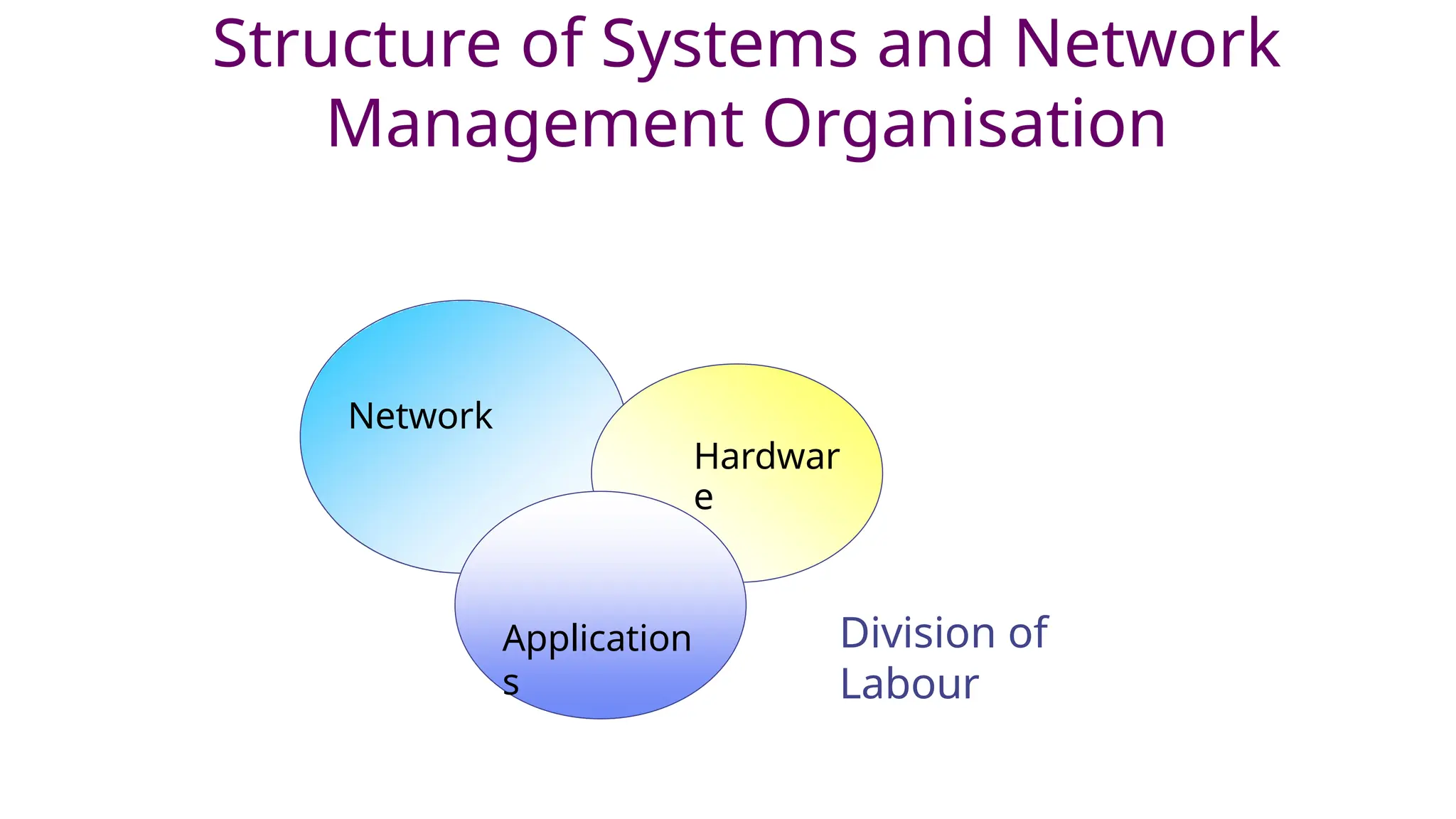
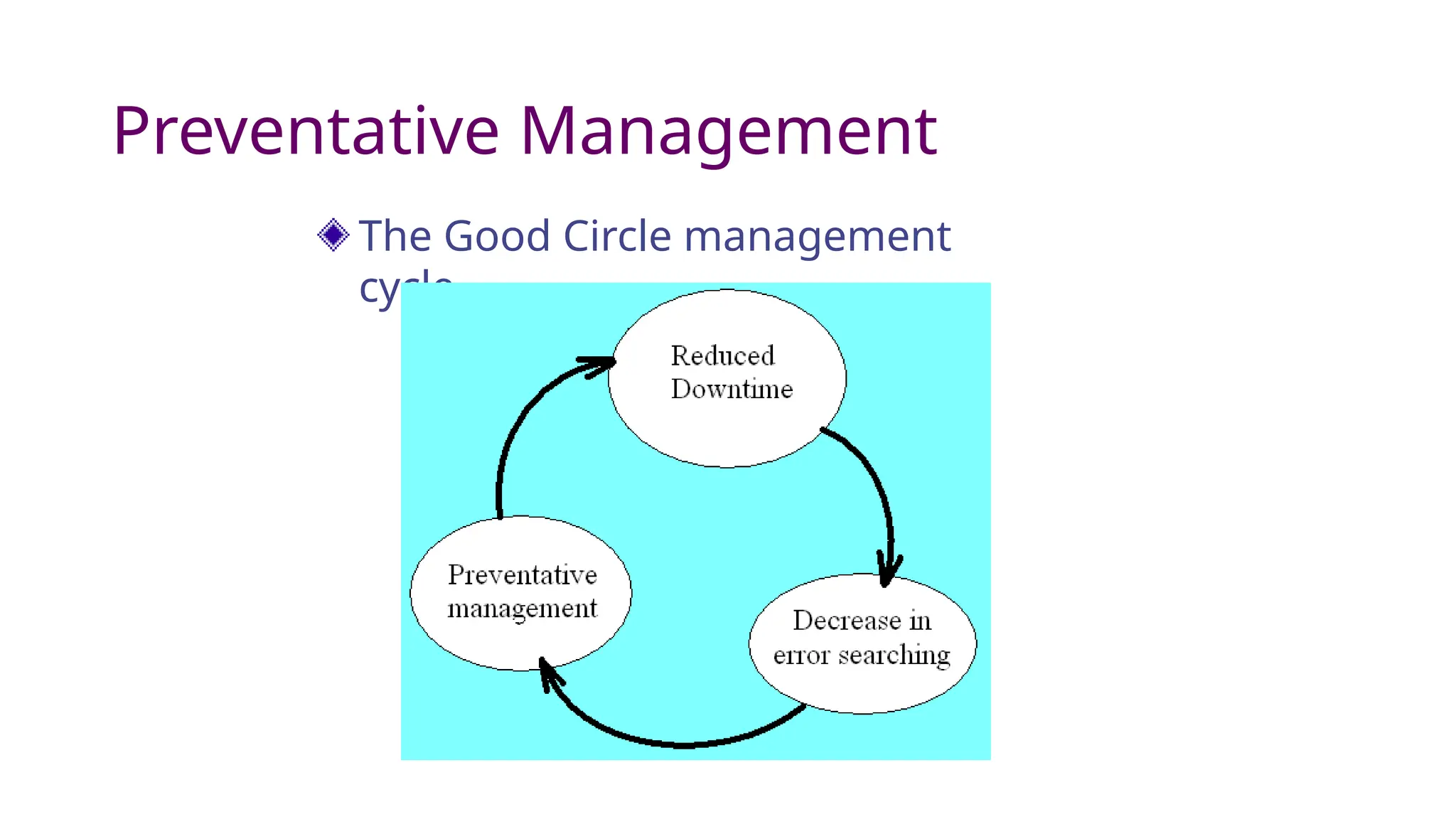
Network administration involves the operational management of human-computer systems, encompassing roles such as fault management, security management, and performance management. It requires planning for growth, managing accounts and user access, and providing support for network applications. Network administrators face challenges like designing efficient networks and implementing security while balancing reactive and proactive management styles.