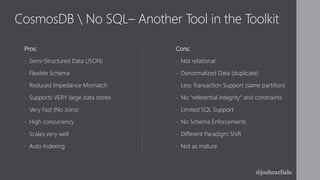
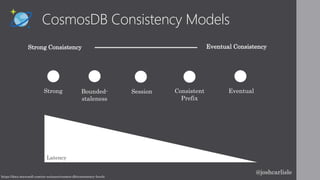
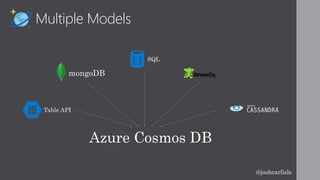
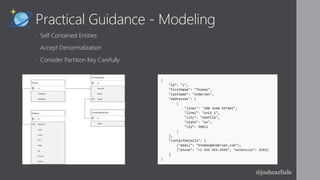
Josh Carlisle introduces Azure Cosmos DB, a globally distributed, multi-model database service. Cosmos DB offers turnkey global distribution, high availability up to 99.999%, and low latency reads and writes typically under 10ms. It uses request units to reserve throughput and ensure service level agreements. Cosmos DB supports multiple APIs including MongoDB, SQL, Cassandra, and table storage and scales elastically.