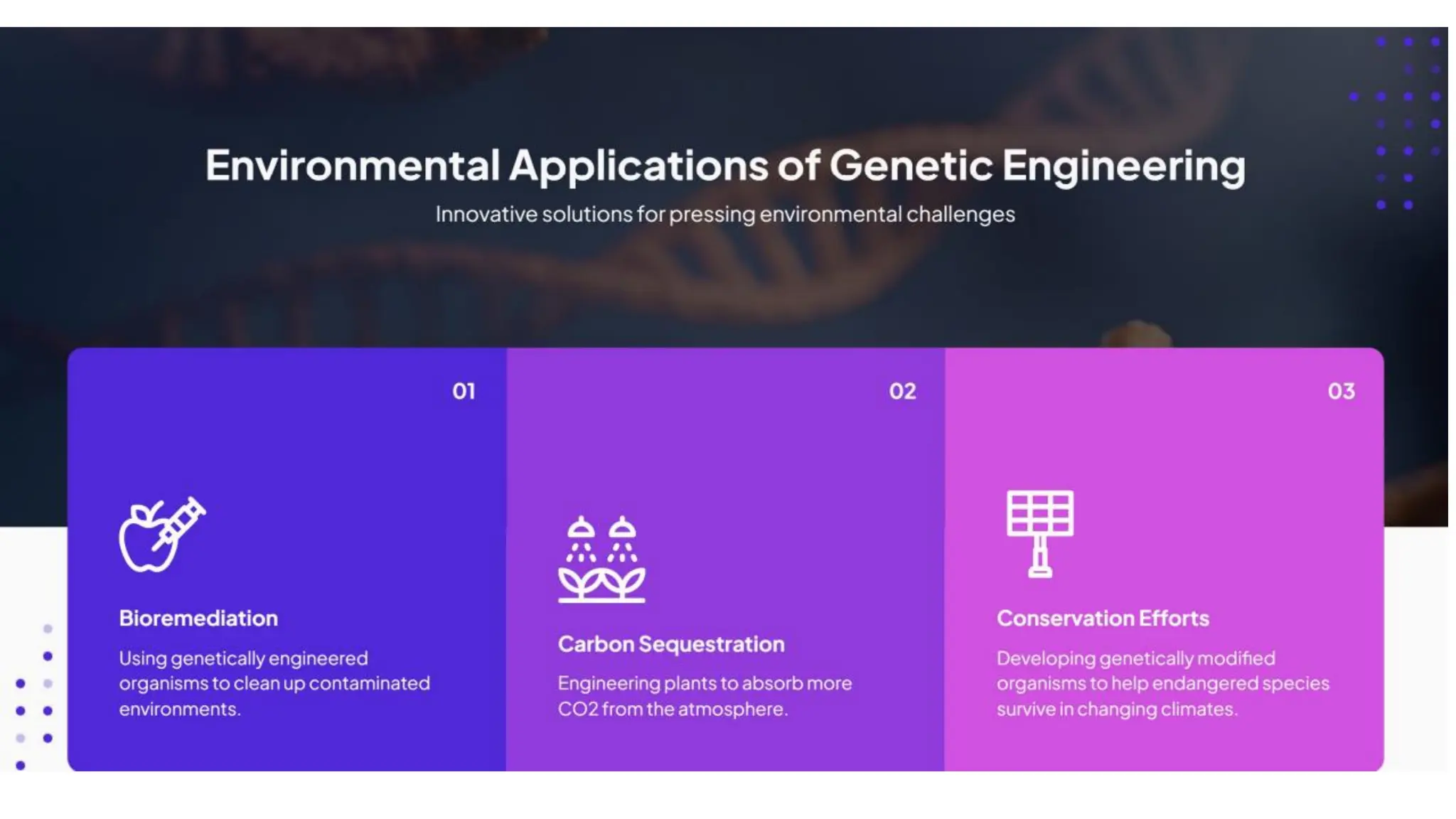
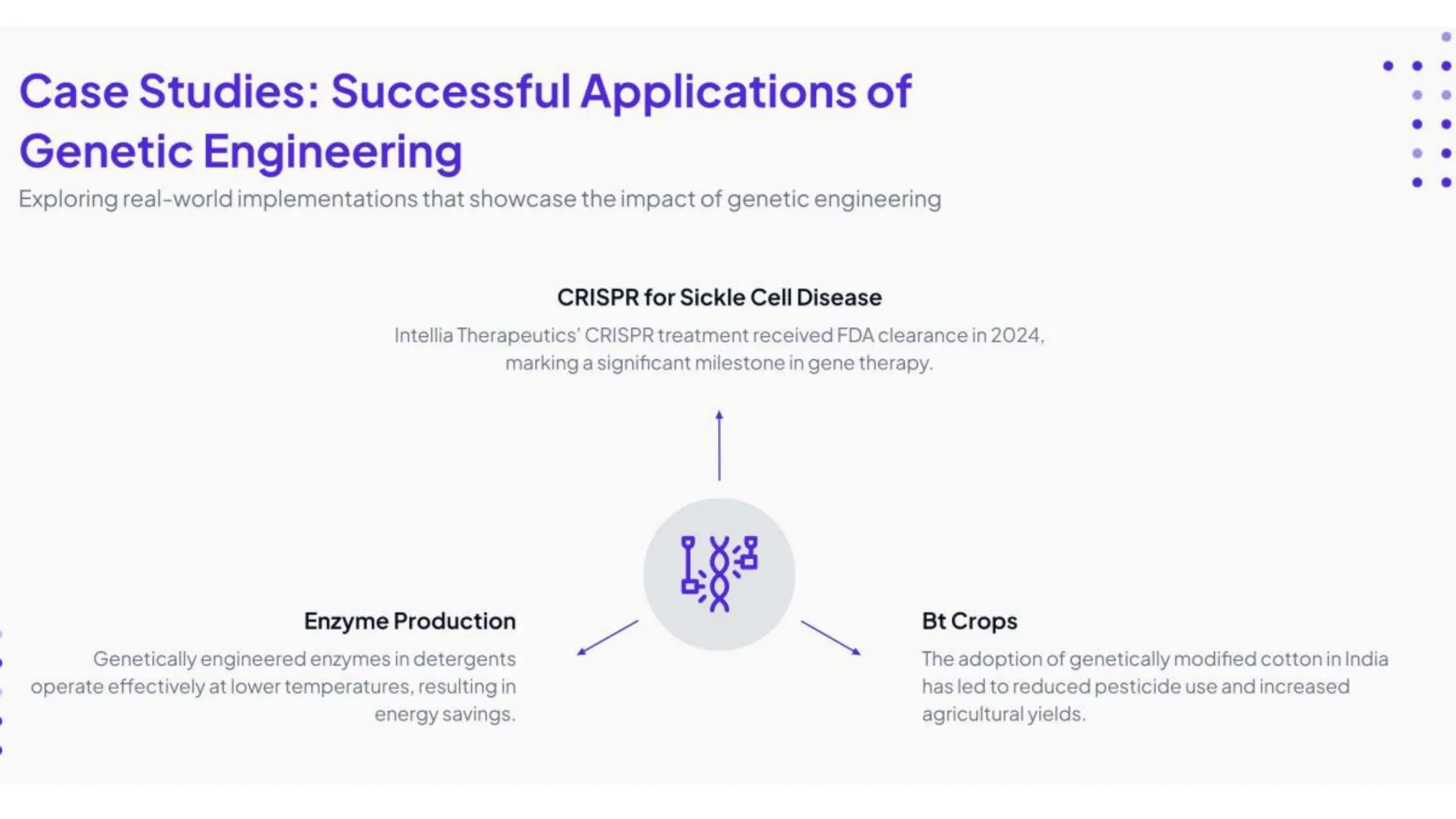
The document discusses key concepts in genetic engineering, including recombinant DNA technology, gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9, and their applications in medicine, agriculture, and industrial biotechnology. It highlights transformative impacts such as gene therapy, sustainable farming practices, and the production of essential drugs, while also addressing ethical considerations and emerging trends, like AI integration and green chemistry. The ethical implications of genetic editing, focusing on potential risks, equity in access to therapies, and privacy concerns, are also critically examined.