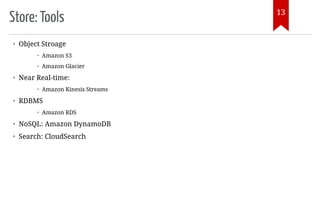
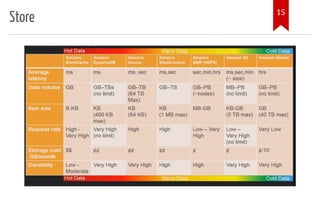
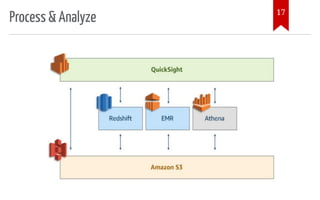
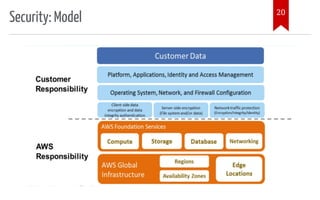
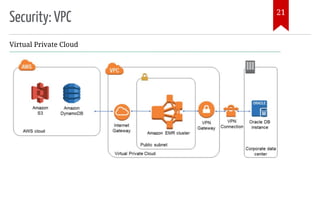
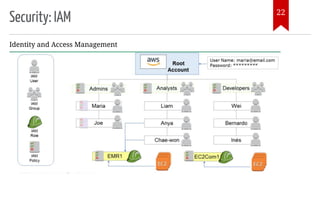
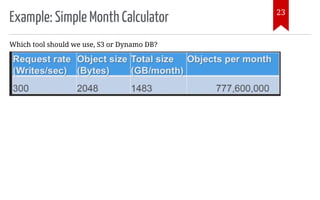
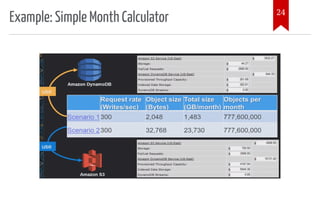
The document introduces AWS Data Pipeline services, outlining key goals such as problem identification and tool implementation. It discusses big data characteristics, AWS advantages, storage types, processing tools, security measures, and cost considerations. A demonstration using AWS services like Glue, Athena, and QuickSight is also included.