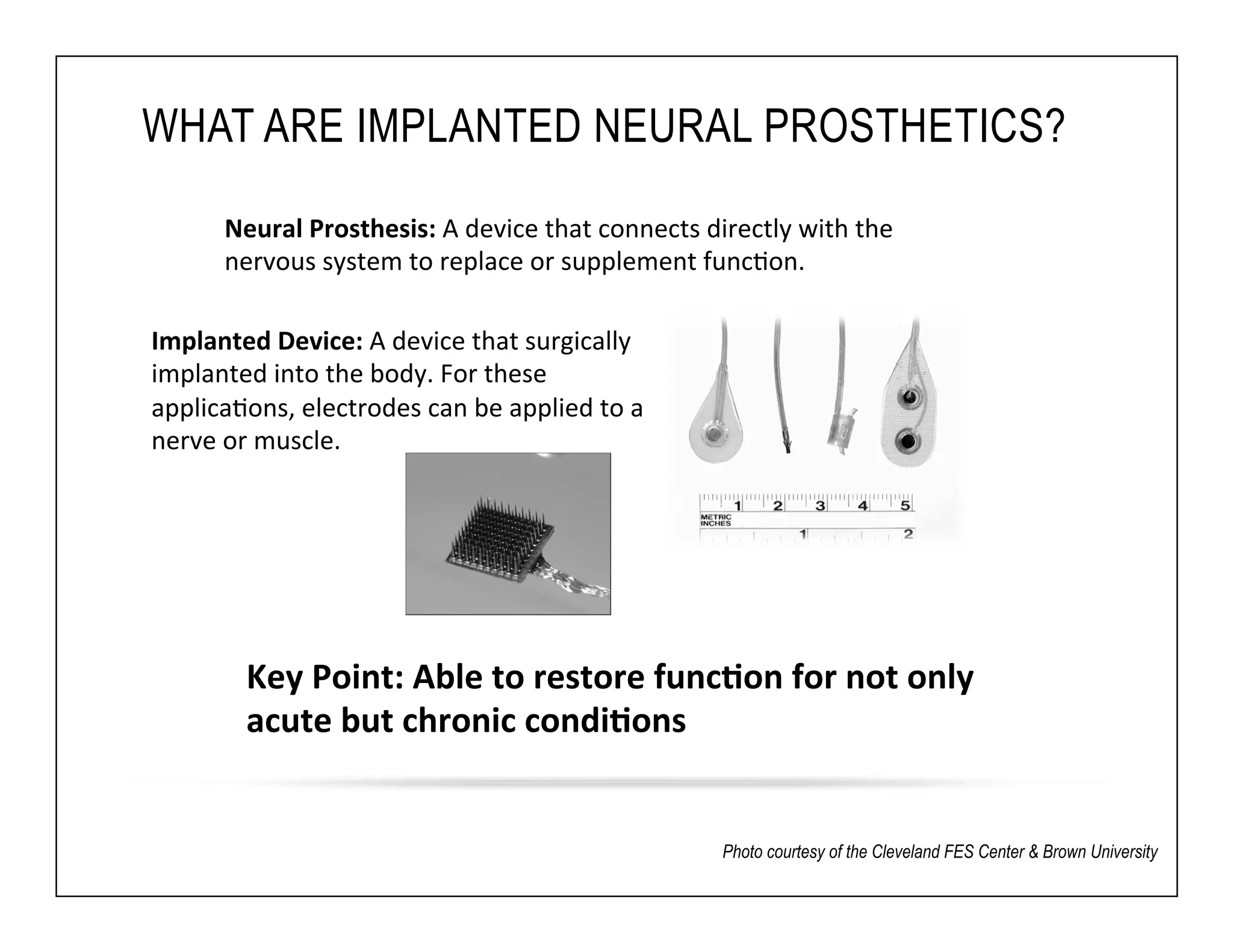
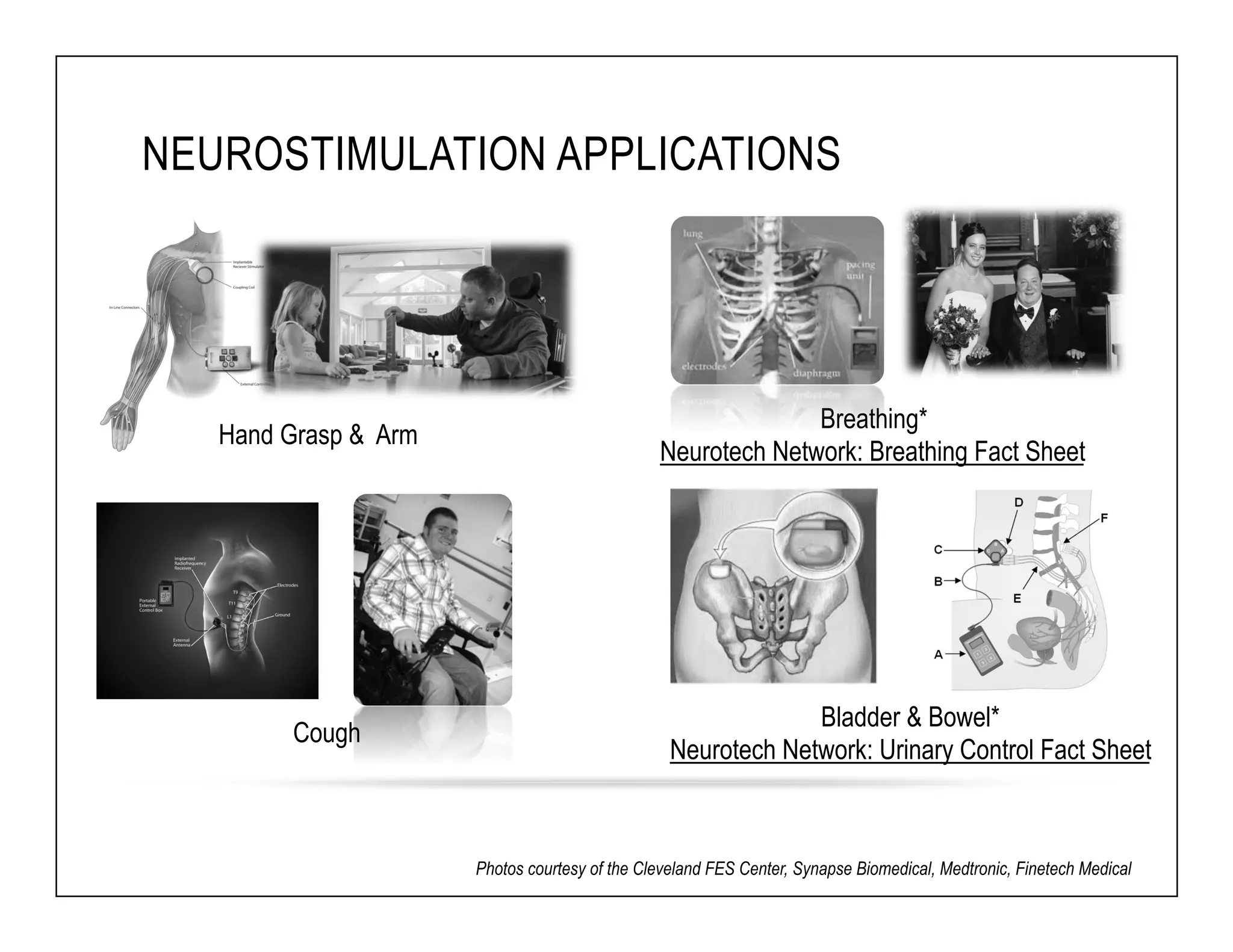
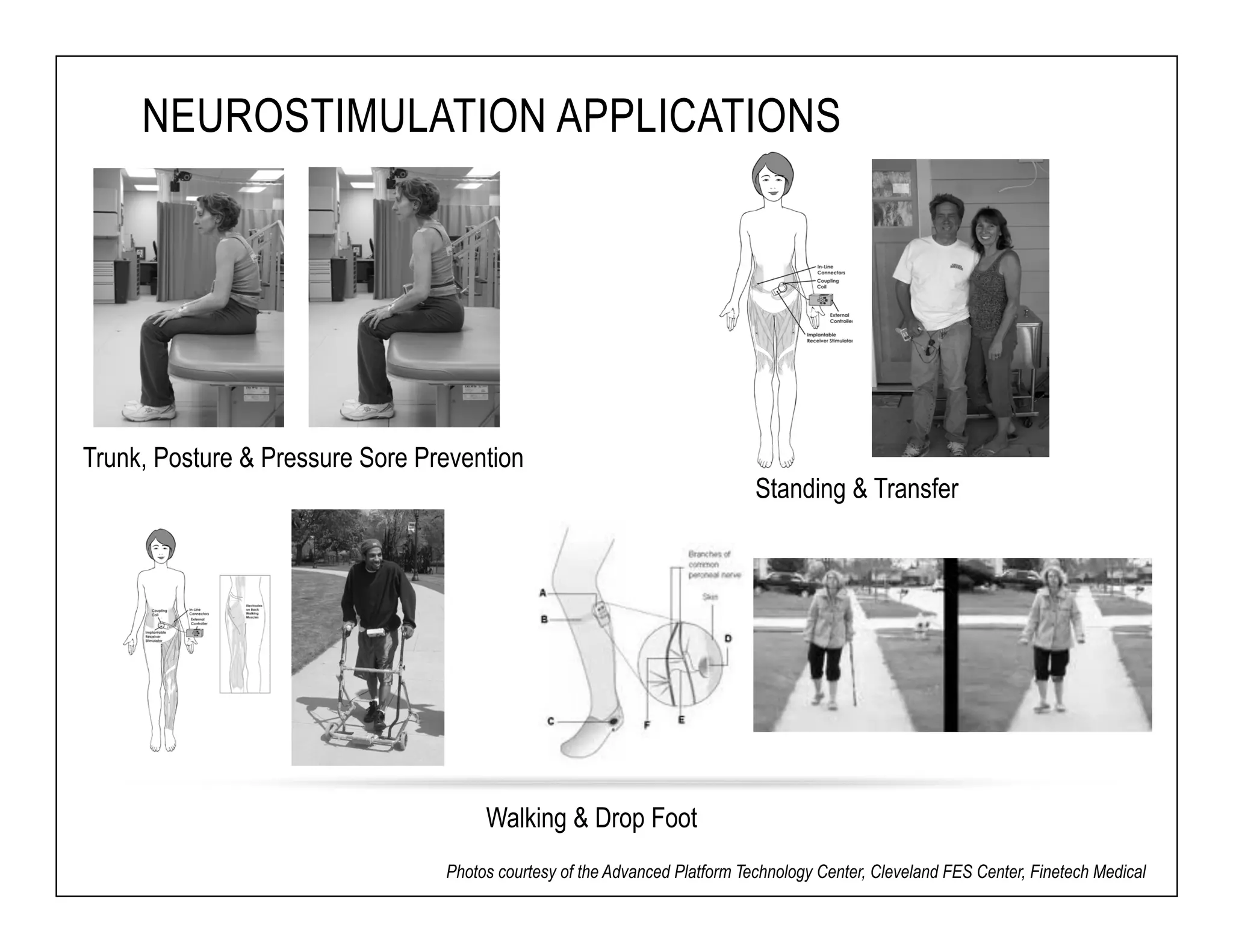
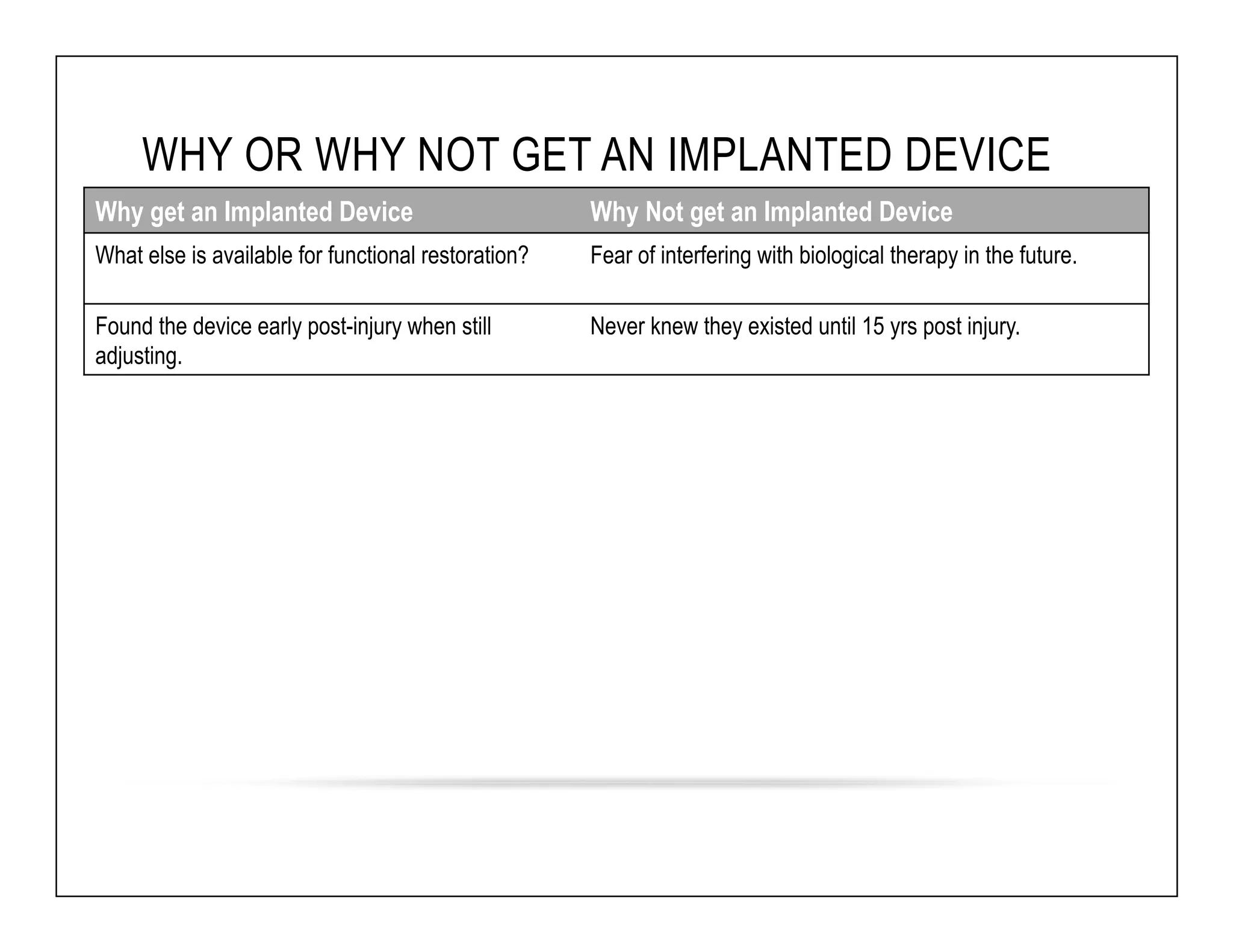
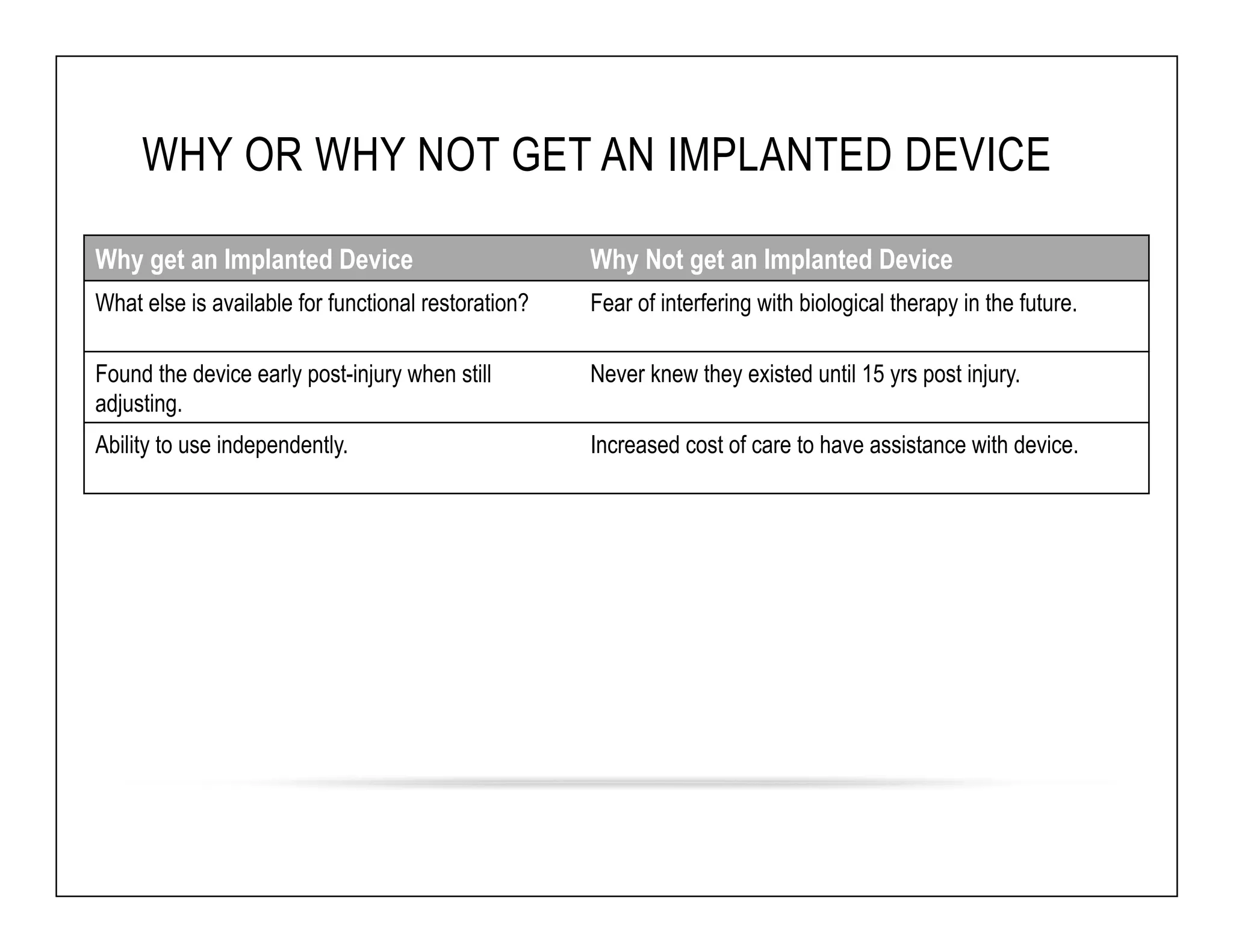
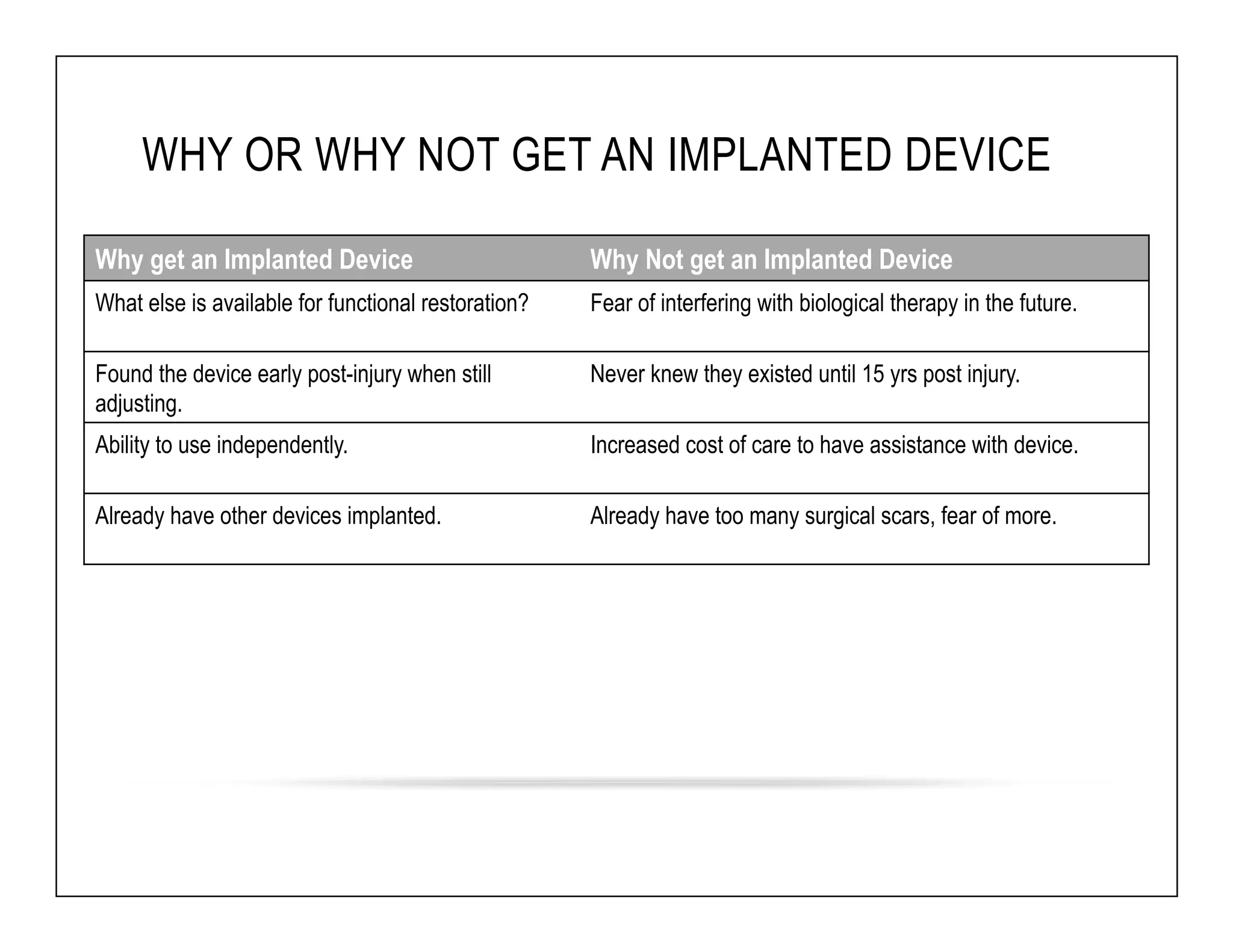
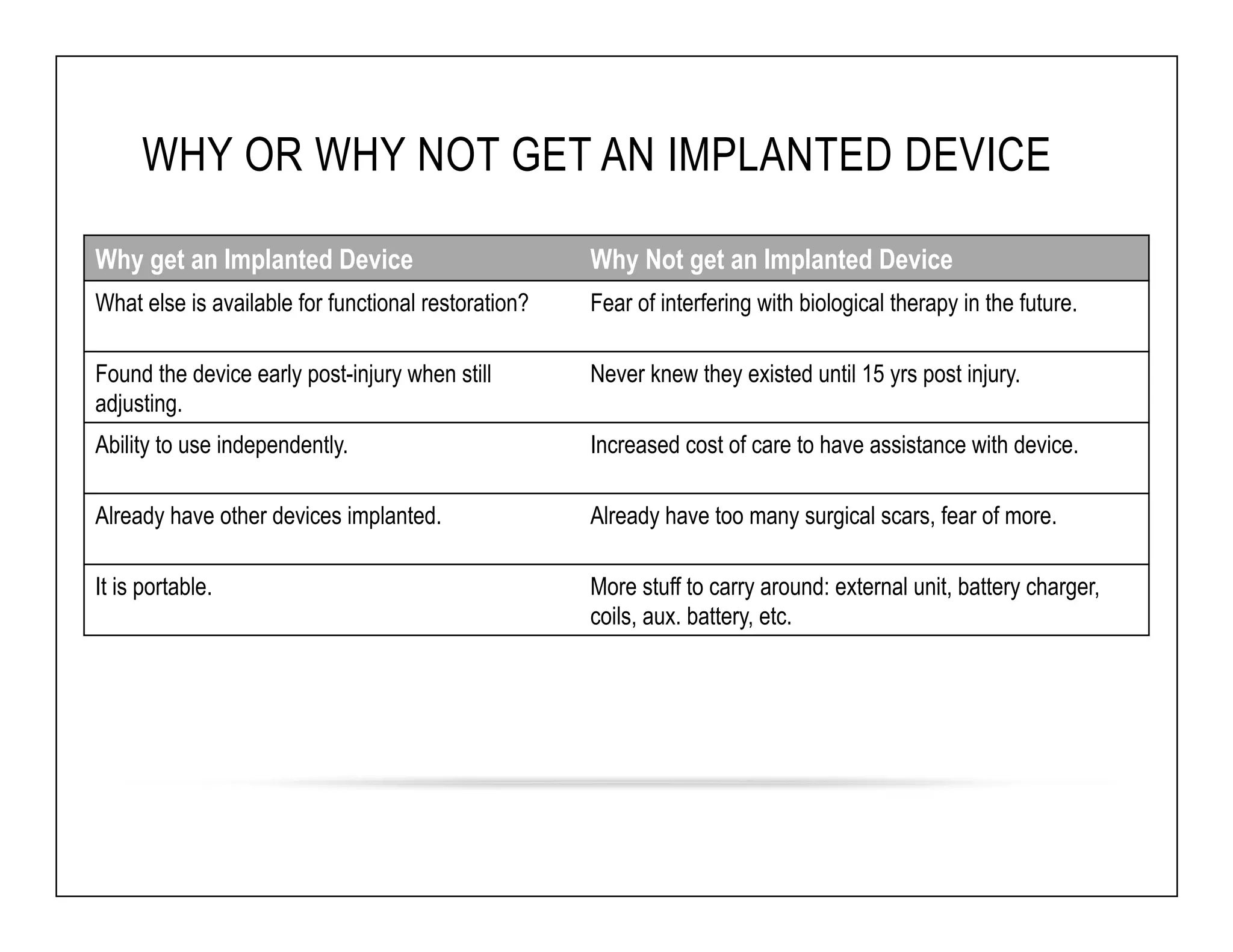
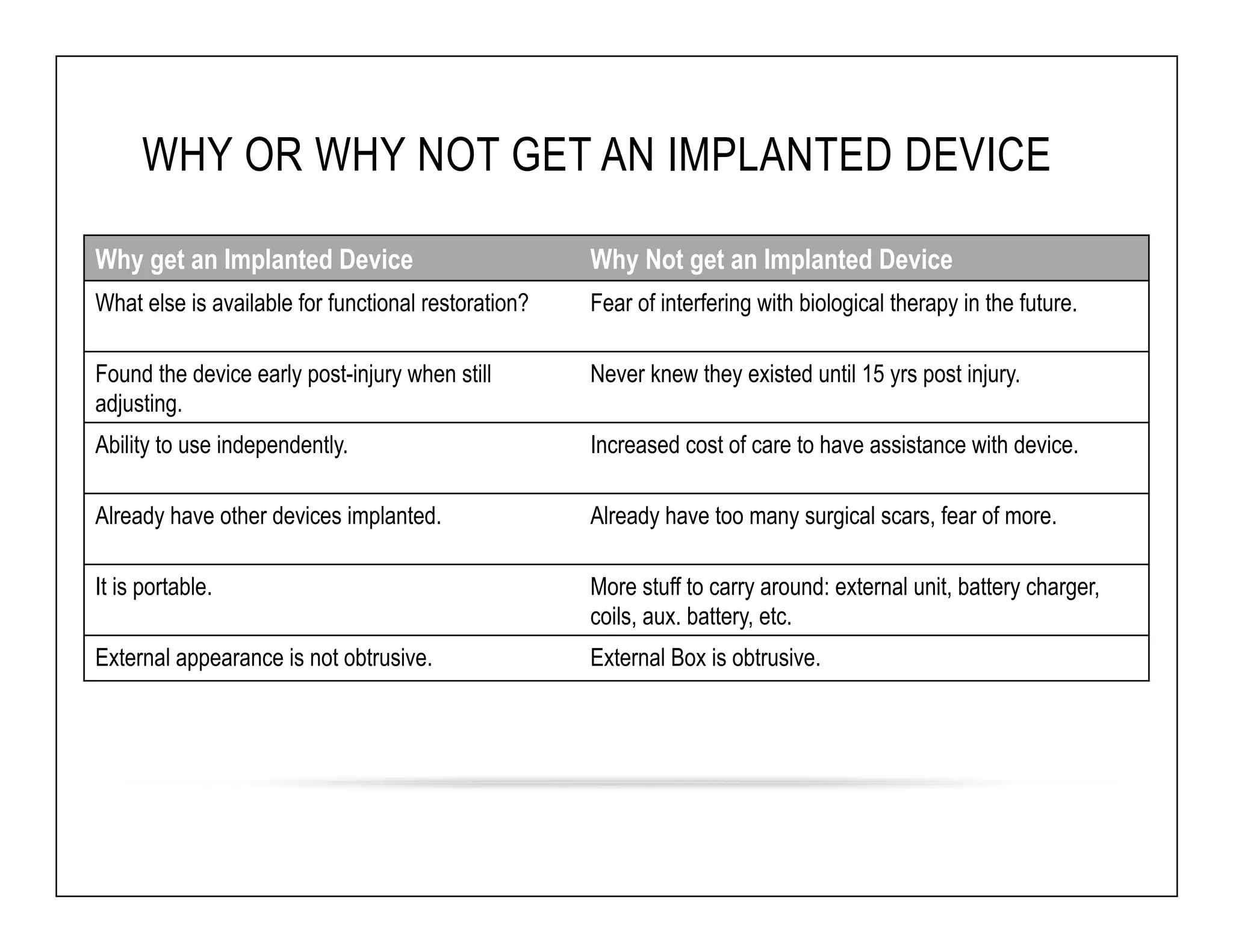
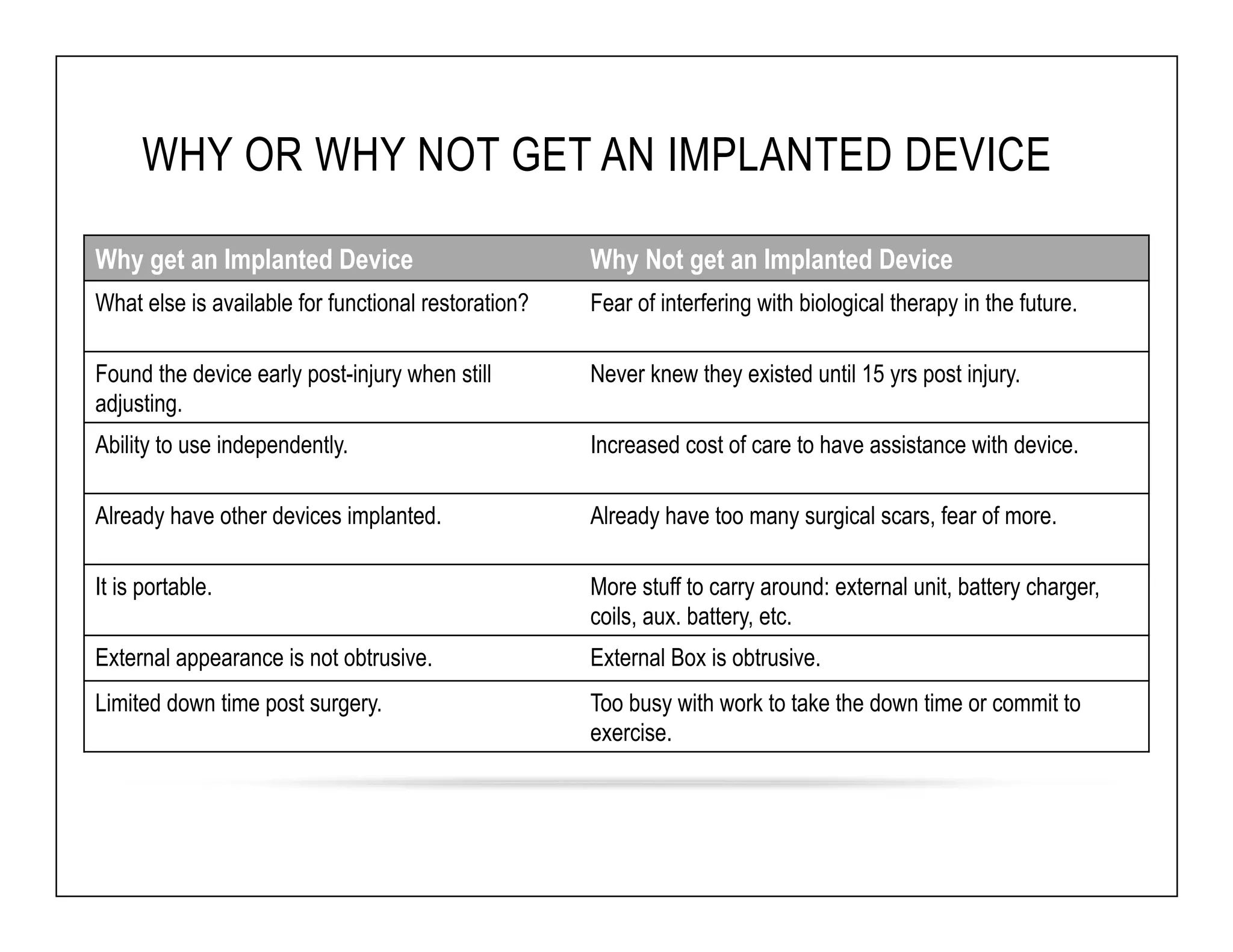
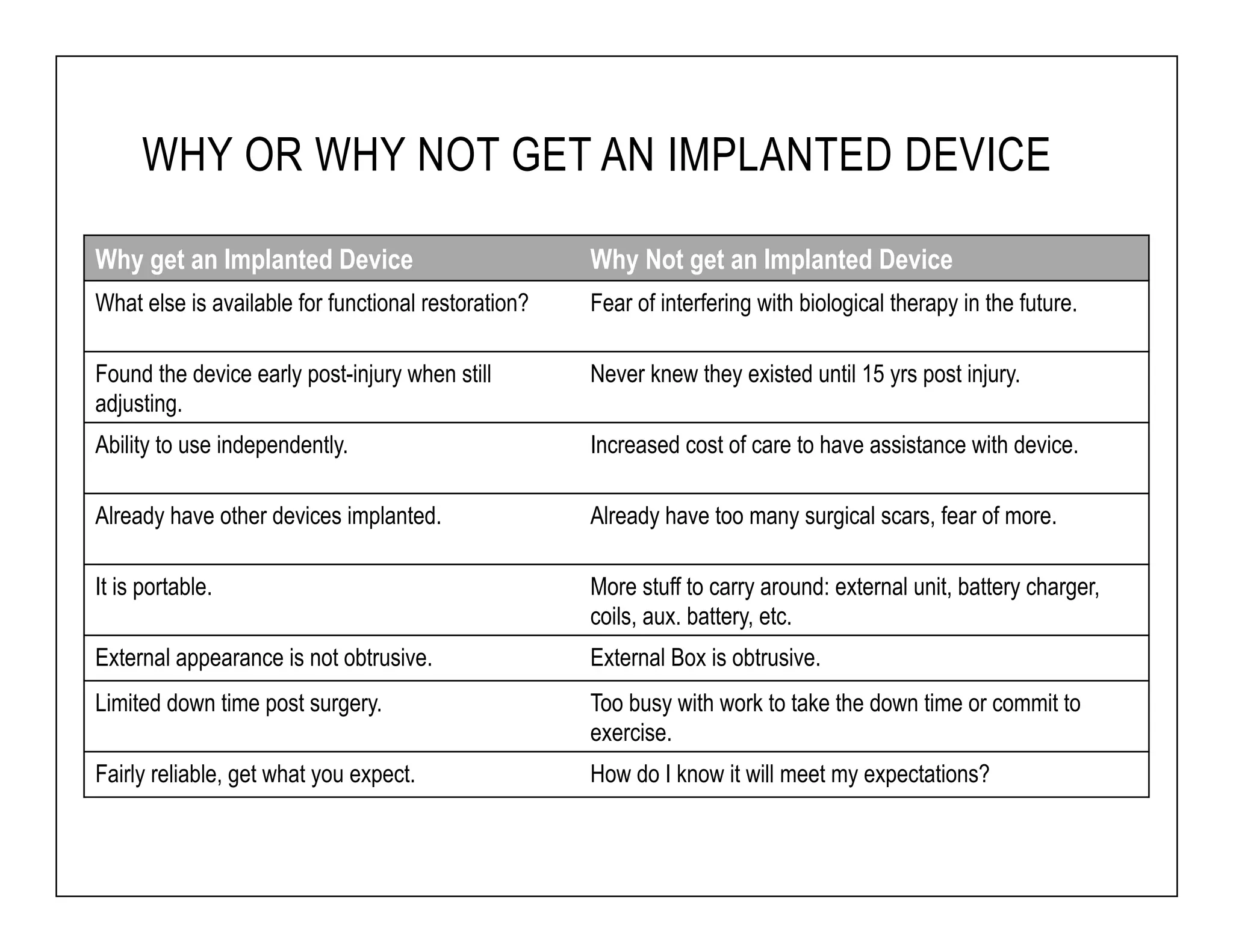
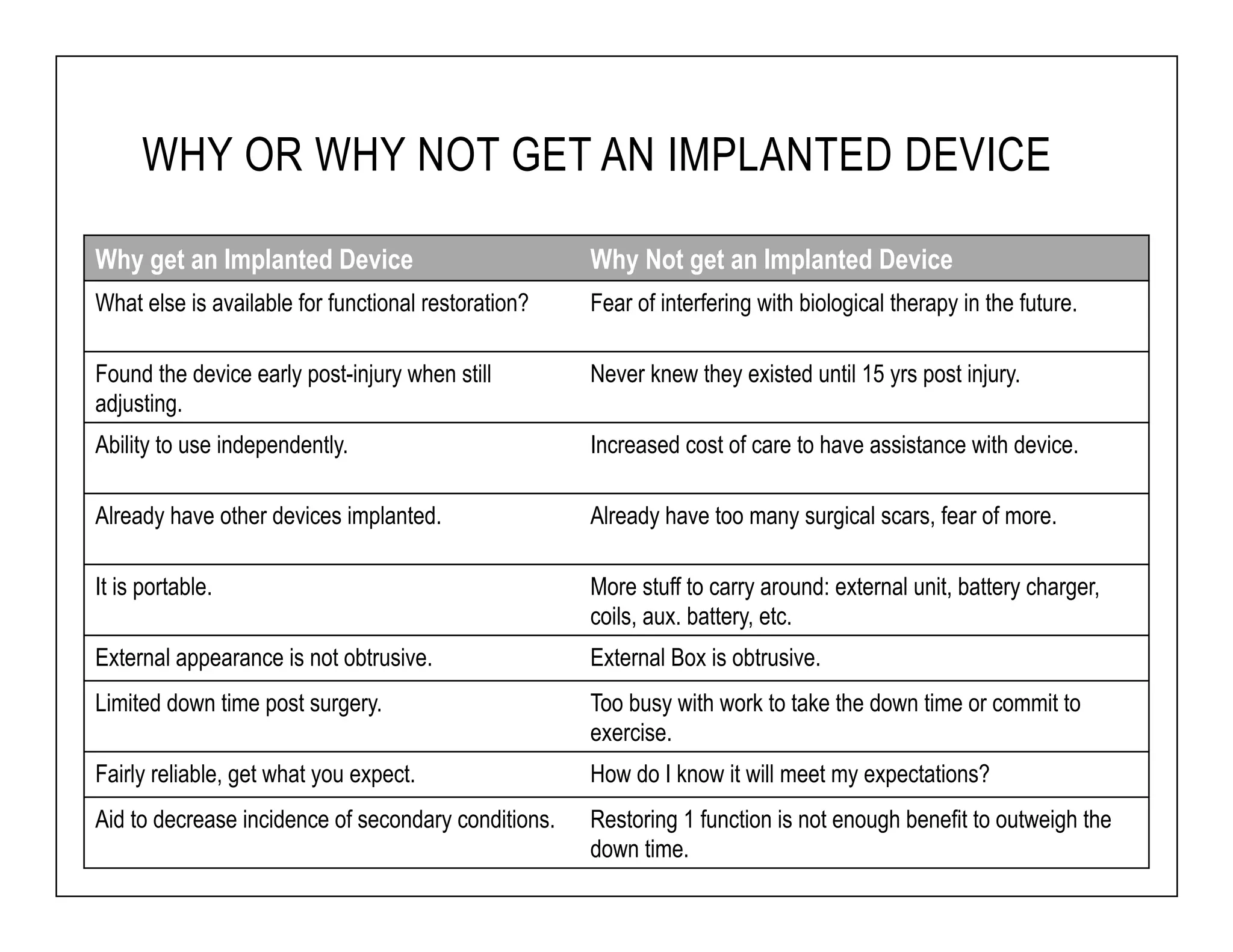
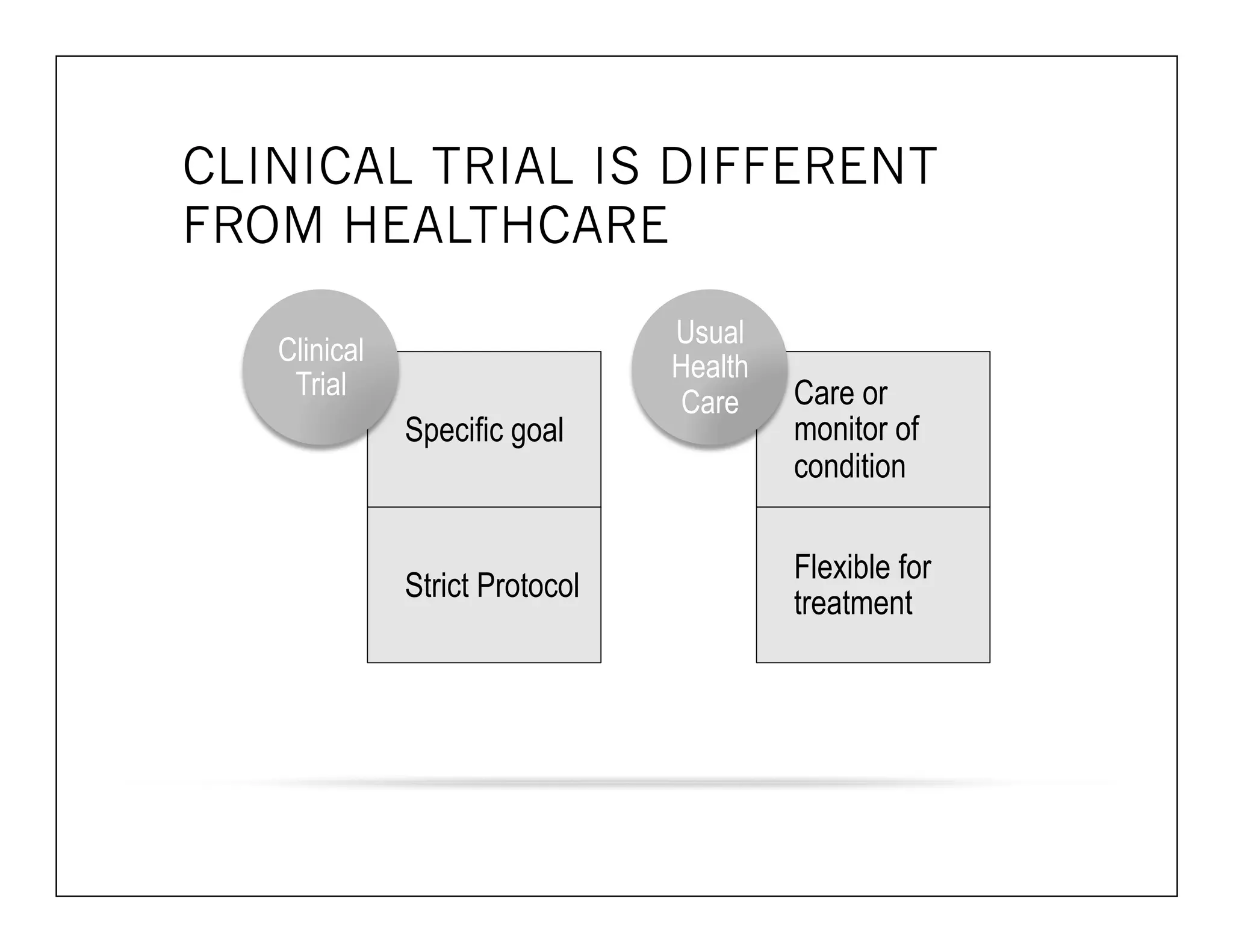
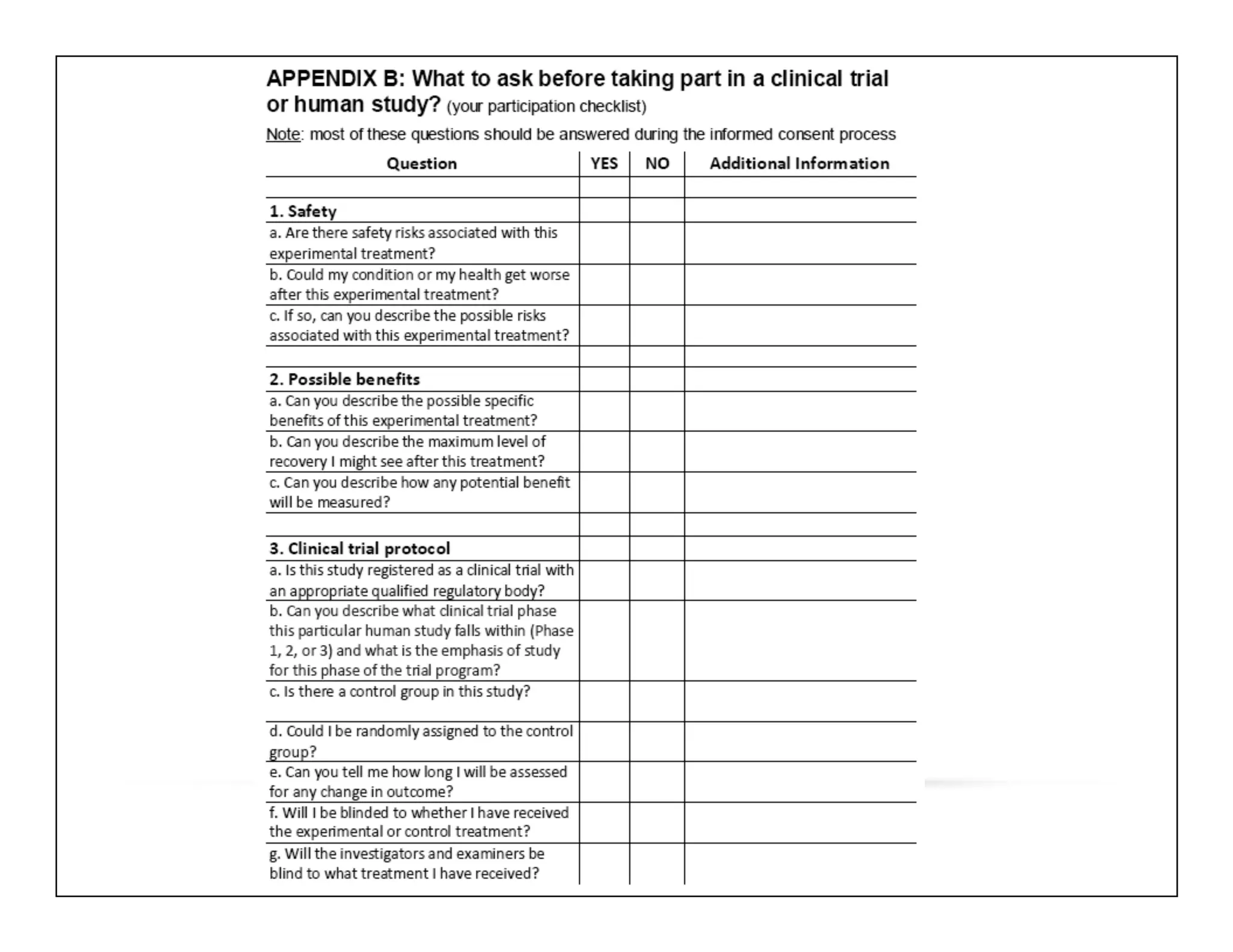
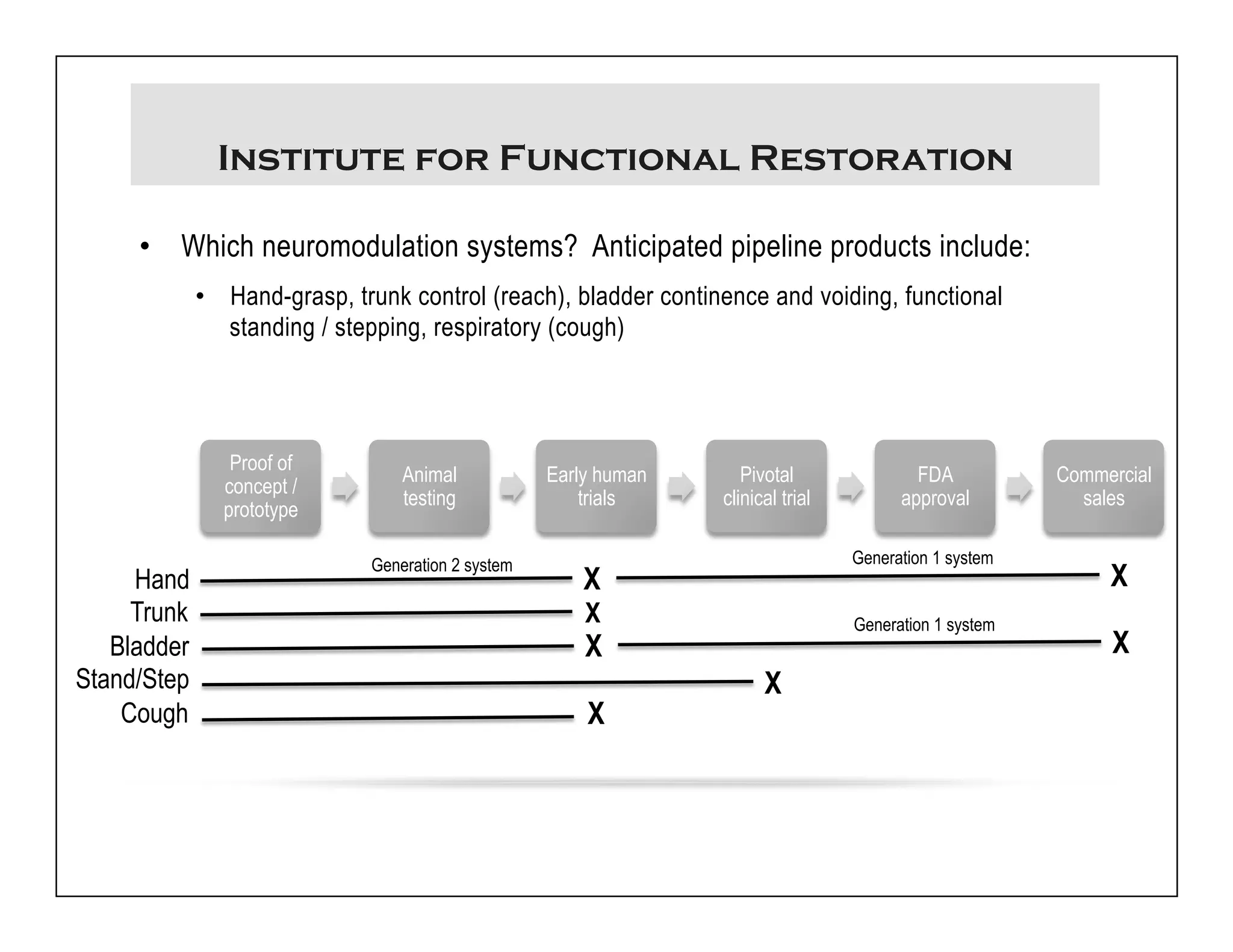
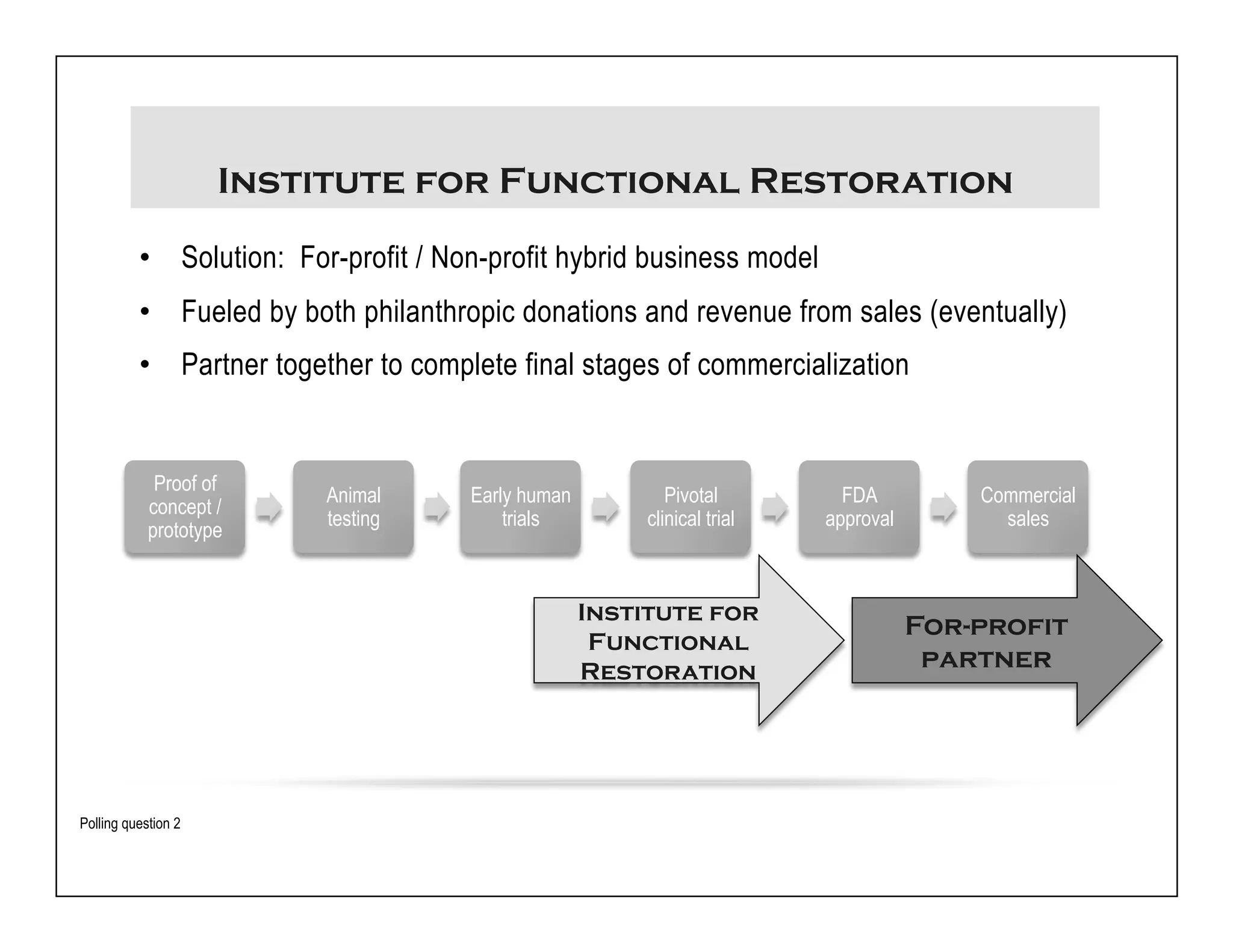
The document discusses a webinar on implanted neural prosthetics aimed at restoring function for individuals with spinal cord injuries, featuring experts from various organizations. It covers topics such as therapeutic and prosthetic applications, neurostimulation methods, clinical trials, and challenges related to device implantation. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for consultation with healthcare professionals and presents various resources for further information on neurotechnology and rehabilitation options.