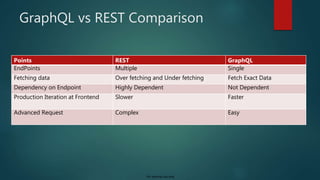
The document provides an introduction to GraphQL, highlighting its creation by Facebook, its advantages over REST, and its growing community. It explains GraphQL as a query language for APIs that allows clients to fetch exactly the data they need through a single endpoint, and outlines its type system and CRUD operations. Additionally, it addresses the potential challenges of transitioning from REST to GraphQL, including learning curves and setup requirements.






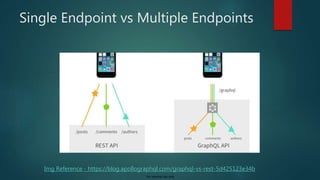

![For internal use only
Data Under fetching
{
"userName" : "moredee", "firstName" :
"Deepak",
"lastName" : "More",
"isActive" : "true",
"email" : "deepak.more@db.com",
"contactNumber" : "9420390095",
….
}
{
"userName" : "moredee", "firstName" :
"Deepak",
"lastName" : "More",
“Address” : [
…
]
}
{
“id" : “123",
“address Line" : “Nagras Road",
“address Line 1" : “Aundh",
“city" : “Pune",
“State" : “Maharashtra",
“PinCode" : “411007",
….
}
URL – /user/10
URL – /address/123](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontographqlautosaved16818-191204193512/85/Introduction-to-Graph-QL-13-320.jpg)


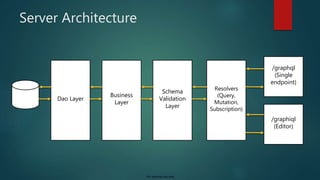
![For internal use only
Schema Basics
GraphQL has its own type system that’s used to define the schema of an API.
The syntax for writing schemas is called Schema Definition Language (SDL).
The ! following the type means that this field is required.
type User {
name: String!
contactNo: Int!
posts: [Post!]
}
type Post{
name: String!
author: User!
}
User Post
1 N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontographqlautosaved16818-191204193512/85/Introduction-to-Graph-QL-17-320.jpg)



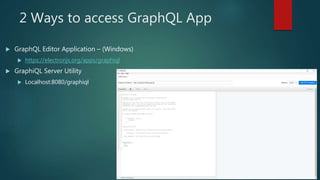
![For internal use only
Validation / Error Handling GraphQL
Error status :
{
"data": null,
"errors": [
{
"message": "Cannot query field ‘names' on type ‘Book'. Did you mean ‘name'? (line 52,
column 5):n namen ^",
"locations": [
{
"line": 52,
"column": 5
}
]
}
]
}
query {
searchbook(name: “java") {
names
author {
firstname
lastName
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontographqlautosaved16818-191204193512/85/Introduction-to-Graph-QL-23-320.jpg)







