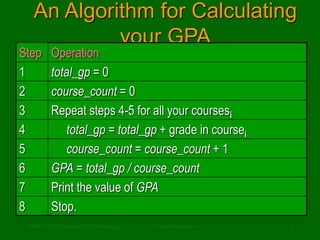
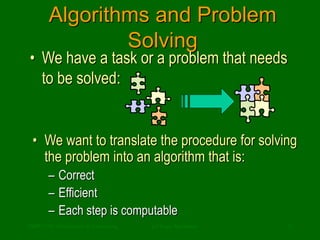
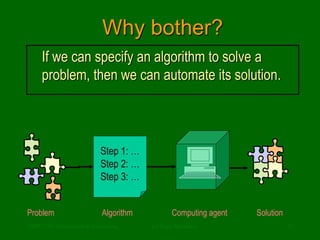
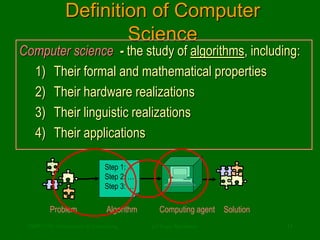
This document discusses the definition of computer science. It begins by addressing common misconceptions, such as the notion that computer science is solely the study of computers, programming, or software applications. It then provides a more accurate definition: that computer science is the study of algorithms, including their properties, implementations in hardware and software, and applications. The document uses examples like recipes and directions to illustrate what algorithms are and how they allow problems to be solved automatically.