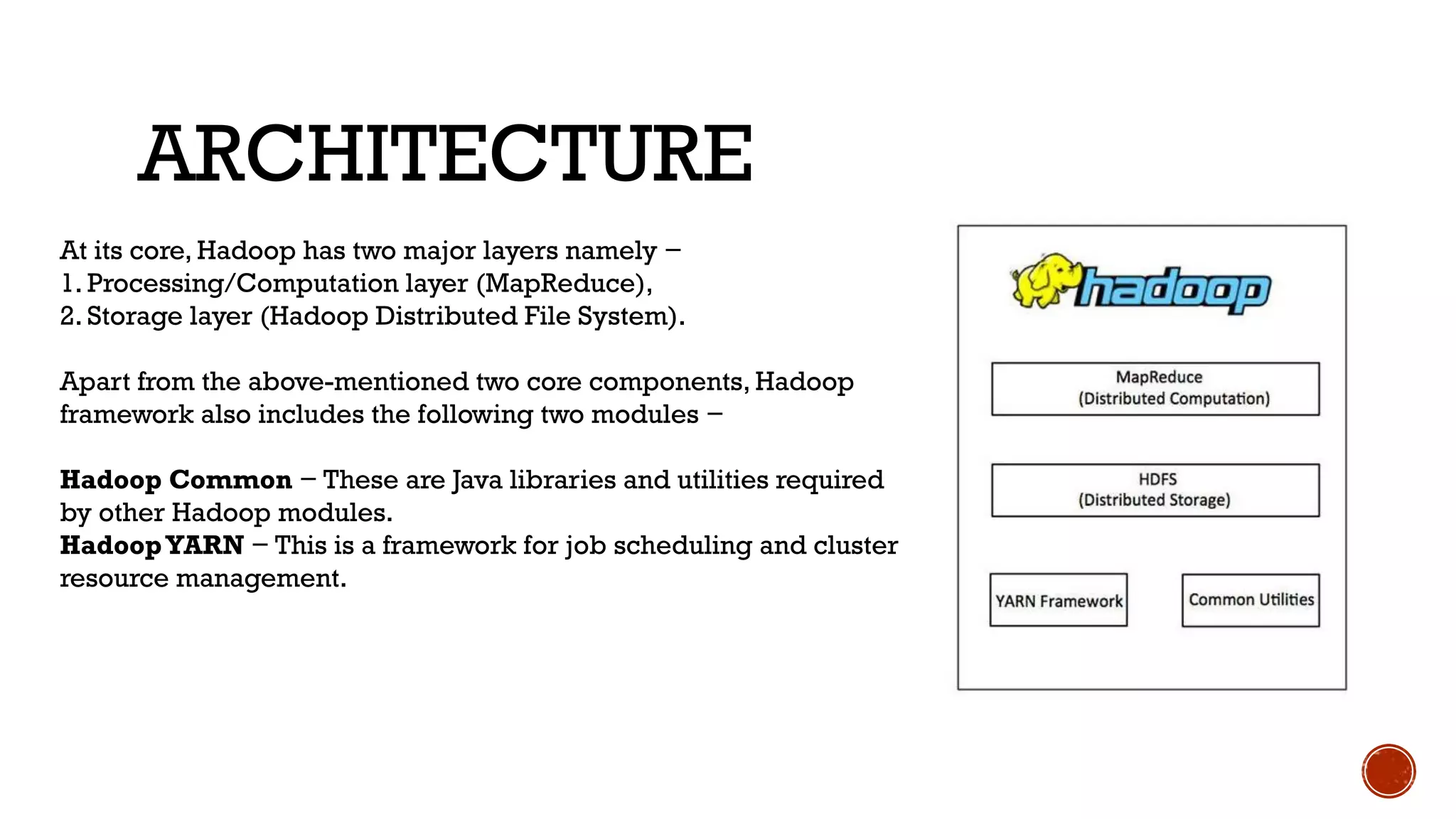
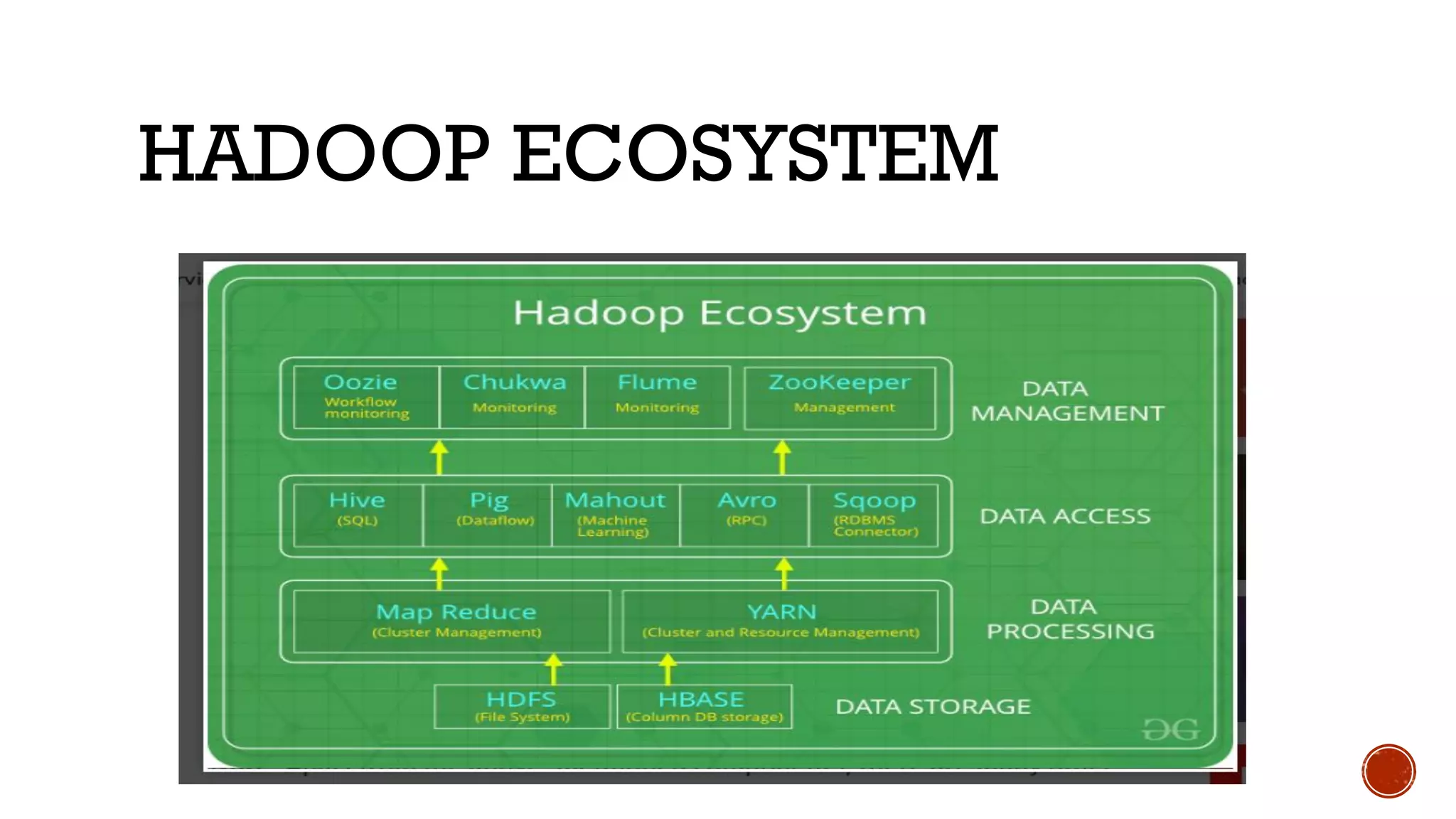
Hadoop is an open source framework that allows distributed processing of large datasets across clusters of computers. It has two major layers - a processing layer called MapReduce that splits data and runs tasks in parallel, and a storage layer called HDFS that stores data across nodes in a cluster. Hadoop can process large amounts of data reliably and at scale, distributing data, tasks and load balancing across nodes in a cluster.