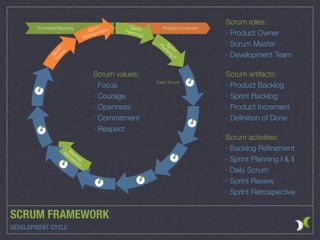
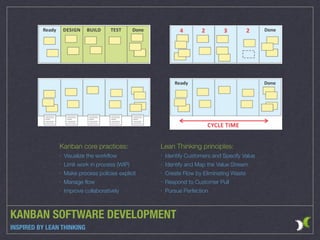
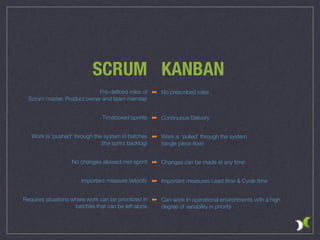
The document outlines various agile methodologies, emphasizing principles from the Agile Manifesto and detailing frameworks such as Scrum and Extreme Programming. It highlights key practices, roles, and values within these frameworks, focusing on customer satisfaction, iterative development, and continuous improvement. Additionally, it contrasts Scrum and Kanban approaches, showcasing their distinct processes and operational environments.