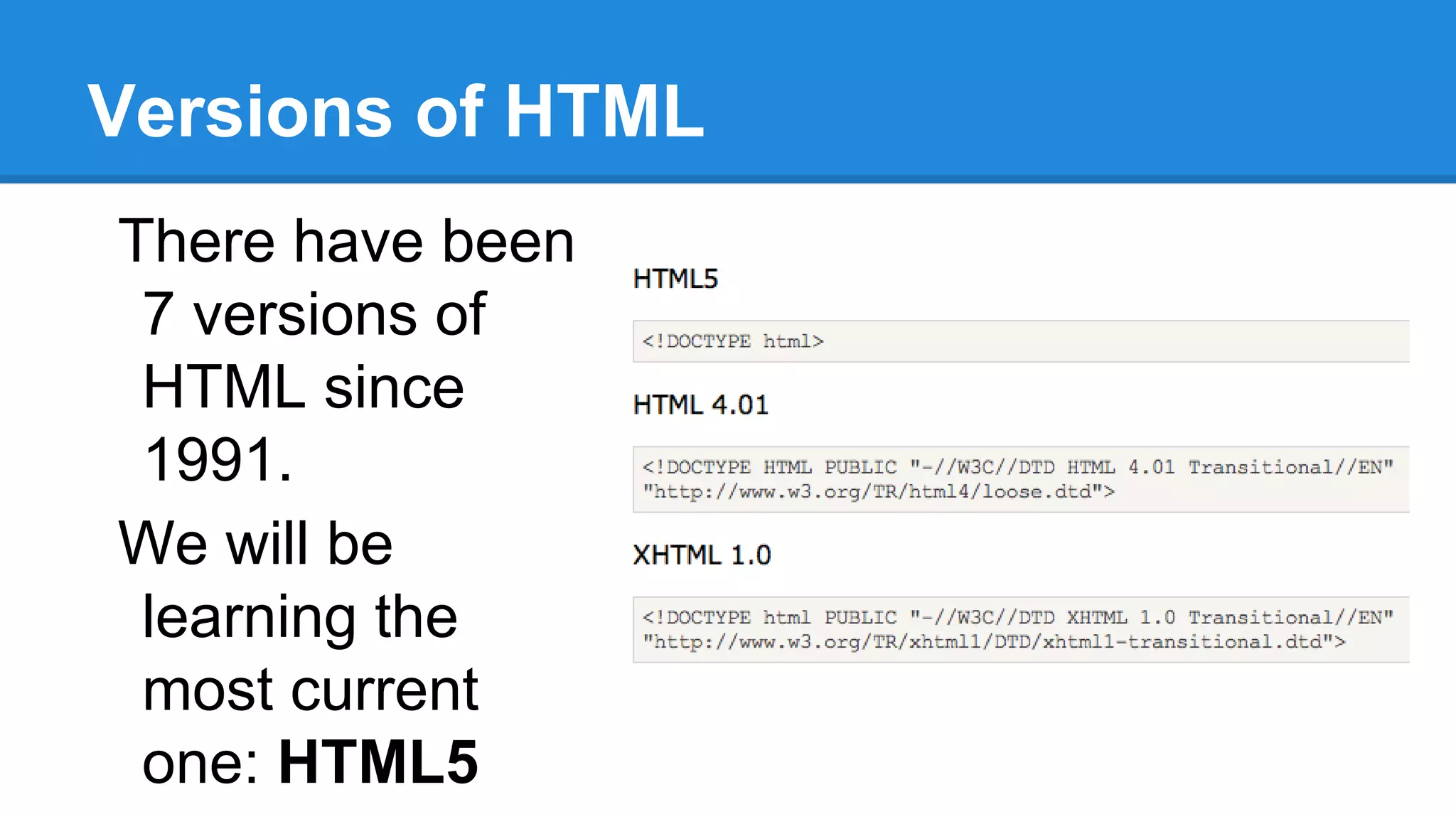
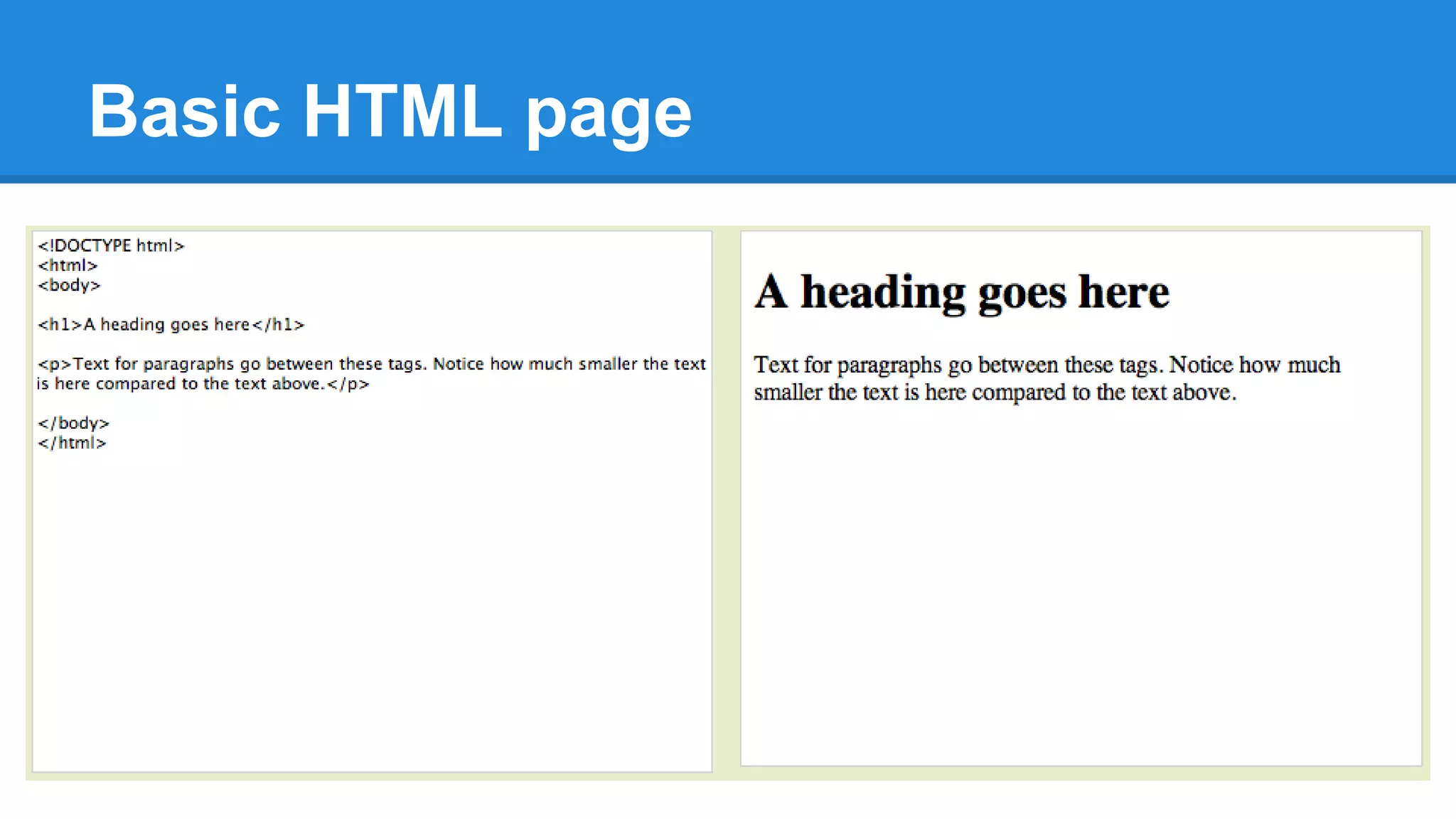
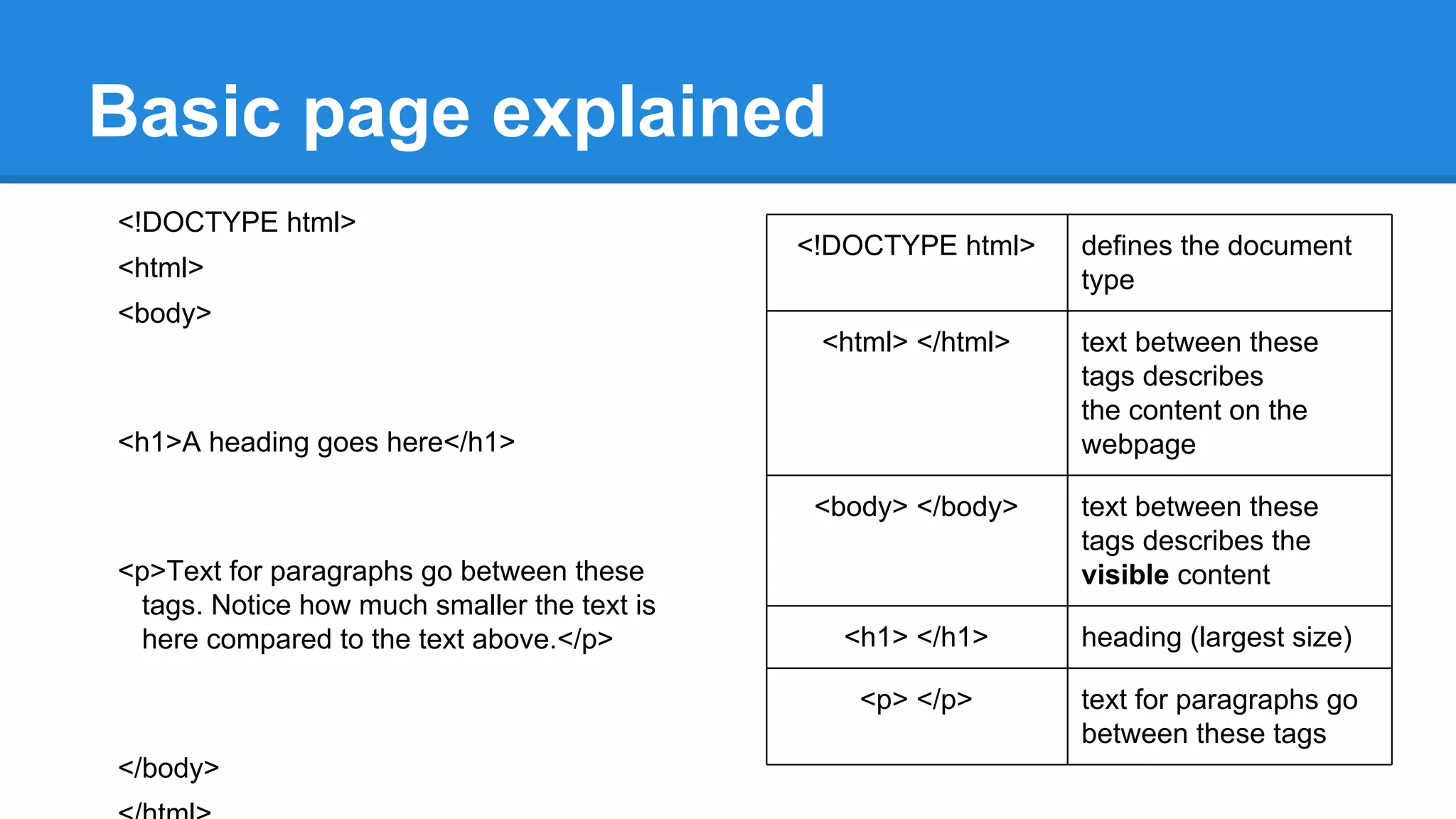
HTML is a markup language used to define the structure and layout of web pages. It uses tags to mark elements like headings, paragraphs, and other semantic elements. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) determines web standards and the most current version of HTML is HTML5. A basic HTML page includes tags like <html>, <body>, <h1> for headings, and <p> for paragraphs that describe the content and its presentation between opening and closing tags.