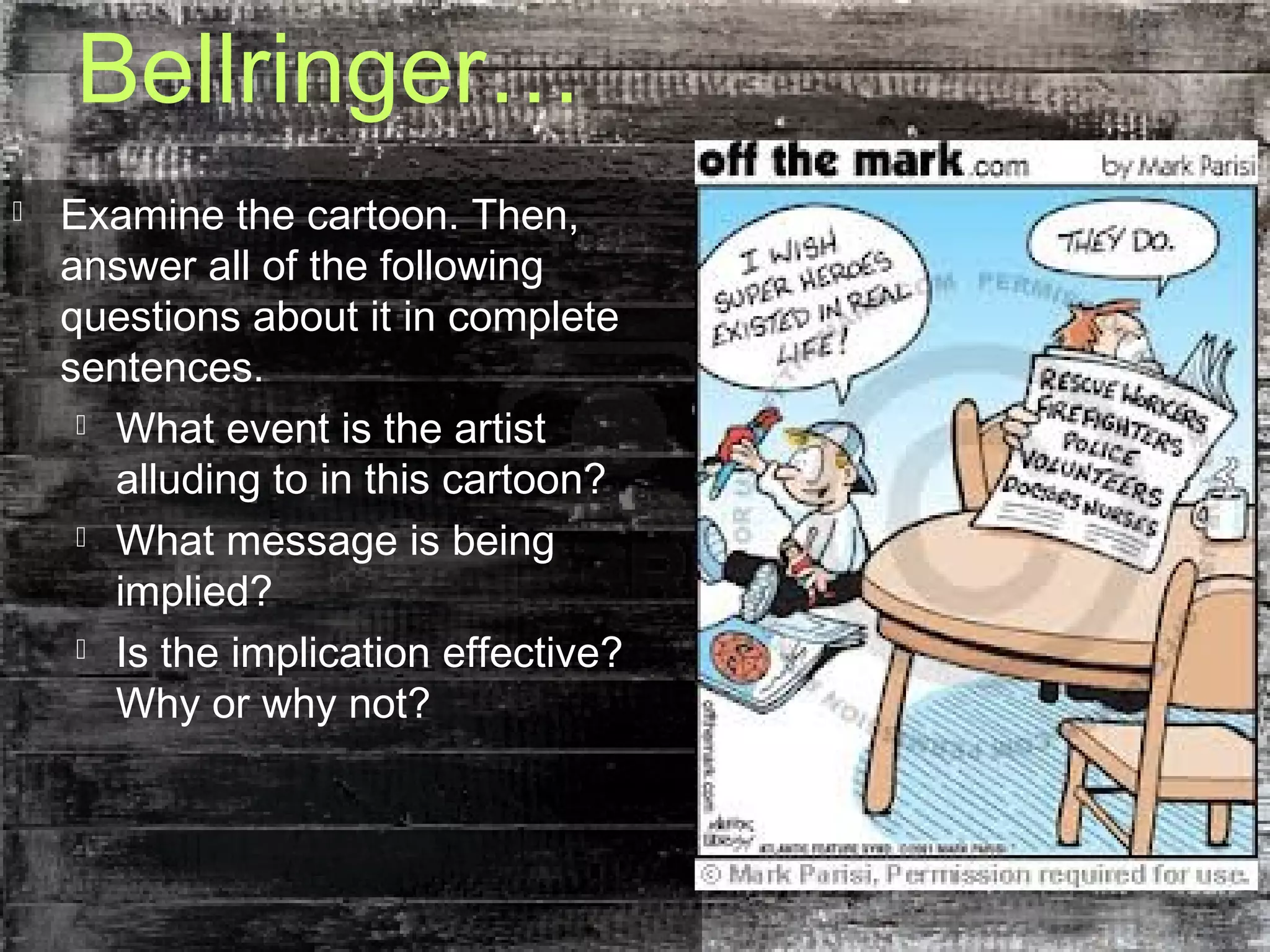
This document provides an overview of satire as a literary genre that uses techniques like irony, wit and sarcasm to critique society and promote reform. It discusses different types of satire, including Horatian satire which gently pokes fun at human folly, and Juvenalian satire which more harshly attacks vice and error. The document also examines characteristics commonly found in satirical writing, such as irony, hyperbole, caricature, wit, sarcasm, ridicule, parody and invective. Students are then assigned to analyze a video for examples of these satirical techniques and classify it as Horatian or Juvenalian satire.