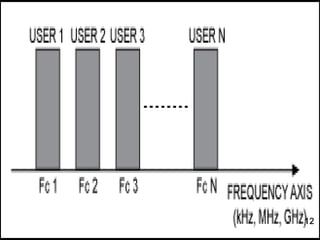
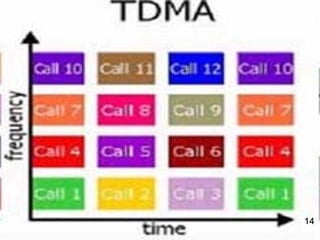
This document discusses 3G wireless technology. 3G allows for faster data transfer rates compared to previous generations, supporting speeds from 128-384 kbps for mobile devices. It evolved from 2G technologies like GSM. 3G uses CDMA and splits signals into parts, using coding to identify destinations. Main 3G technologies include HSPA, which enables speeds up to 3.6 Mbps, and HSPA+, enabling up to 21 Mbps. To use 3G, a user needs a compatible device, a service provider subscription, and a SIM or data card connected to the provider's 3G network. Disadvantages of 3G include high infrastructure costs, potential health impacts, and initially high service prices.