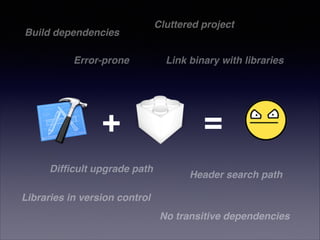
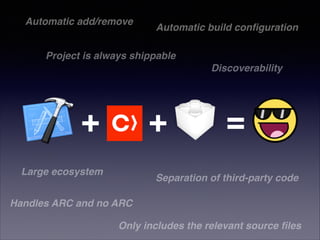
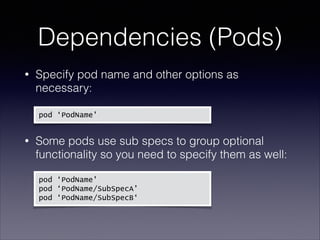
The document provides a comprehensive guide on using CocoaPods for dependency management in Xcode, detailing the installation process and outlining the creation of a Podfile. It discusses the various configurations for specifying dependencies, versioning, and handling targets within an Xcode project. Additionally, it emphasizes best practices for using pods effectively, including checking pod sources and documentation.




















![Targets
Use link_with to specify multiple targets for all
pod dependencies:
pod ‘PodName’
link_with [‘MyApp’,’MyAppDemo’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoapods-140123202709-phpapp02/85/Using-Cocoapods-24-320.jpg)


![Hooks
post_install
Make any changes to the generated Pods project,
or any other tasks you might want to perform.
!
post_install do |installer_representation|
installer_representation.project.targets.each do |target|
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
config.build_settings['GCC_ENABLE_OBJC_GC'] = 'supported'
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoapods-140123202709-phpapp02/85/Using-Cocoapods-27-320.jpg)


