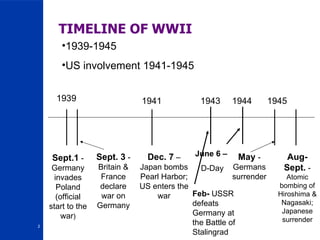
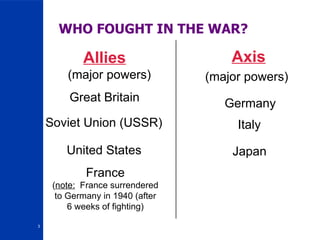
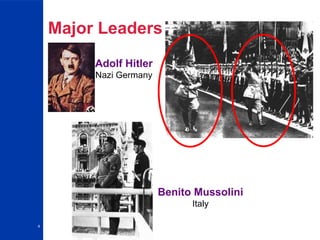
World War II began in 1939 with Germany's invasion of Poland and ended in 1945. Major Allied powers including the United Kingdom, France, the Soviet Union and the United States fought against the Axis powers of Germany, Italy and Japan. Some key events included Germany's invasion of Poland beginning the war, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor bringing the US into the war, the Battle of Stalingrad which marked a turning point, D-Day which opened a Western front, and the US dropping atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki leading to Japan's surrender and the war's end. Underlying causes included the Treaty of Versailles which weakened Germany economically and politically as well as the worldwide Great Depression which helped Hitler rise to power.