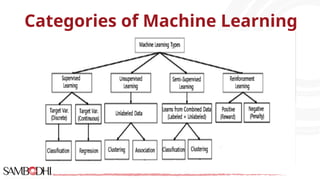
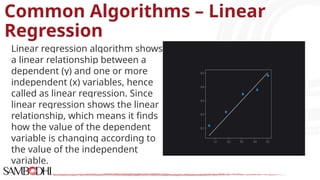
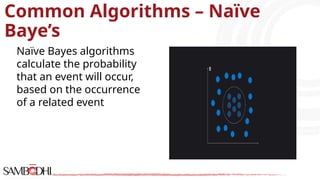
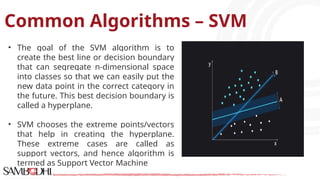
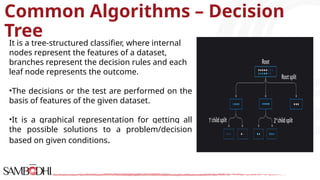
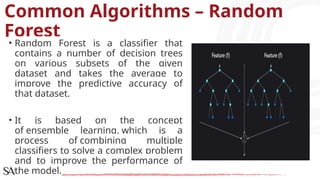
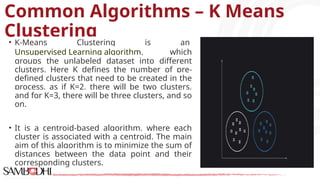
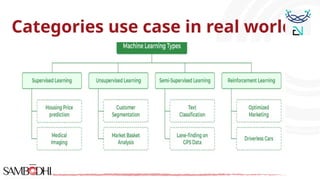
The document provides an overview of data science tools, specifically focusing on machine learning and visualization techniques. It outlines various machine learning algorithms, including linear regression, Naïve Bayes, SVM, decision trees, KNN, random forest, and K-means clustering, explaining their functionalities and use cases. Additionally, it presents the machine learning process and compares supervised and unsupervised learning approaches.