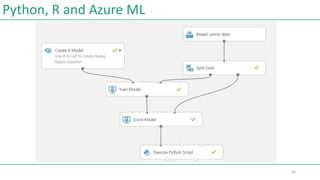
This document provides an introduction to Jupyter Notebook and Azure Machine Learning Studio. It discusses popular programming languages like Python, R, and Julia that can be used with these tools. It also summarizes key features of Jupyter Notebook like code cells, kernels, and cloud deployment. Examples are given of using Python and R with Azure ML to fetch and transform data in Jupyter notebooks.















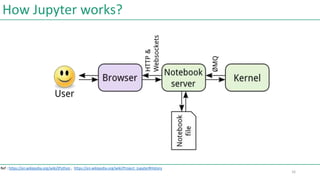


![Jupyter Notebook on Cloud
• Navigate to https://notebooks.azure.com/
• Click Samples to navigate to https://notebooks.azure.com/Microsoft/libraries/samples
• Click anyone of the sample
• Click Clone option (You may get login dialog (if you’re not signed in, use your Hotmail/outlook/skype)
and login.)
• Enter library name and click Clone button
• Click on “Introduction to Python” sample and it launches, Jupyter notebook on Azure
• Select the statements on starts with In[1] … and select click Run button in the toolbar.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojupyternotebookgeeknight-181123050220/85/Introduction-to-Jupyter-notebook-and-MS-Azure-Machine-Learning-Studio-20-320.jpg)




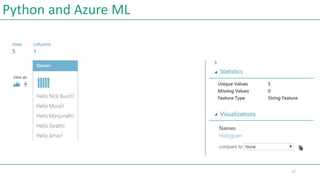
![Python and Azure ML
import pandas as pd
def azureml_main(dataframe1):
for index, row in dataframe1.iterrows():
row[0]="Hello " + row[0] +"!"
# Return value must be of a sequence of pandas.DataFrame
return dataframe1
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontojupyternotebookgeeknight-181123050220/85/Introduction-to-Jupyter-notebook-and-MS-Azure-Machine-Learning-Studio-26-320.jpg)