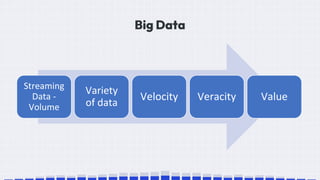
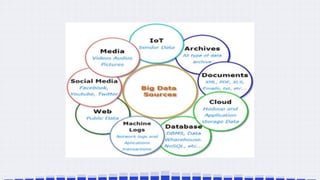
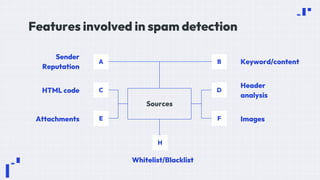
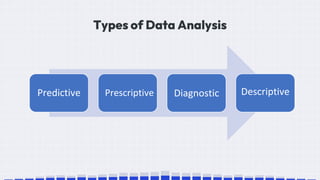
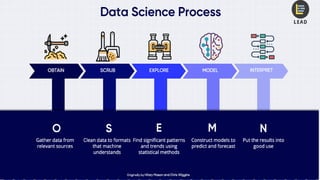
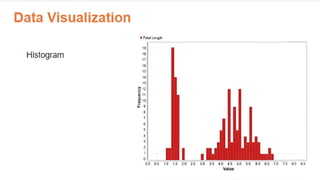
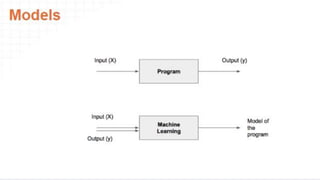
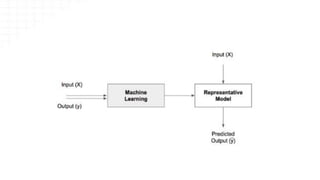
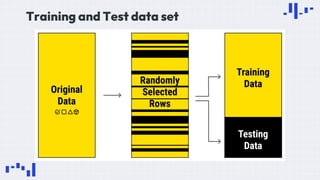
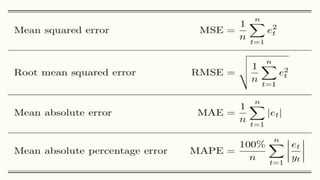
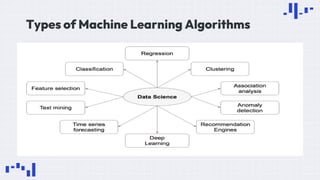
The document provides an overview of data science, emphasizing its multidisciplinary nature that combines programming, statistics, and domain expertise to derive insights from large datasets. It discusses the necessity of data science in handling big data challenges and application areas such as predictive modeling, product recommendations, and spam detection. Additionally, the document outlines essential skills and resources needed for a successful career in data science.