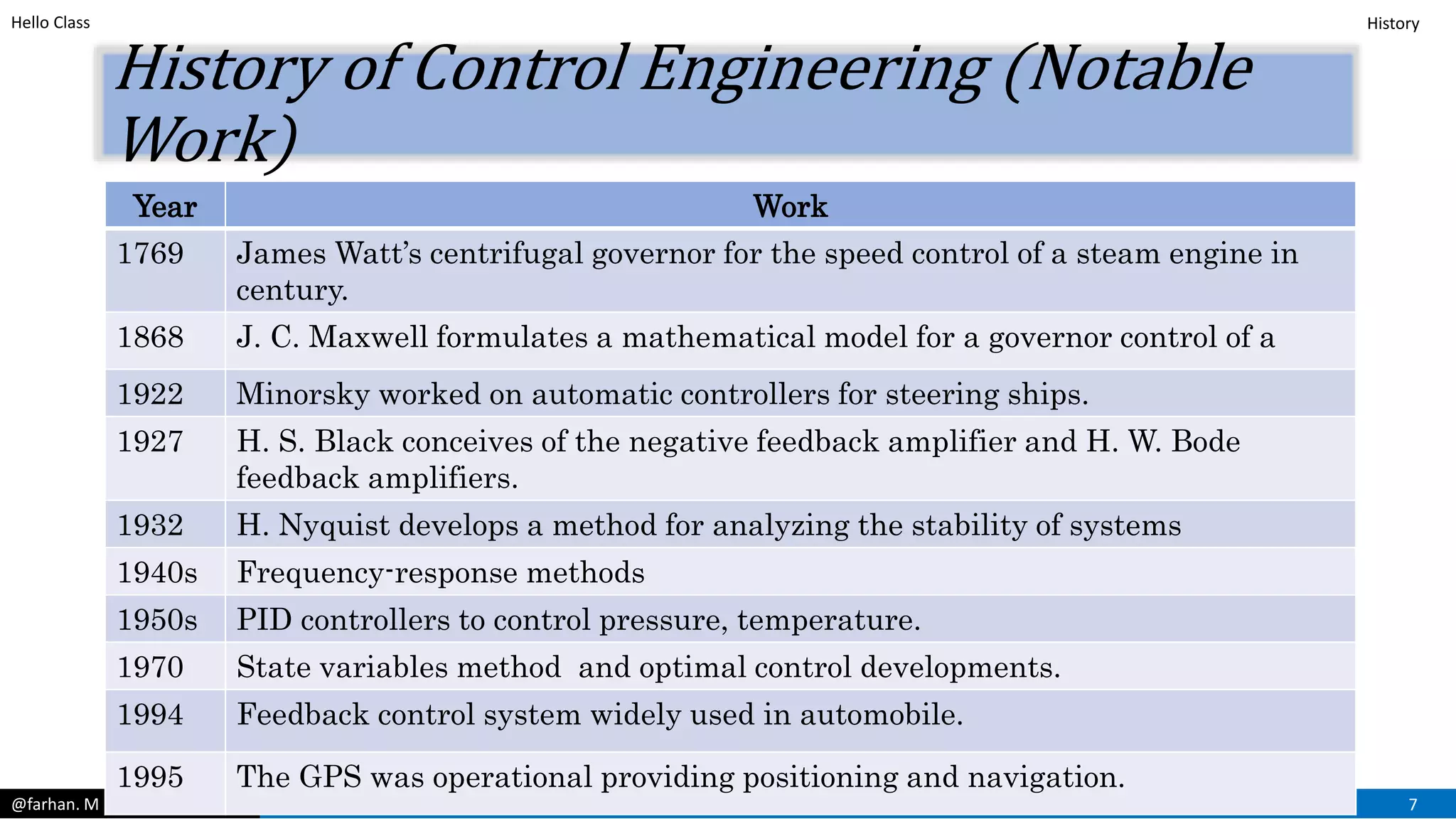
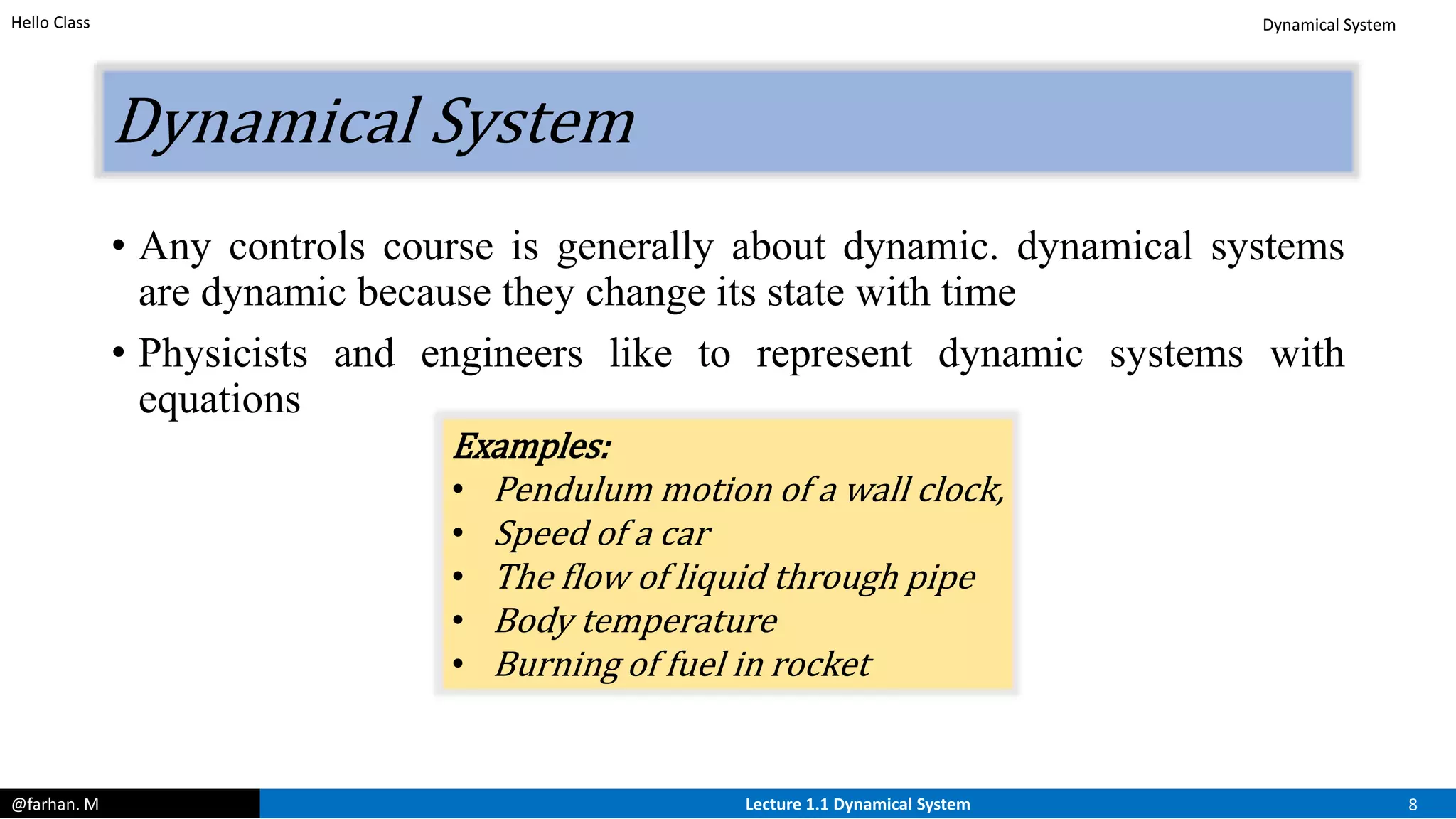
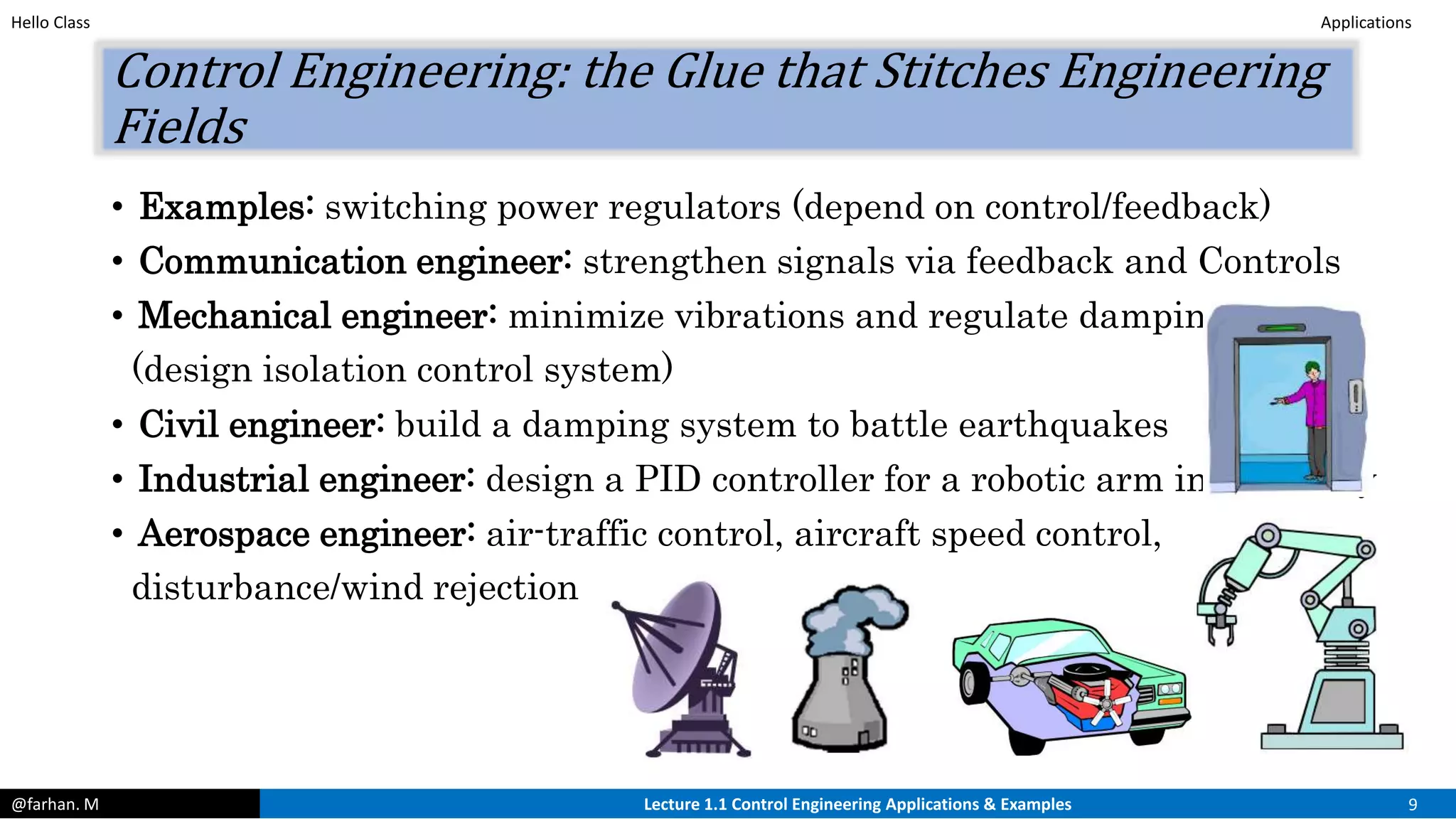
This document provides an introduction and overview of control systems. It discusses the following key points in 3 sentences:
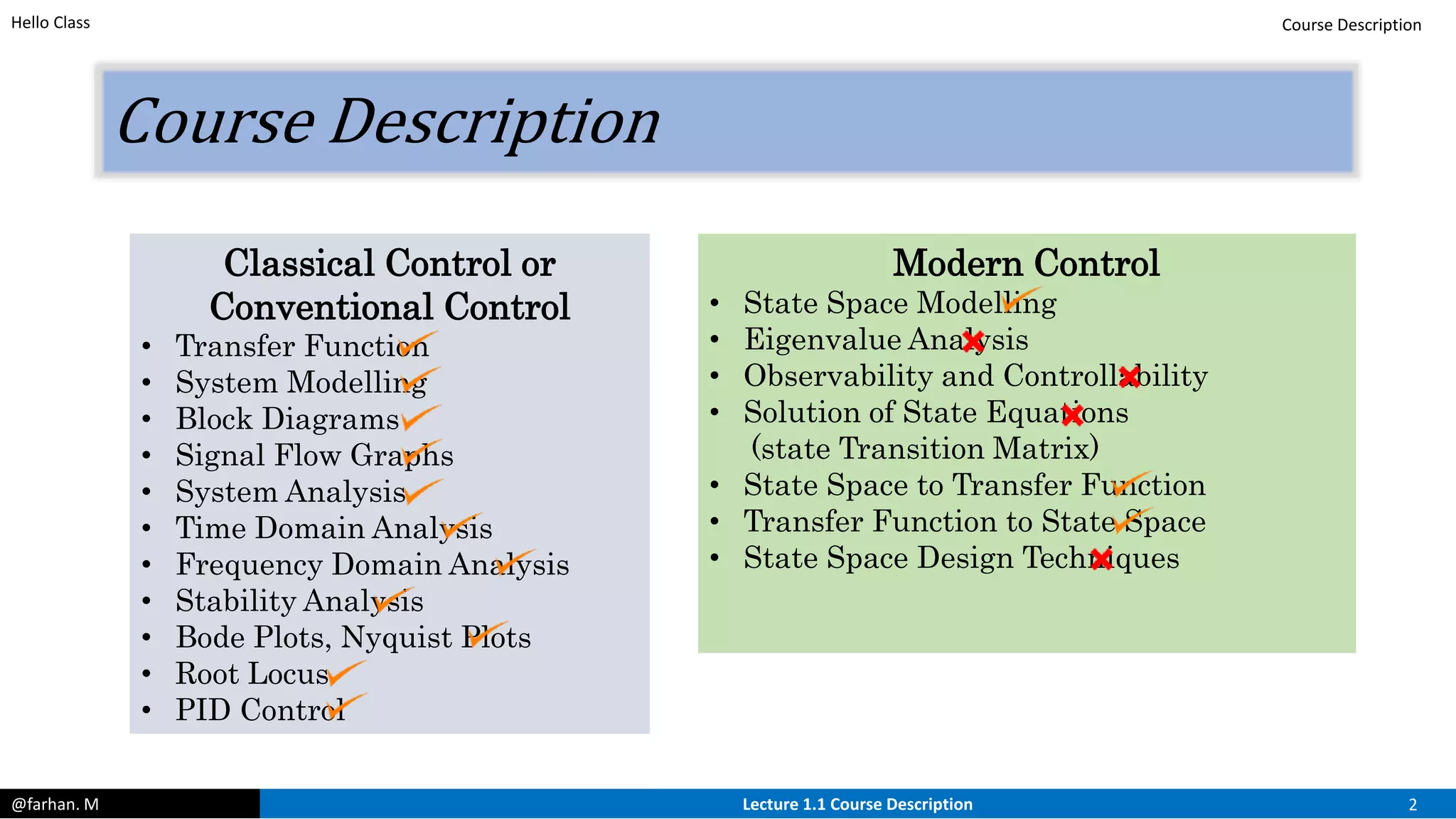
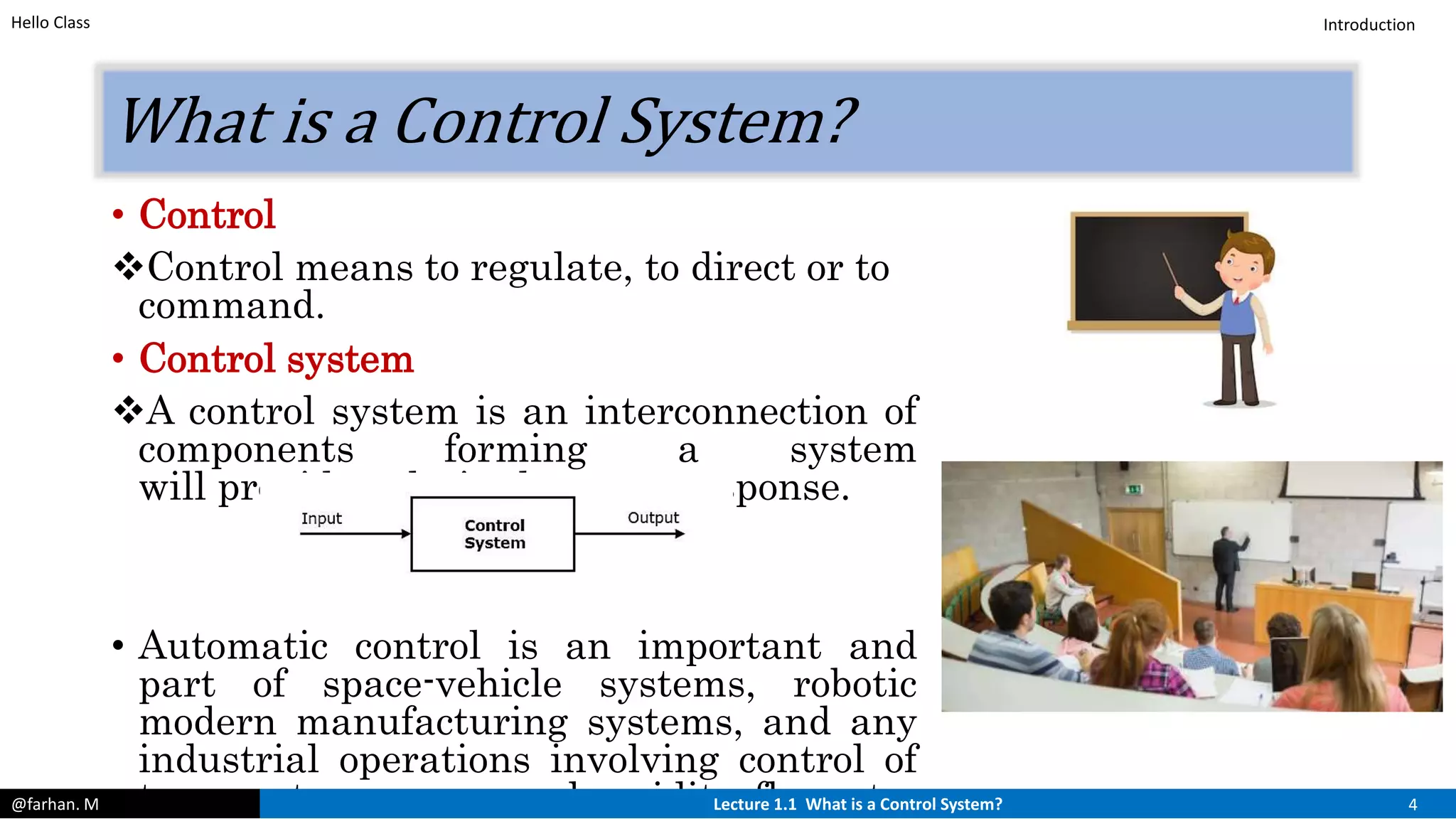
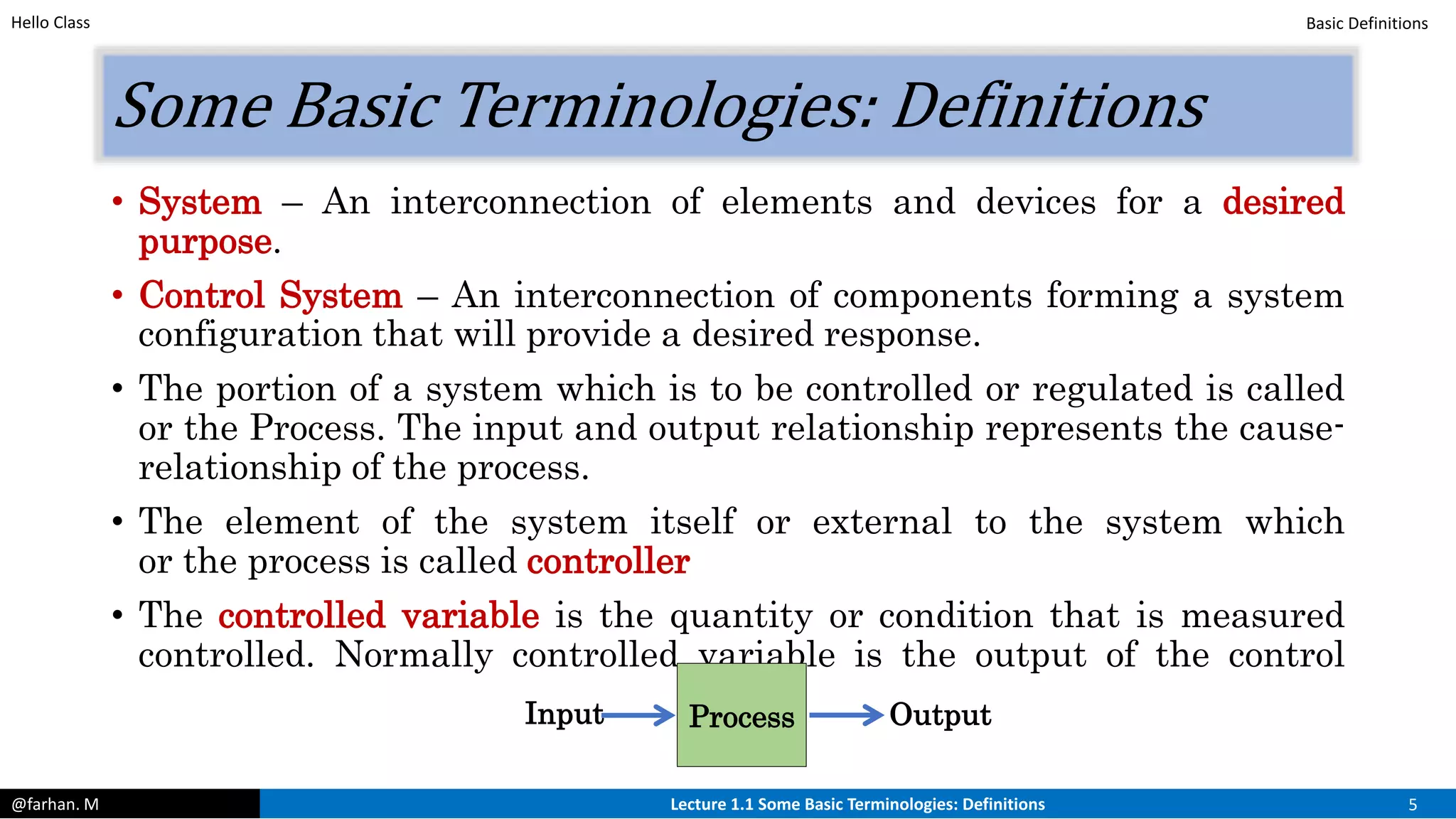
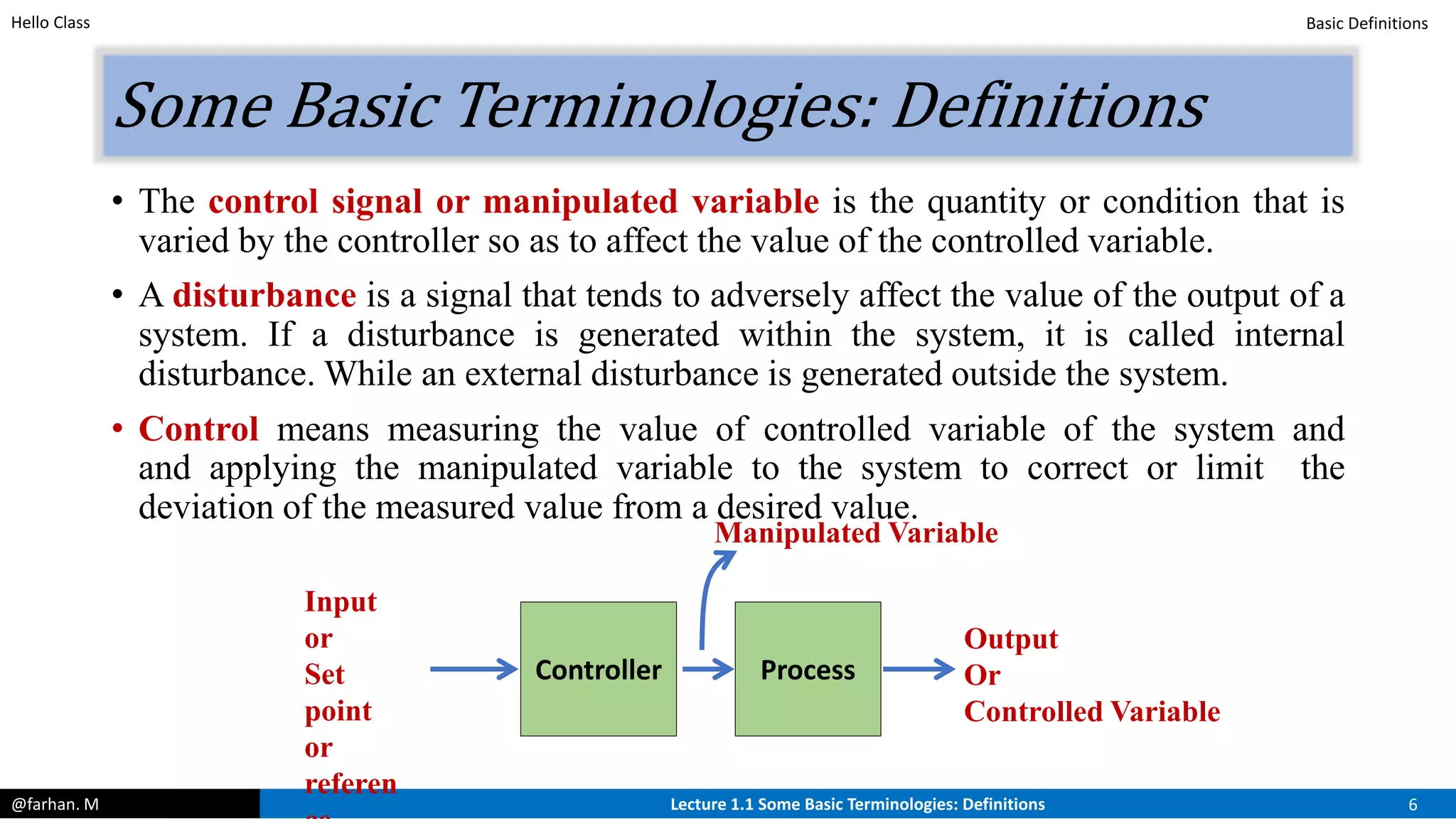
The course will cover both classical and modern control techniques, including transfer functions, state space modeling, stability analysis, and PID control. Prerequisites include a background in differential equations, Laplace transforms, and MATLAB will likely be used. The lecture defines control systems and their basic components like controllers, processes, manipulated and controlled variables, and disturbances.