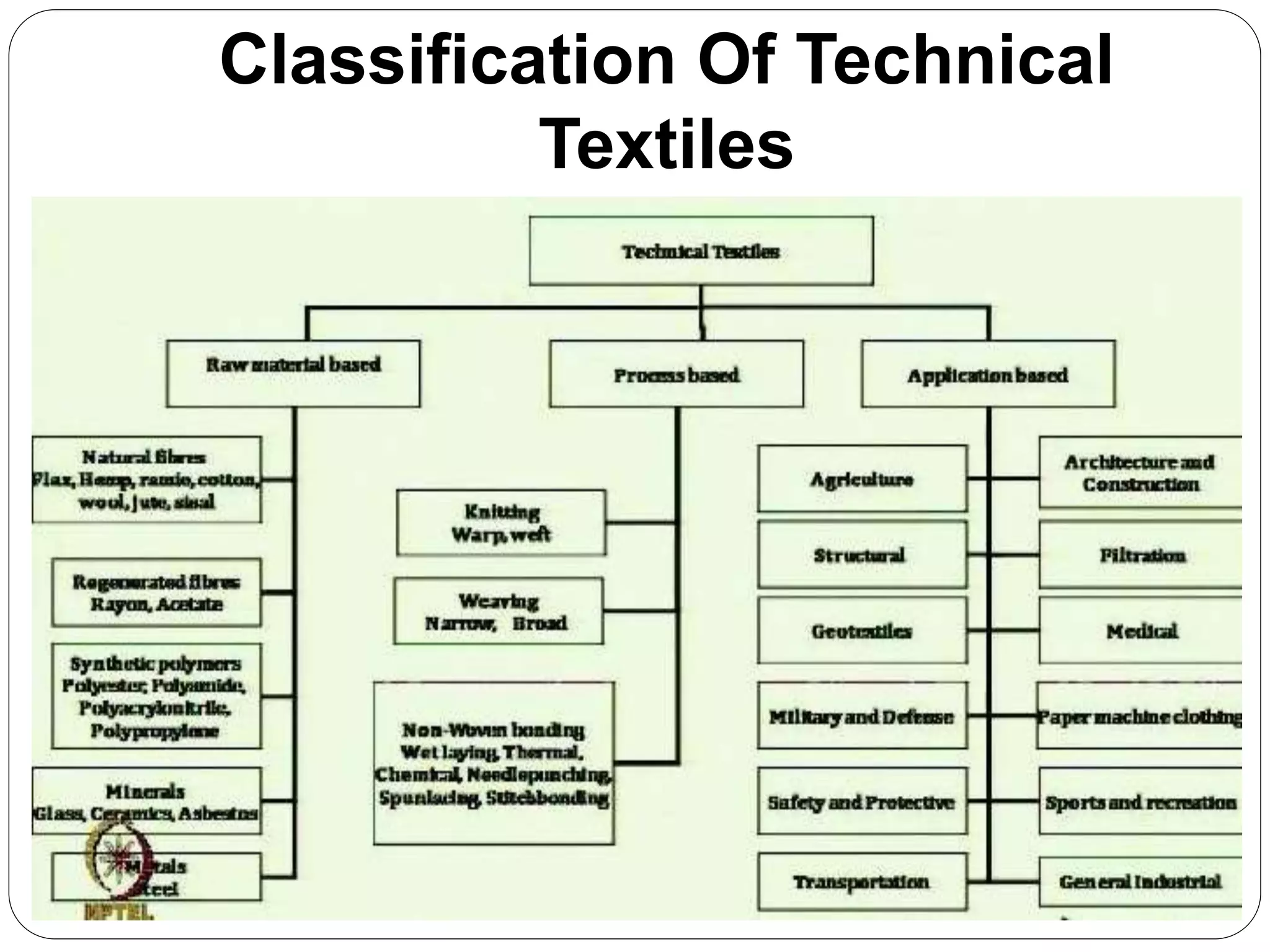
The document discusses technical textiles in India. It notes that India's specialty fabric industry is still developing compared to global players. The government is focusing on upgrading infrastructure using technical textiles like geosynthetics and automotive nonwovens. Other niche areas seeing growth are medical, agricultural, and protective textiles. The document also outlines 12 main categories of technical textiles and variables involved in their production like polymers, fibers, yarns, fabrics, and finishing techniques.