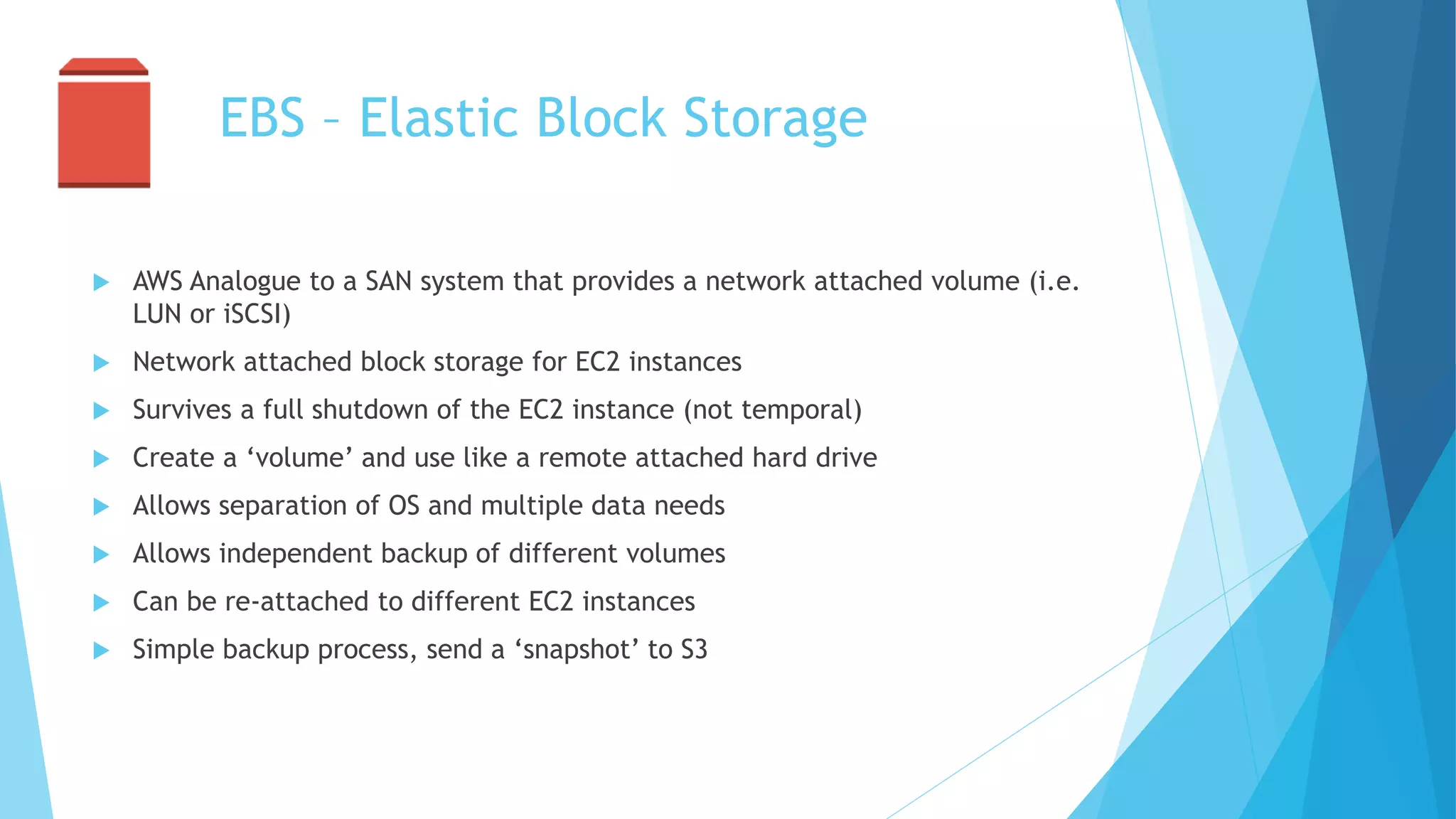
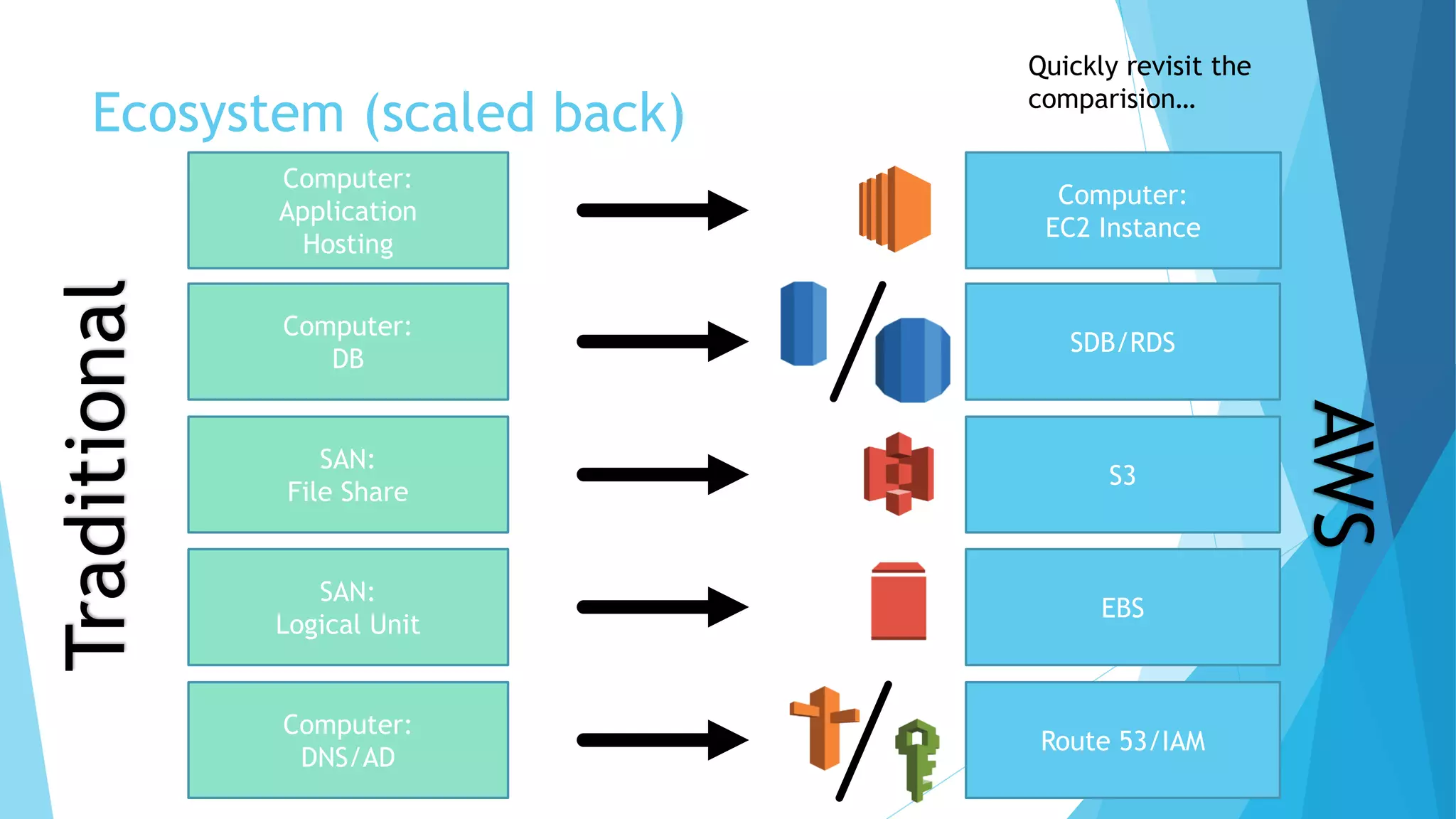
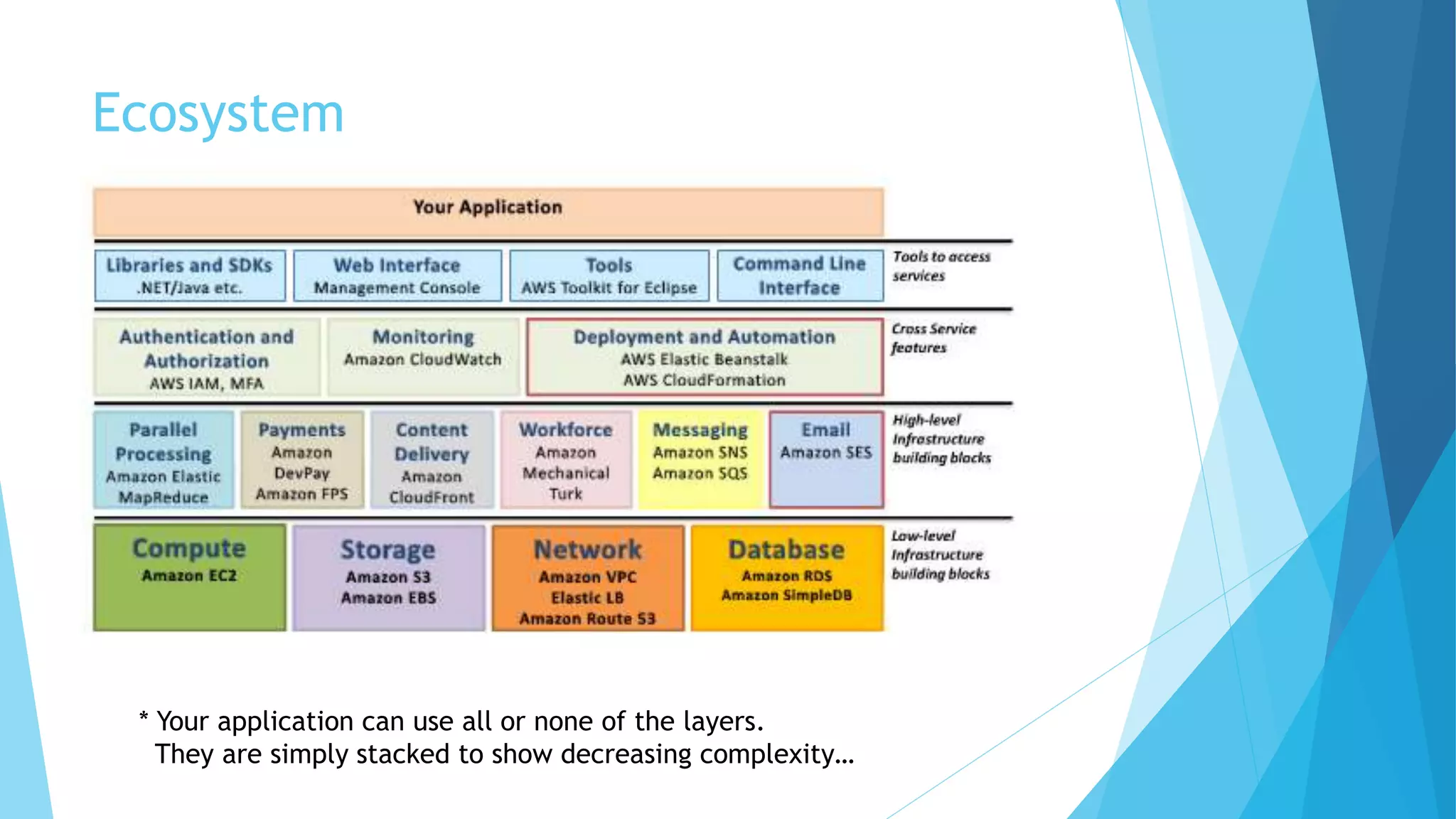
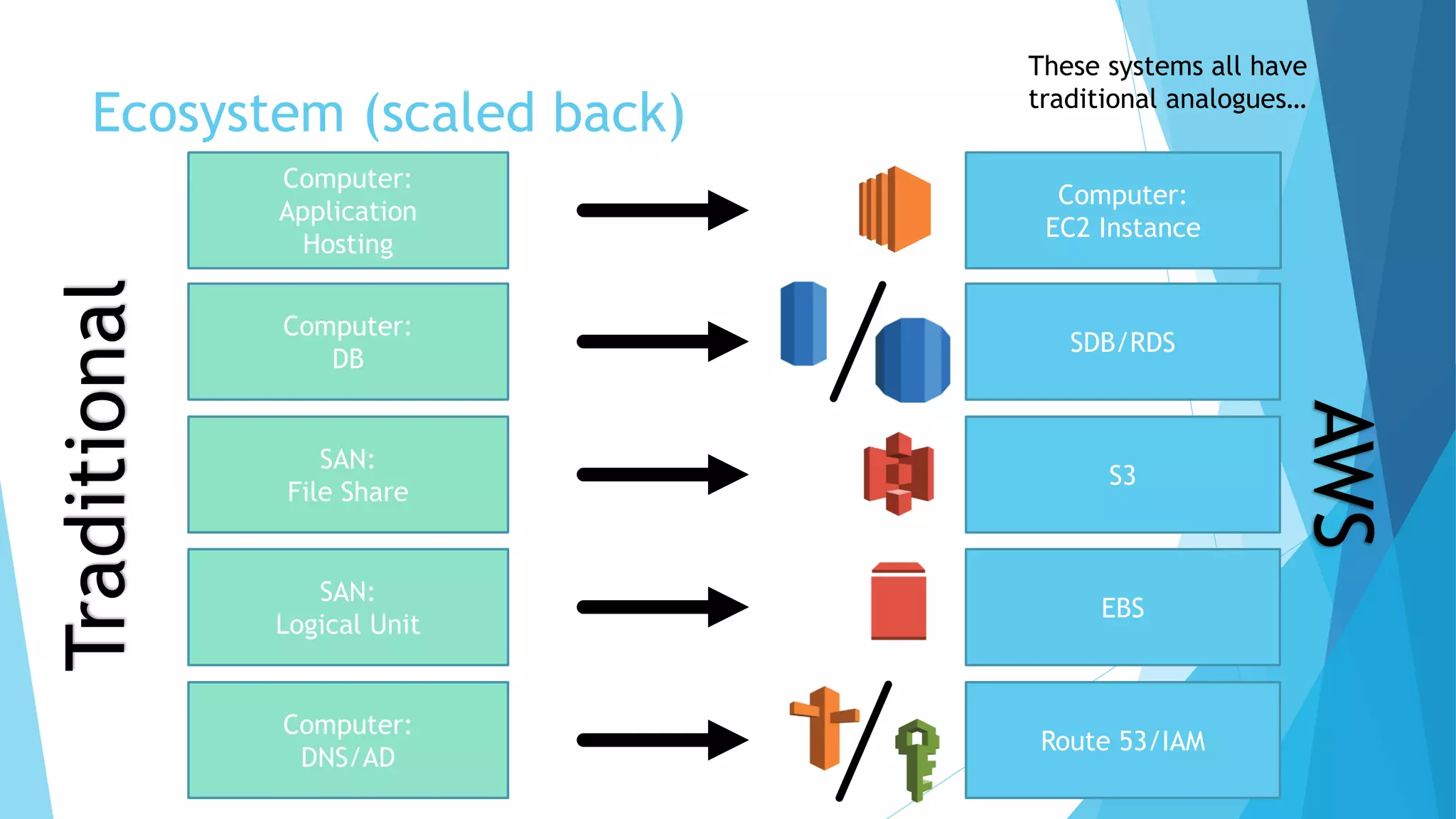
This document provides an overview of Amazon Web Services (AWS) and its core components. It describes AWS as an ecosystem of interconnected services that provides scalable compute power, database storage, file storage, networking and security - with analogues for traditional on-premise IT infrastructure. Key AWS services covered include Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) for virtual servers, Simple Database (SDB) and Relational Database Service (RDS) for databases, Simple Storage Service (S3) for file storage, Elastic Block Storage (EBS) for disk volumes, Route 53 for DNS and Identity and Access Management (IAM) for security and user management.

![EC2 – Elastic Compute Cloud
AWS analogue to a server
Physical or virtual “instance” of a computer
Configurable memory, CPU power, and hard disk space
Can change underlying machine configuration without re-installing
Pre configured and patched version of Windows (or others) available [AMI –
Amazon Machine Instance]
Can turn on and off as needed (only pay while running)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/awsoverview-140520144518-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-AWS-4-2048.jpg)
![S3 – Simple Storage Service
AWS Analogue to a SAN or server with a file share
Shared file storage accessed via a web service
Create ‘buckets’ which are like parent folders
Create ‘items’ with keys to fetch later
Items can be keyed with [group/]file.txt to create the illusion of folders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/awsoverview-140520144518-phpapp01/75/Intro-to-AWS-6-2048.jpg)