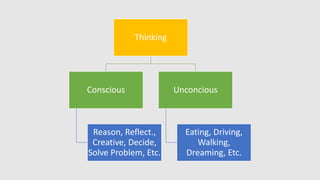
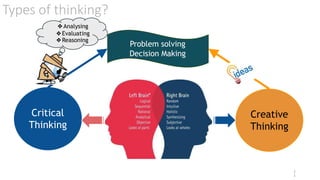
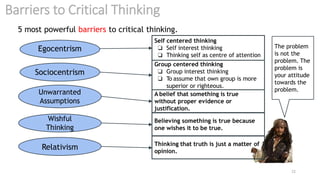
The document discusses critical thinking and problem-solving as essential skills in education and the workplace. It outlines types of thinking, characteristics of critical thinkers, activities involved in critical thinking, and barriers to effective thinking. Emphasizing the importance of these skills, it identifies benefits in both professional and daily life contexts.