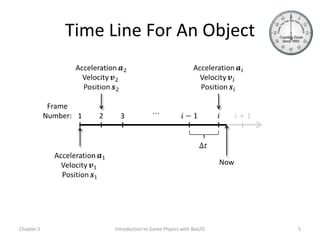
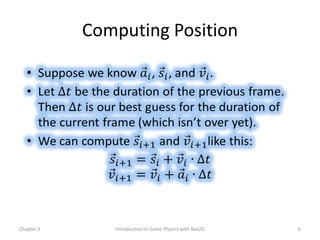
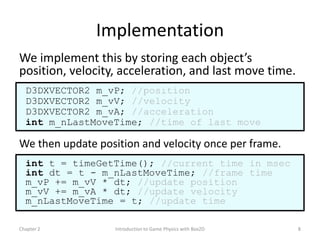
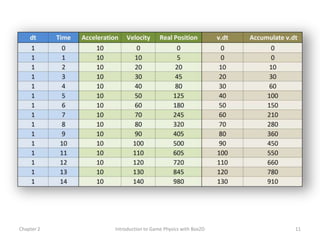
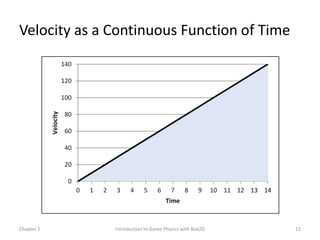
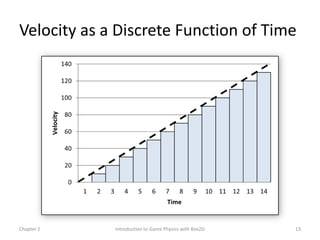
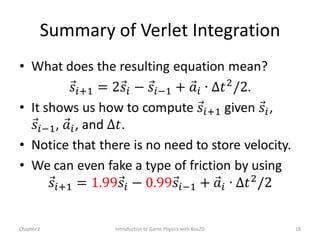
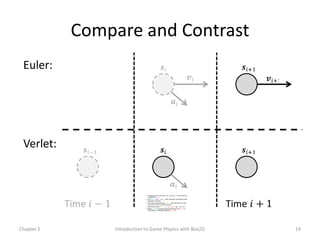
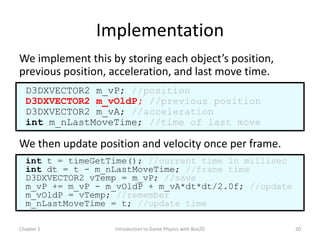
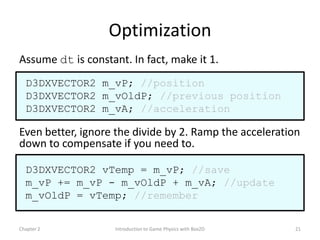
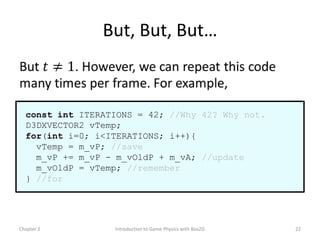
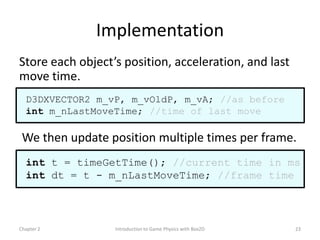
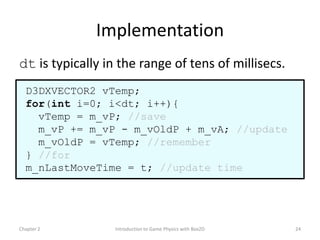
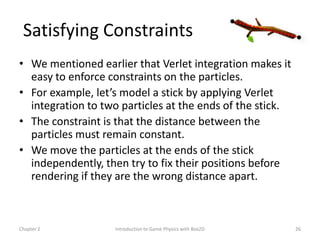
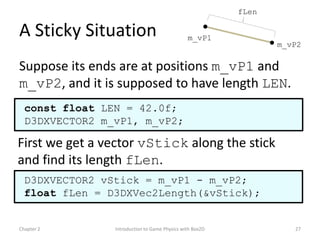
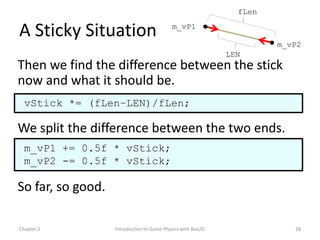
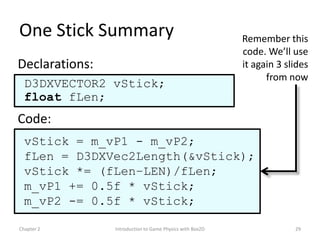
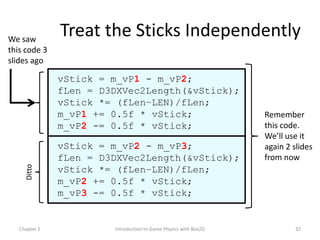
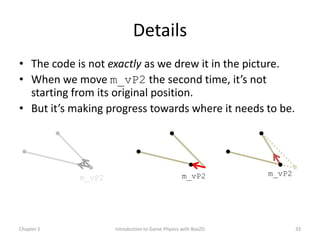
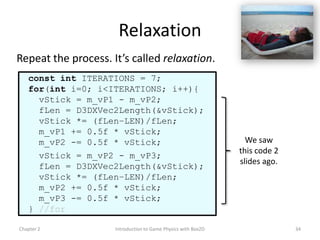
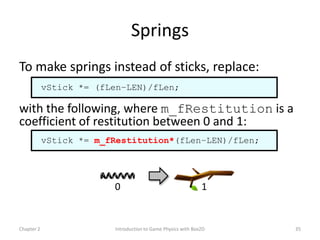
This document discusses different methods for calculating motion in digital simulations, including Euler integration, Verlet integration, and Gauss-Seidel relaxation. Euler integration approximates movement by assuming constant velocity over each time step. Verlet integration stores both the current and previous position and calculates the new position based on those values and acceleration. Gauss-Seidel relaxation is an iterative method that can be used to satisfy multiple constraints simultaneously by treating them independently over several iterations.