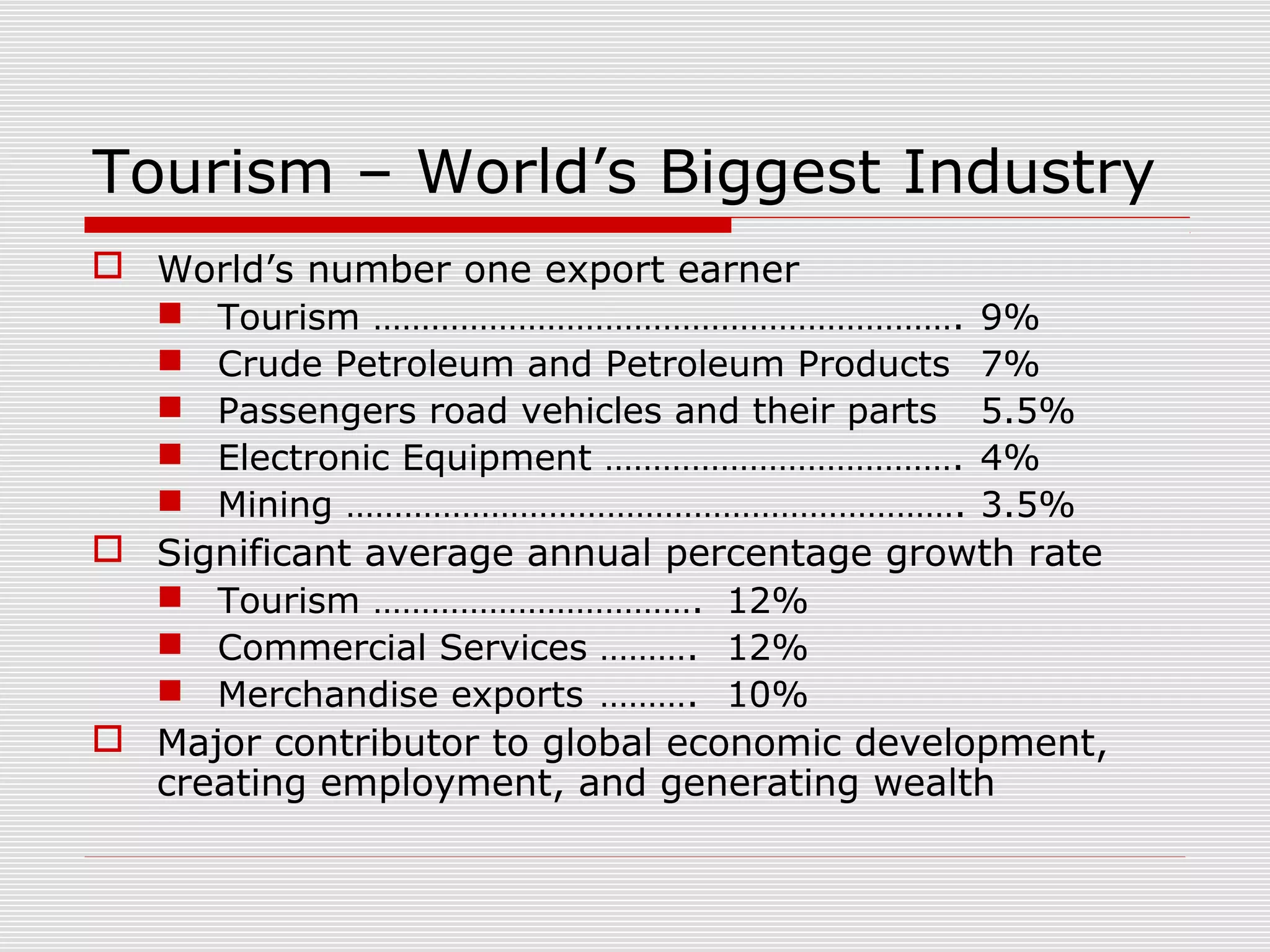
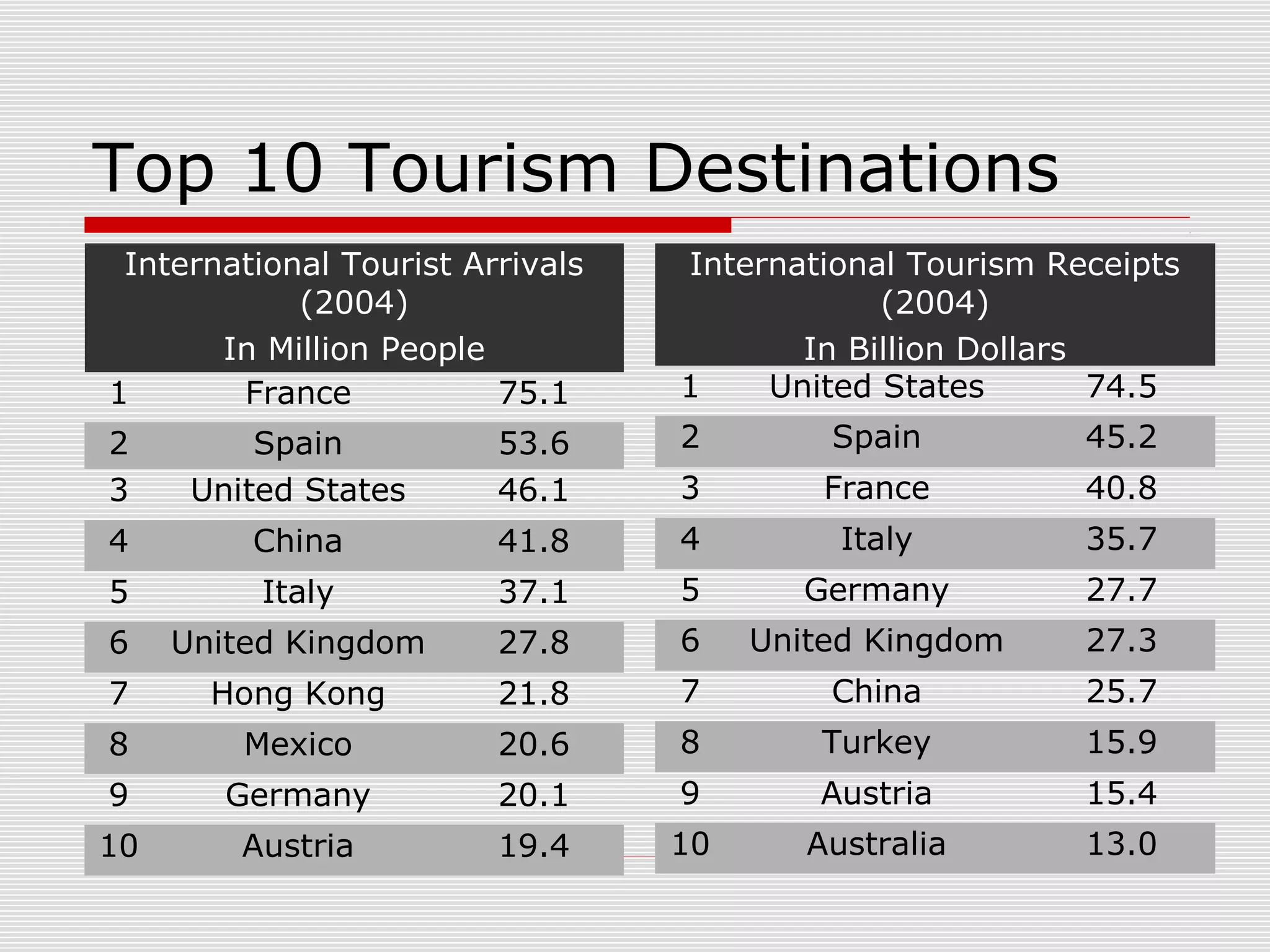
Tourism is the world's largest industry, contributing significantly to global economic development and job creation. While tourism generates wealth and employment, it can also negatively impact the environment and local cultures. The large numbers of visitors can cause overcrowding, pollution, damage to ecosystems, and changes to traditional ways of life. However, tourism also supports conservation efforts and cultural heritage programs when managed sustainably.