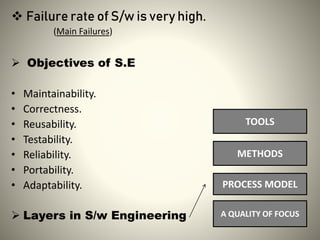
The presentation introduces software engineering and defines software as a program running on computers, highlighting its dual role as both a product and a delivery vehicle. It discusses essential components and characteristics of software, outlines application domains, and emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach in software engineering practices. The conclusion asserts that software is ubiquitous and has a significant impact on society.




![ Essential Components of Software
• Instructions :- 1).Function 2). Perfomance
• Data Structures :- Maintains the data
• Documents :- 1). User Manual
2). Design Manual
Characteristics of Software
• S/w is developed or engineered; it is not manufactured.
• S/w doesn’t “wear out.”
• S/w is custom built.
Software can have huge impact in any
aspect of our society.
Software
Data
Structu
re
Docume
nts
Instructi
ons
[PROGRA
M]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontosoftwareengineering-240627073129-0122c7f1/85/Introduction-to-Software-Engineering-pptx-5-320.jpg)