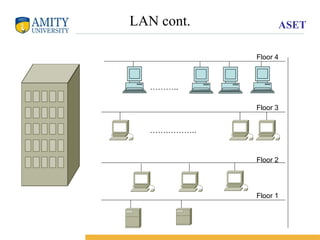
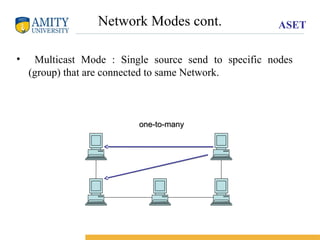
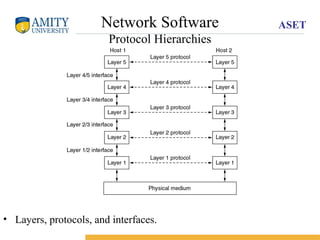
The document provides an overview of data communication, including key components such as sender, receiver, transmission medium, and protocol. It explains data flow types (simplex, half-duplex, duplex) and various network classifications (PAN, LAN, CAN, MAN, WAN) along with their characteristics and criteria for performance, reliability, and security. Additionally, it discusses network modes (unicast, multicast, broadcast) and references models like OSI and TCP/IP.