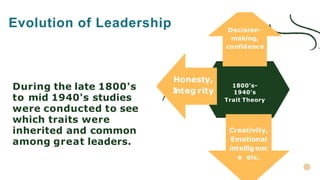
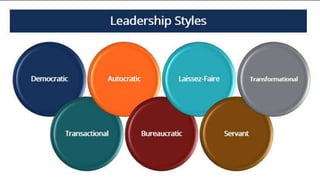
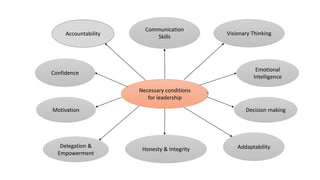
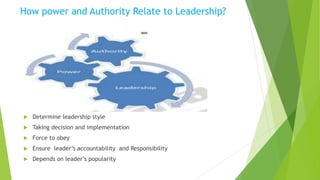
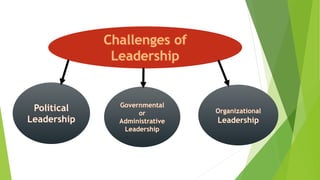
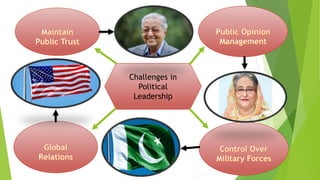
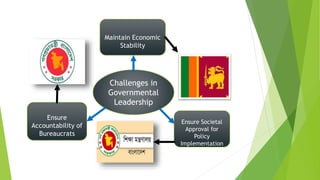
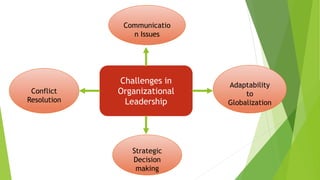
This document provides a comprehensive overview of leadership, detailing its definitions, evolution, components, various styles, and functions. It emphasizes the importance of effective leadership across different domains, including the relationships between leadership, management, and organizational success. Key principles such as influence, follower engagement, goal setting, and ethical considerations are highlighted as critical elements that contribute to a leader's effectiveness.