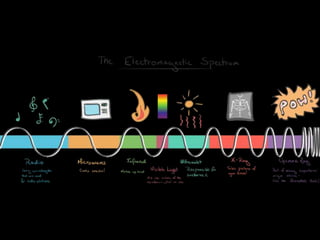
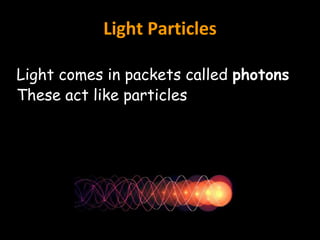
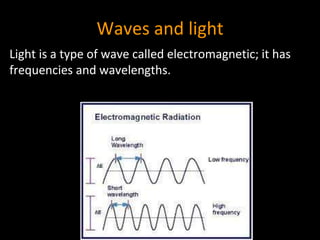
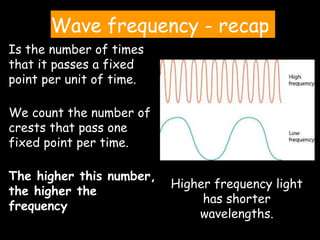
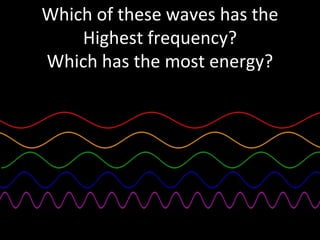
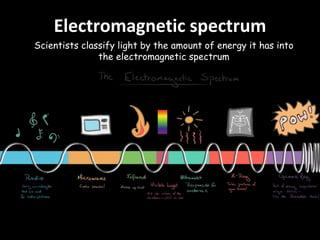
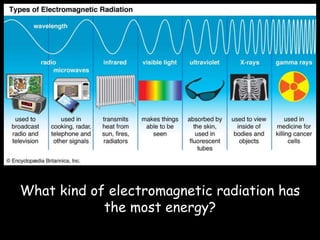
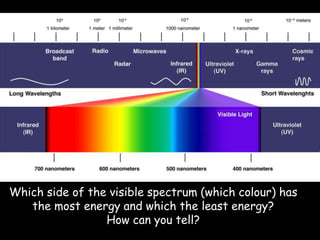
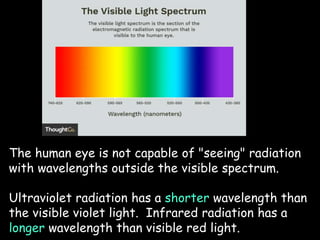
Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that behaves as both a particle and wave. It comes in packets called photons that act like particles. As a wave, light has frequencies and wavelengths. The frequency is the number of times the wave passes a fixed point per unit of time, and higher frequencies correspond to shorter wavelengths. Different frequencies and wavelengths of light carry different amounts of energy. The electromagnetic spectrum classifies light based on its energy, with some types like ultraviolet and infrared having wavelengths just outside the visible light range that the human eye can see. Visible light corresponds to wavelengths from 400-700 nanometers and is experienced as the colors violet, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red from shortest to longest wavelength.