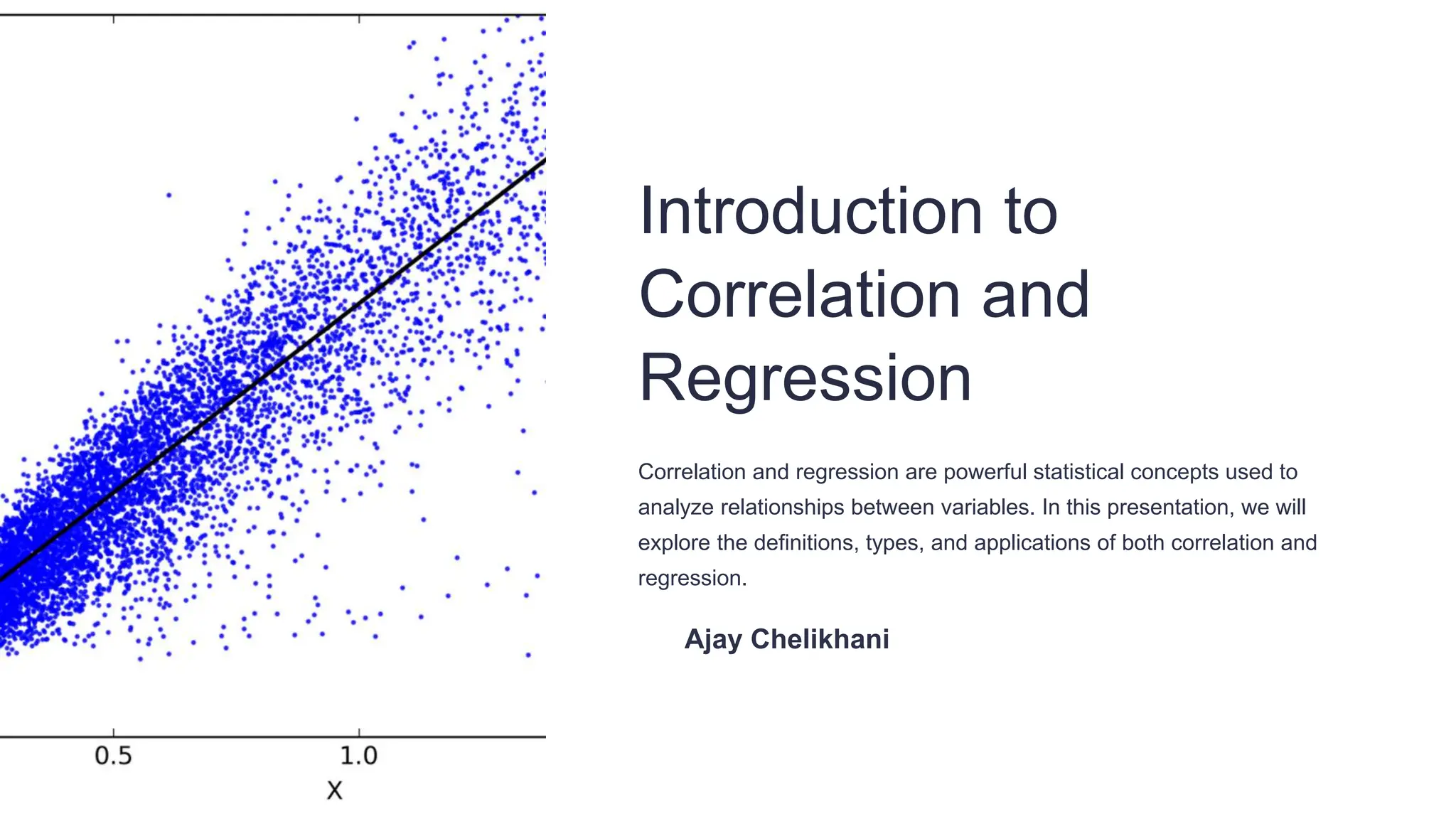
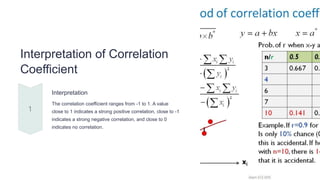
The document provides an overview of correlation and regression, defining correlation as a measure of the strength and direction of relationships between two variables and regression as a method for modeling relationships between dependent and independent variables. It distinguishes between types of correlation (positive, negative, and zero) and outlines the calculation and interpretation of the correlation coefficient. Additionally, it describes simple and multiple regression methods and their applications in various fields such as economics and social sciences.