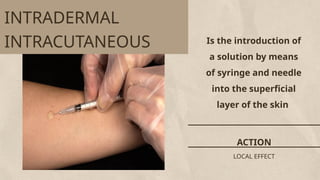
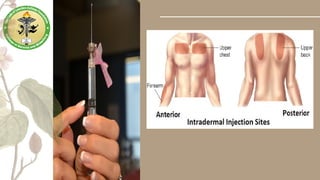
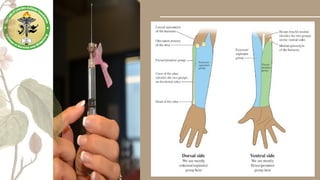
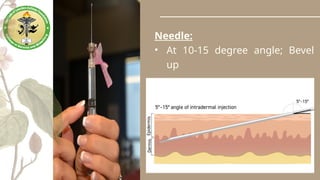
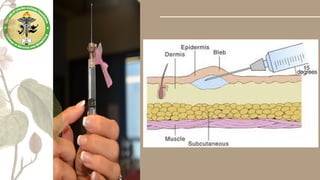
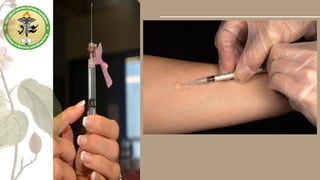
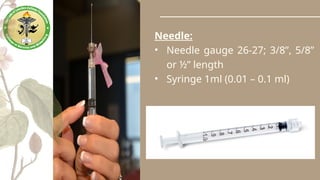
Parenteral medication administration involves administering drugs via injection using aseptic techniques, requiring specific skills to ensure correct drug delivery. Careful selection of the injection site is crucial to avoid complications such as infection or discomfort, with considerations for site cleanliness and needle technique. Minimizing patient discomfort during the procedure is essential, and nurses are advised to follow best practices for injection preparation and administration.