Embed presentation
Downloaded 48 times








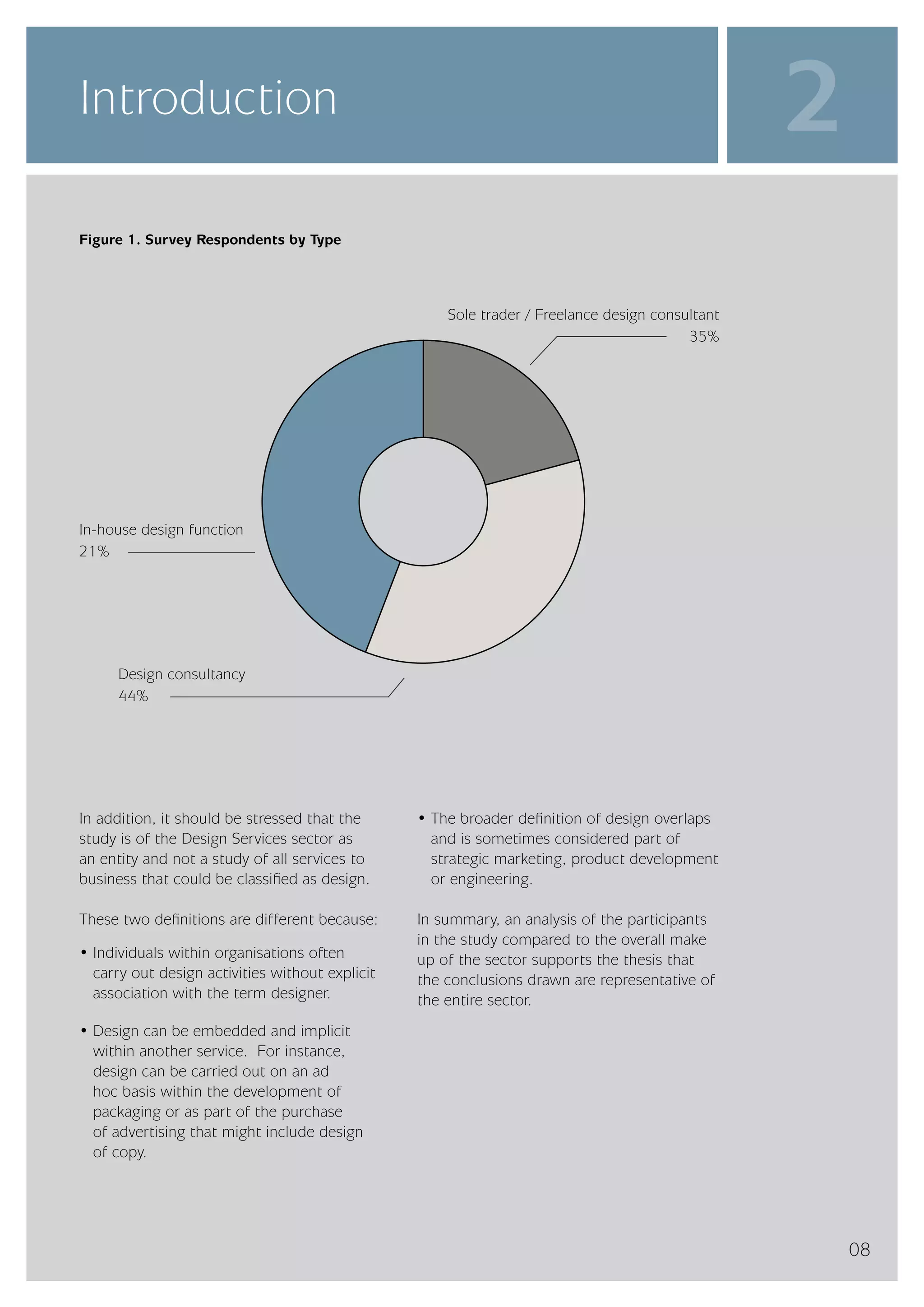
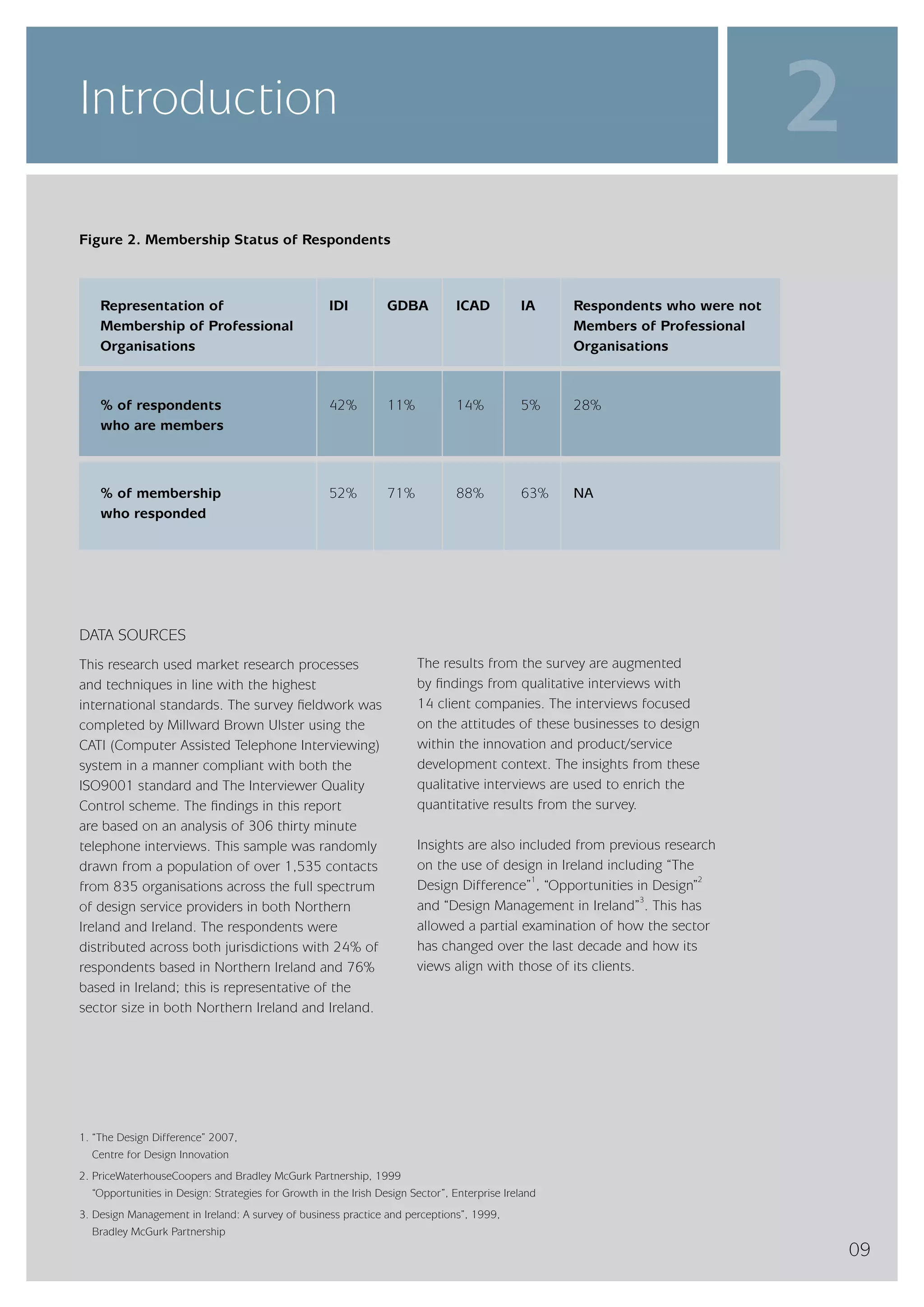

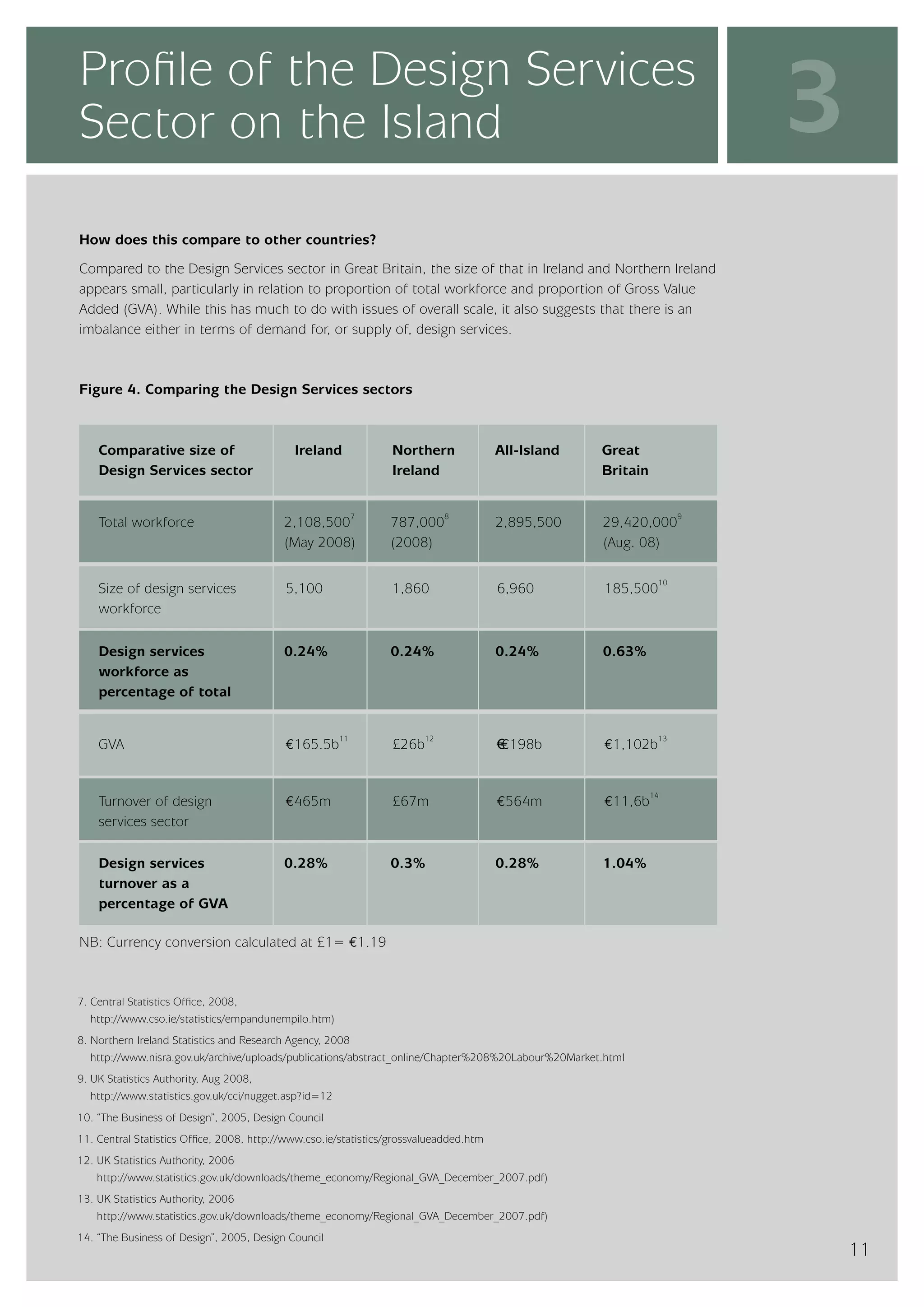

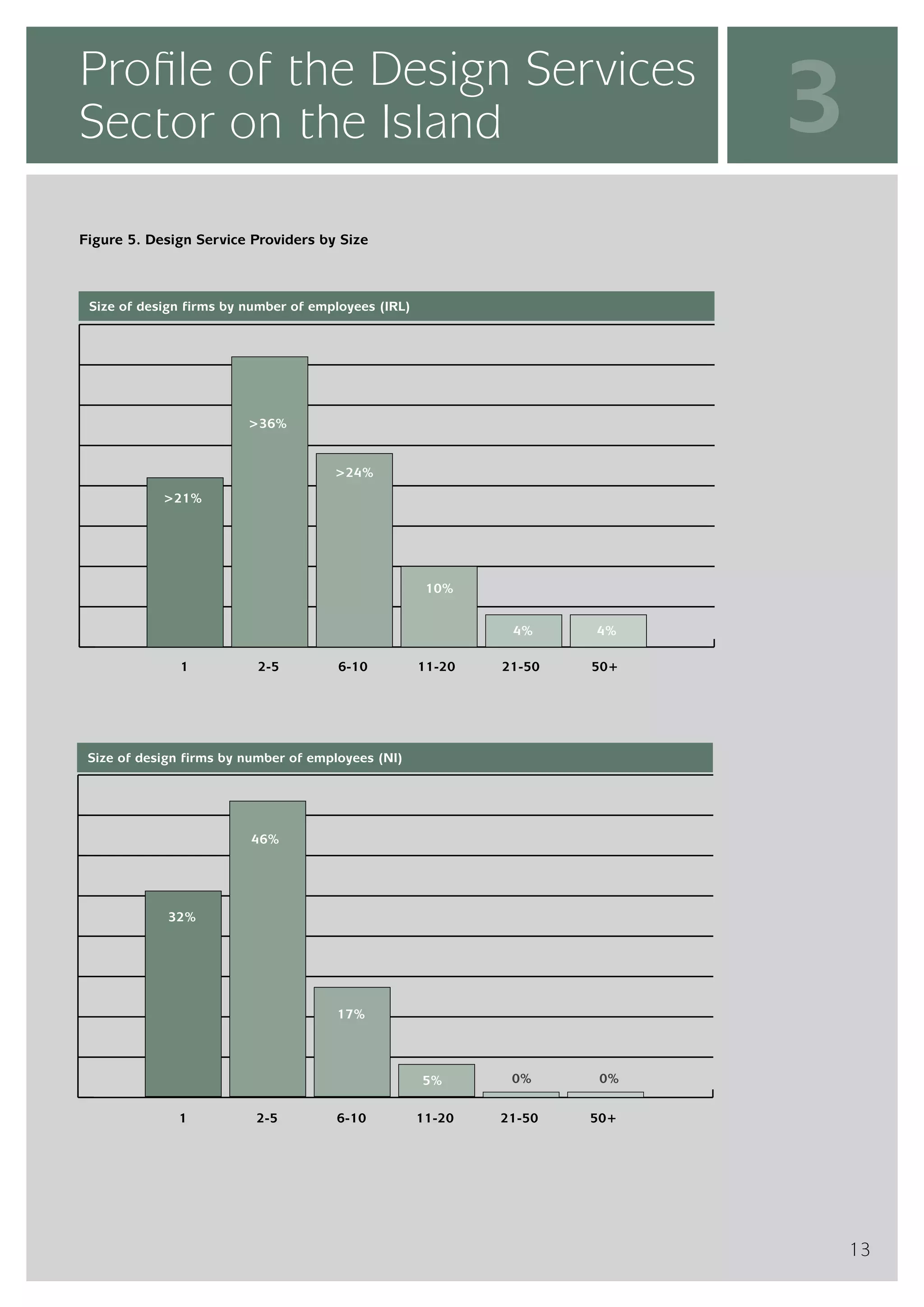
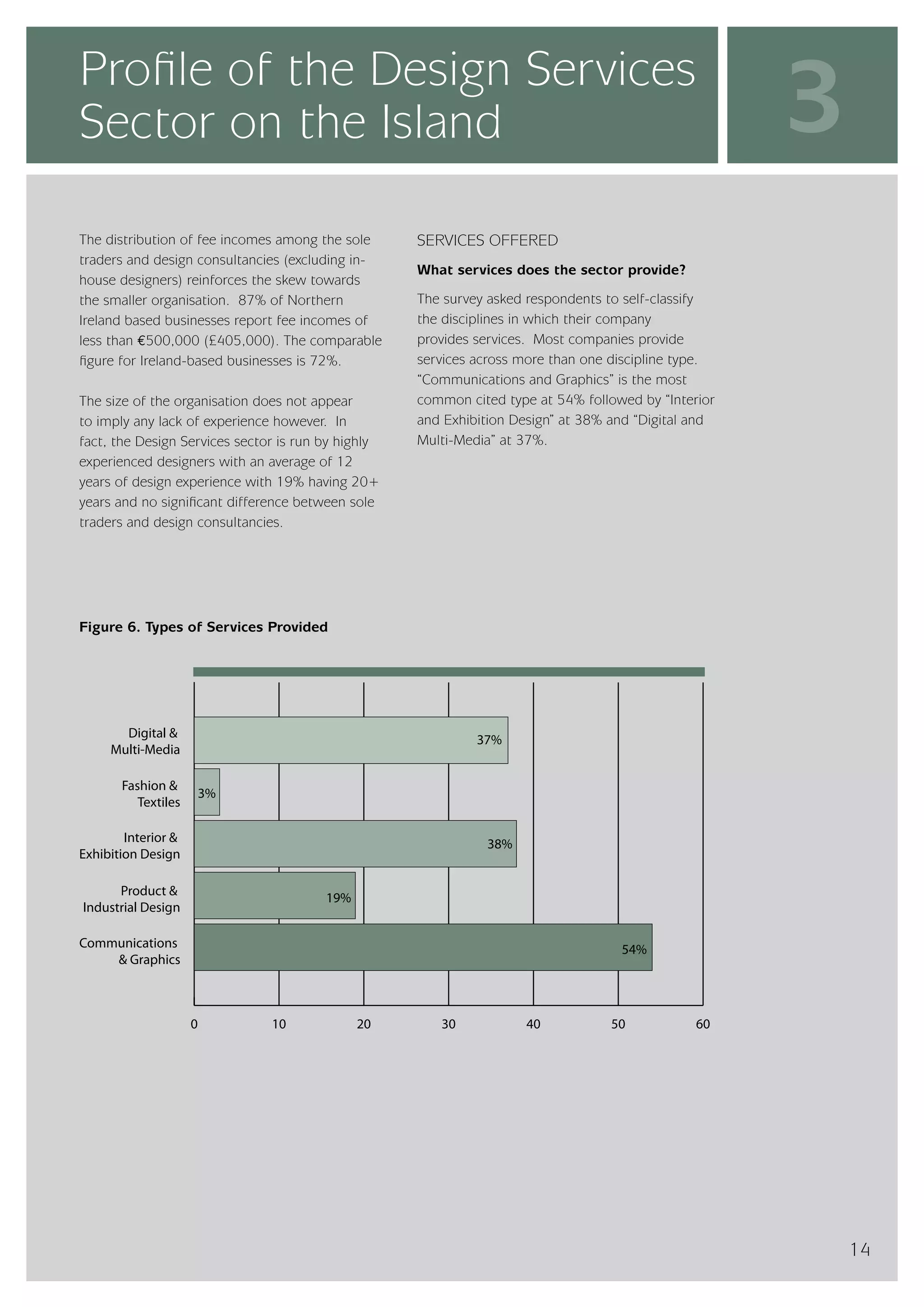
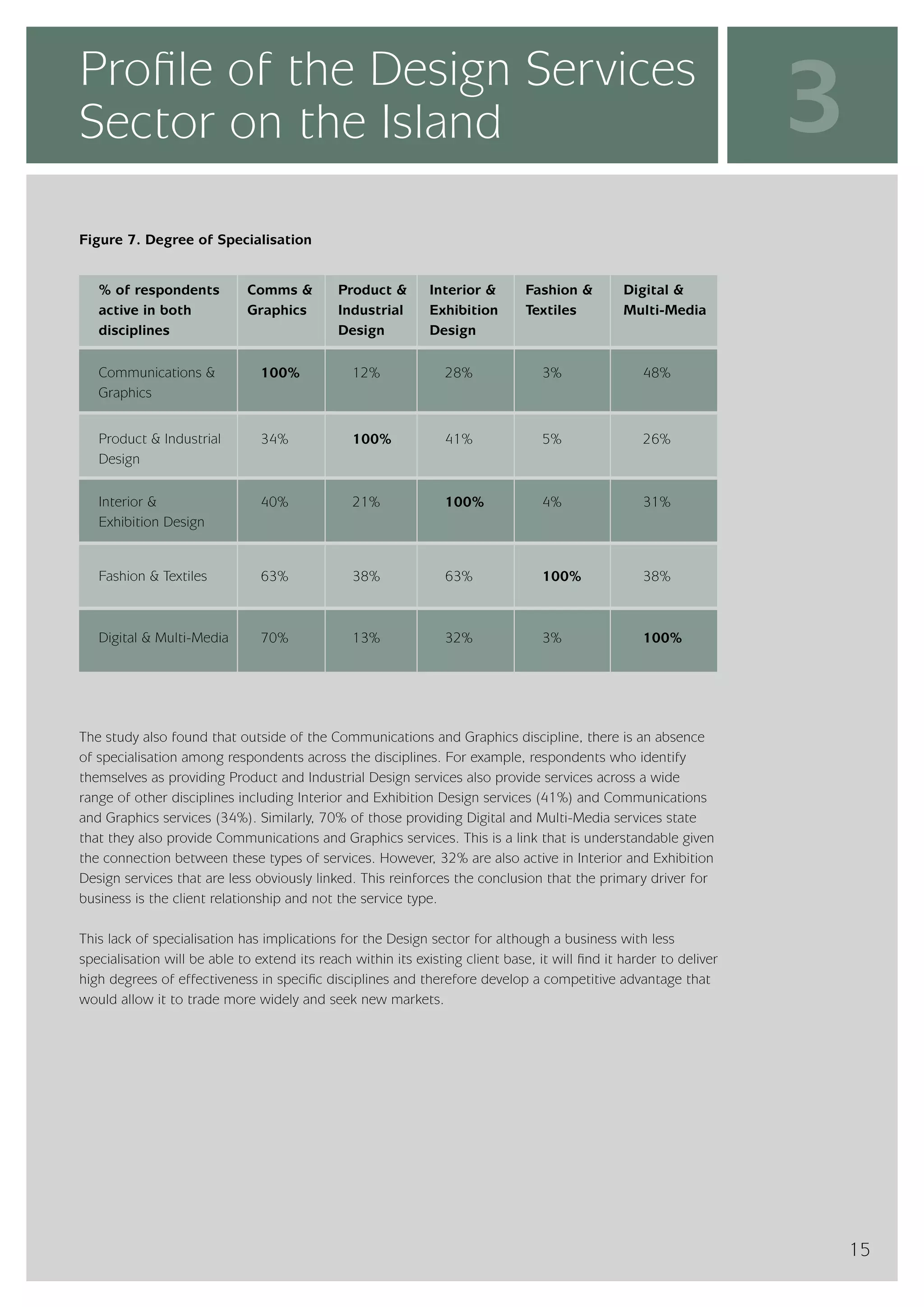
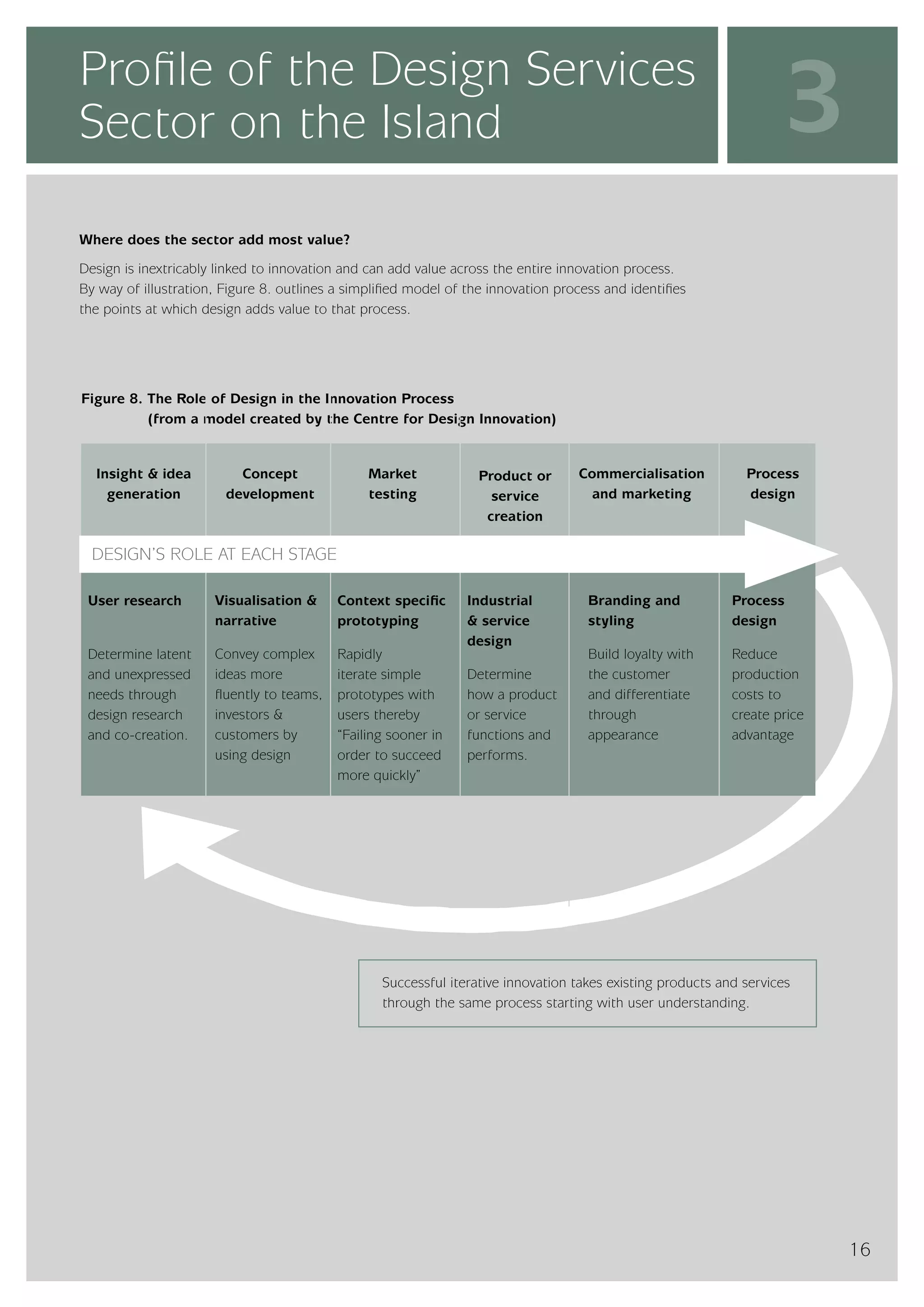
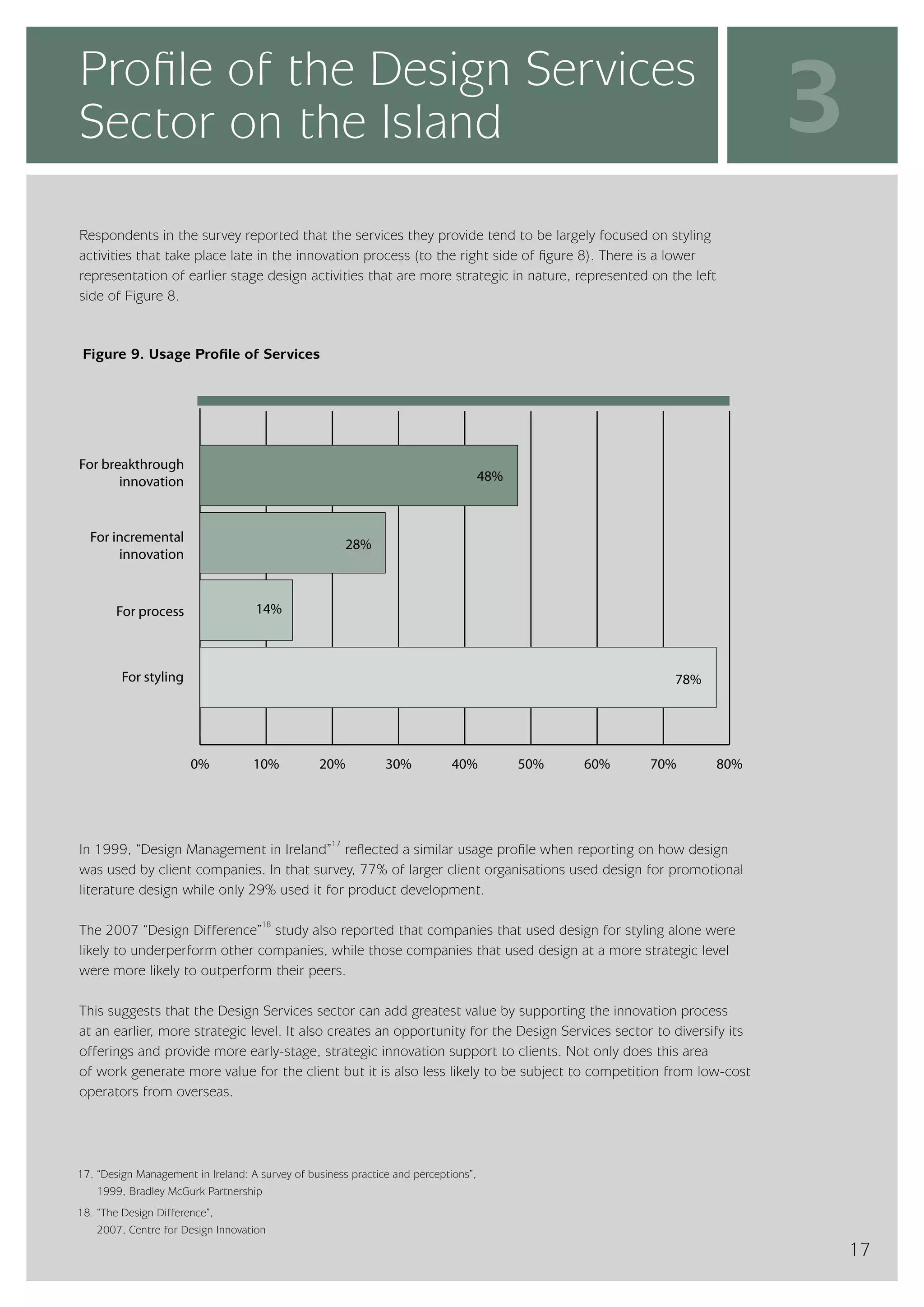
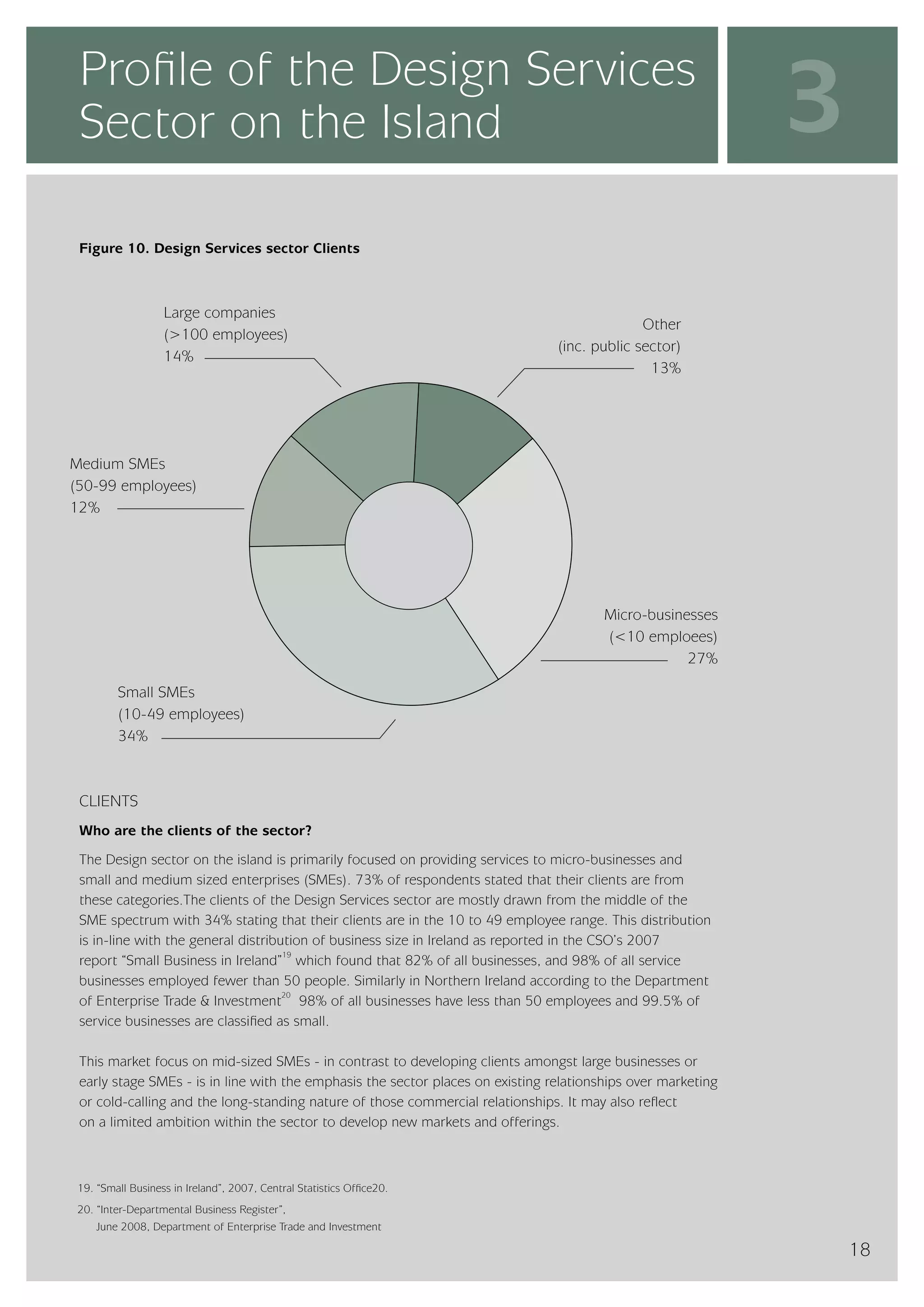

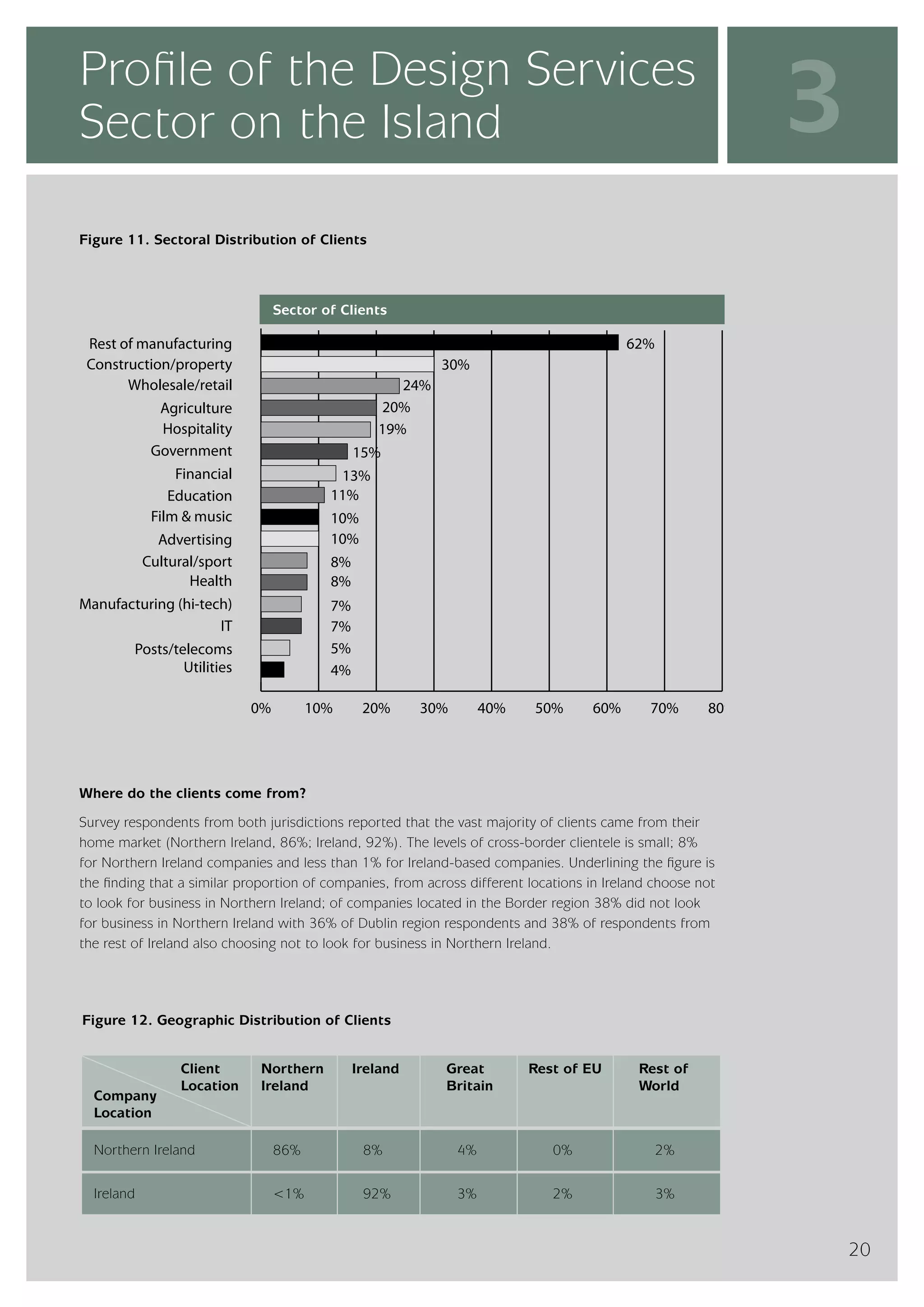
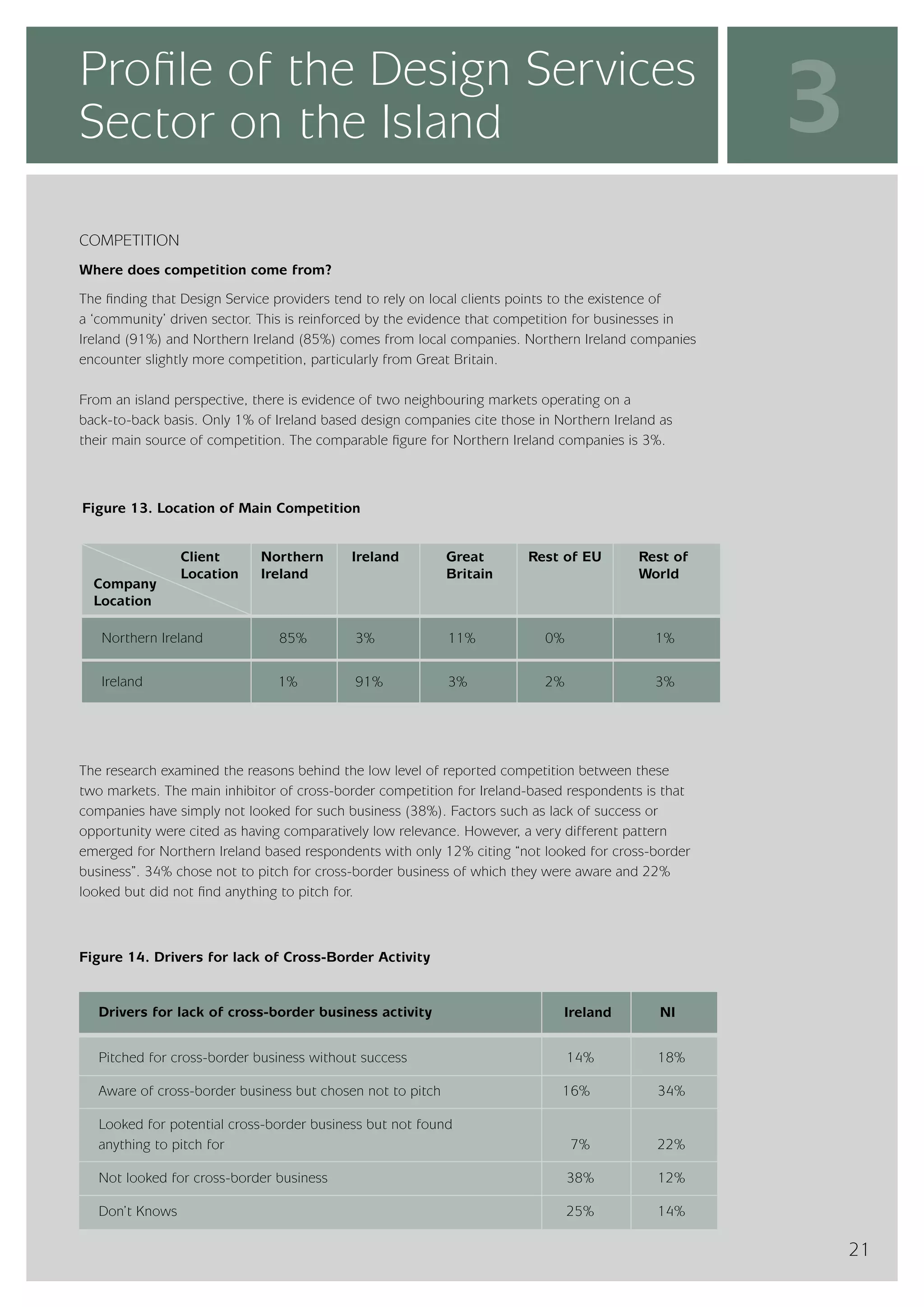
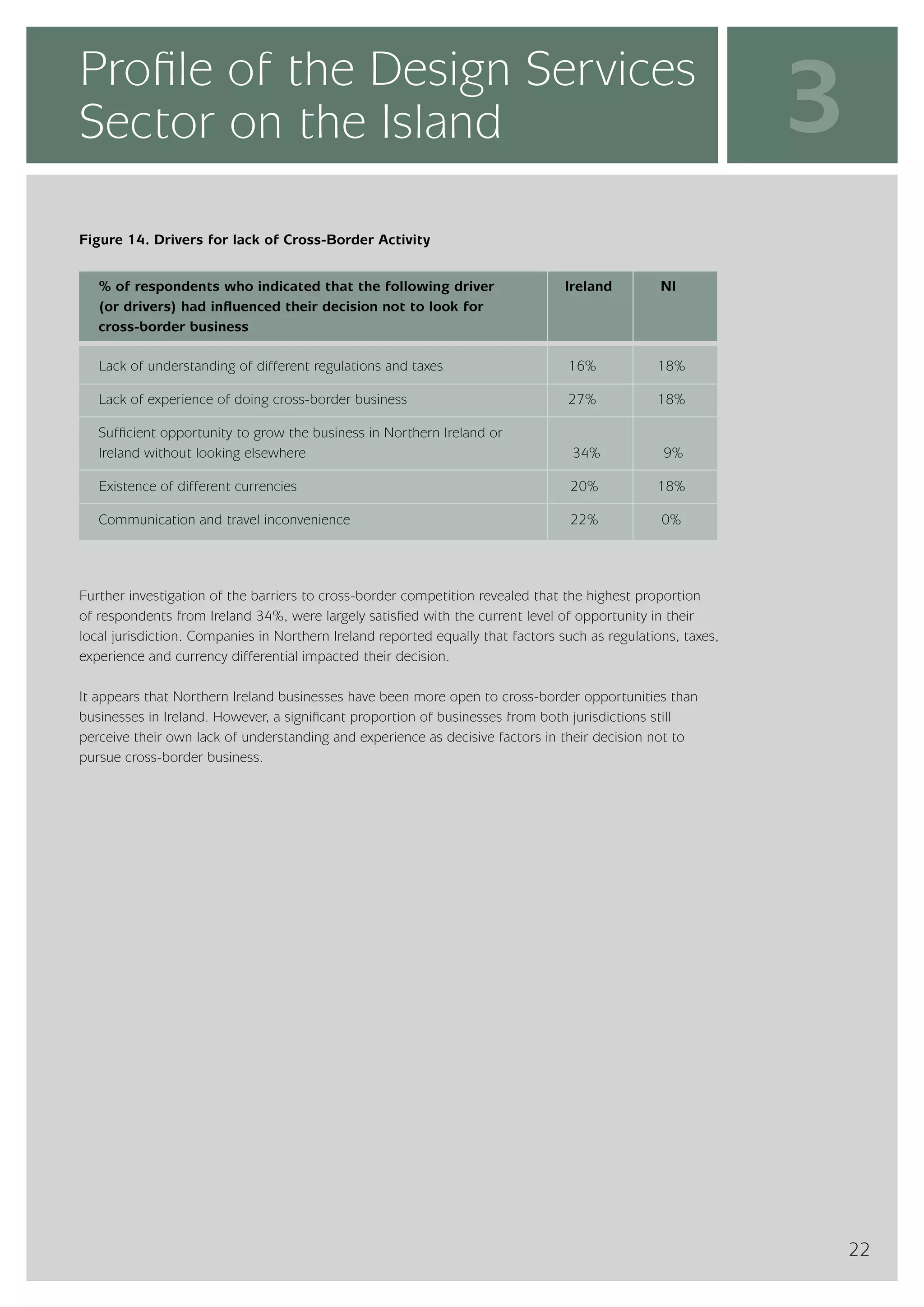
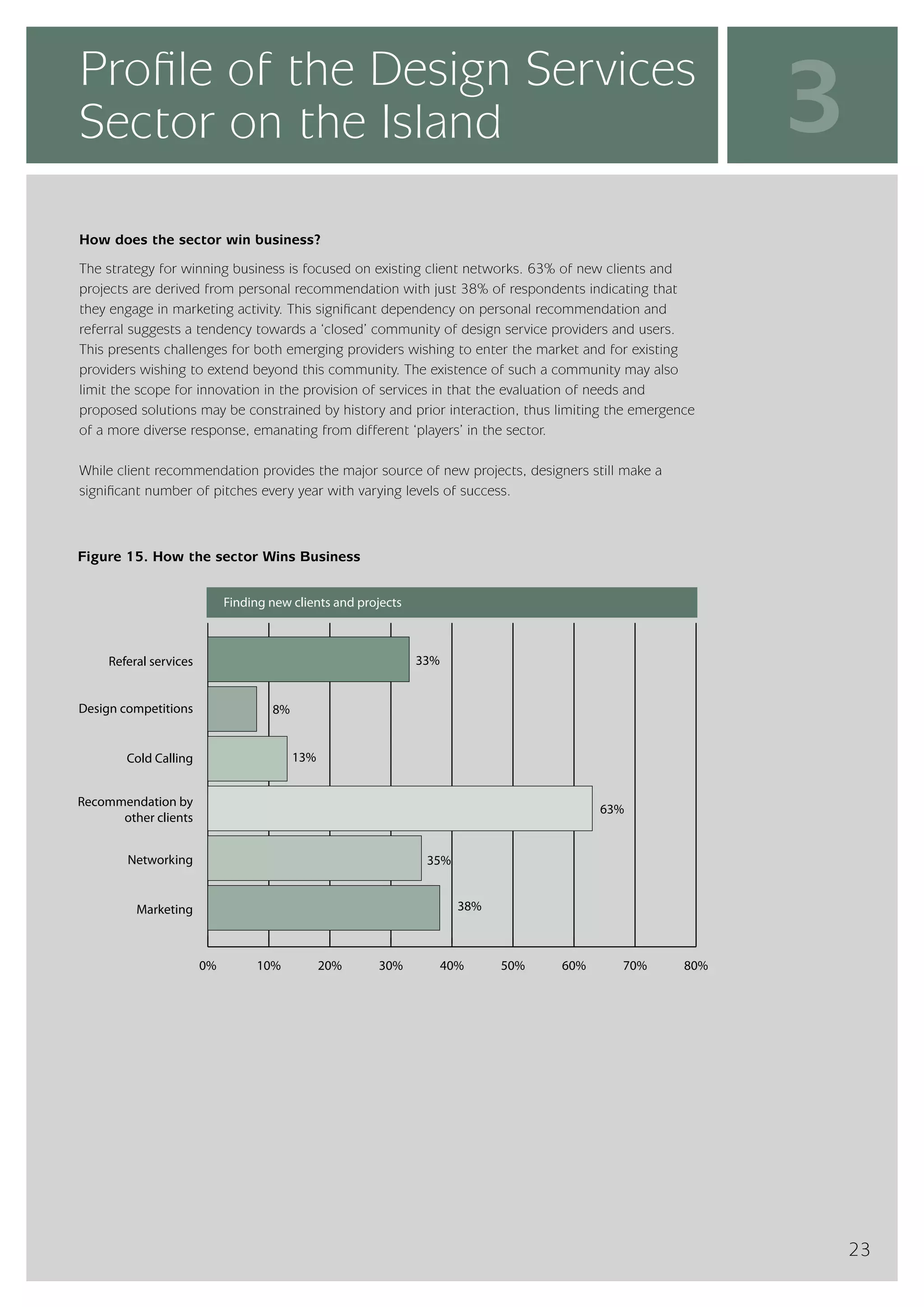
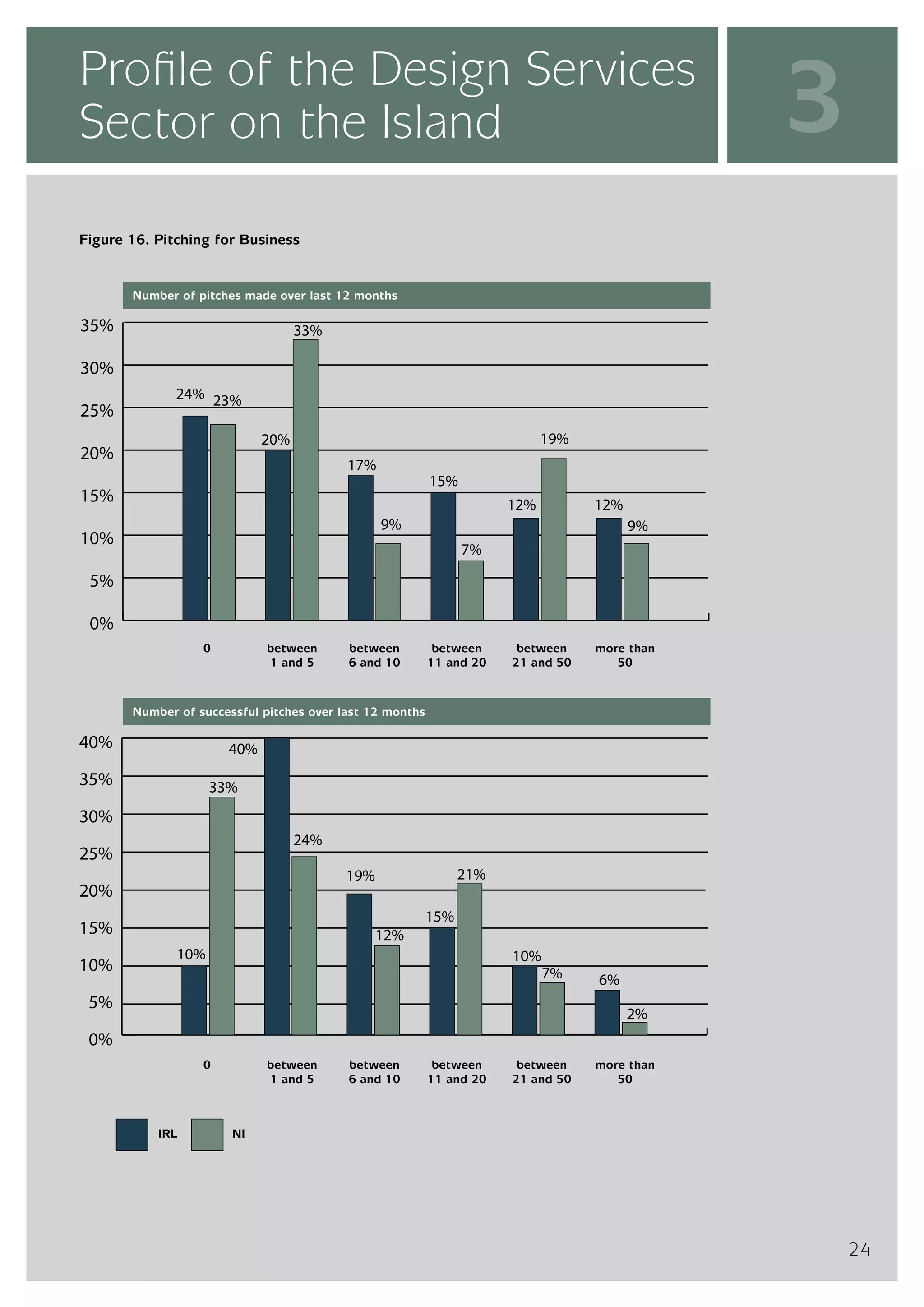
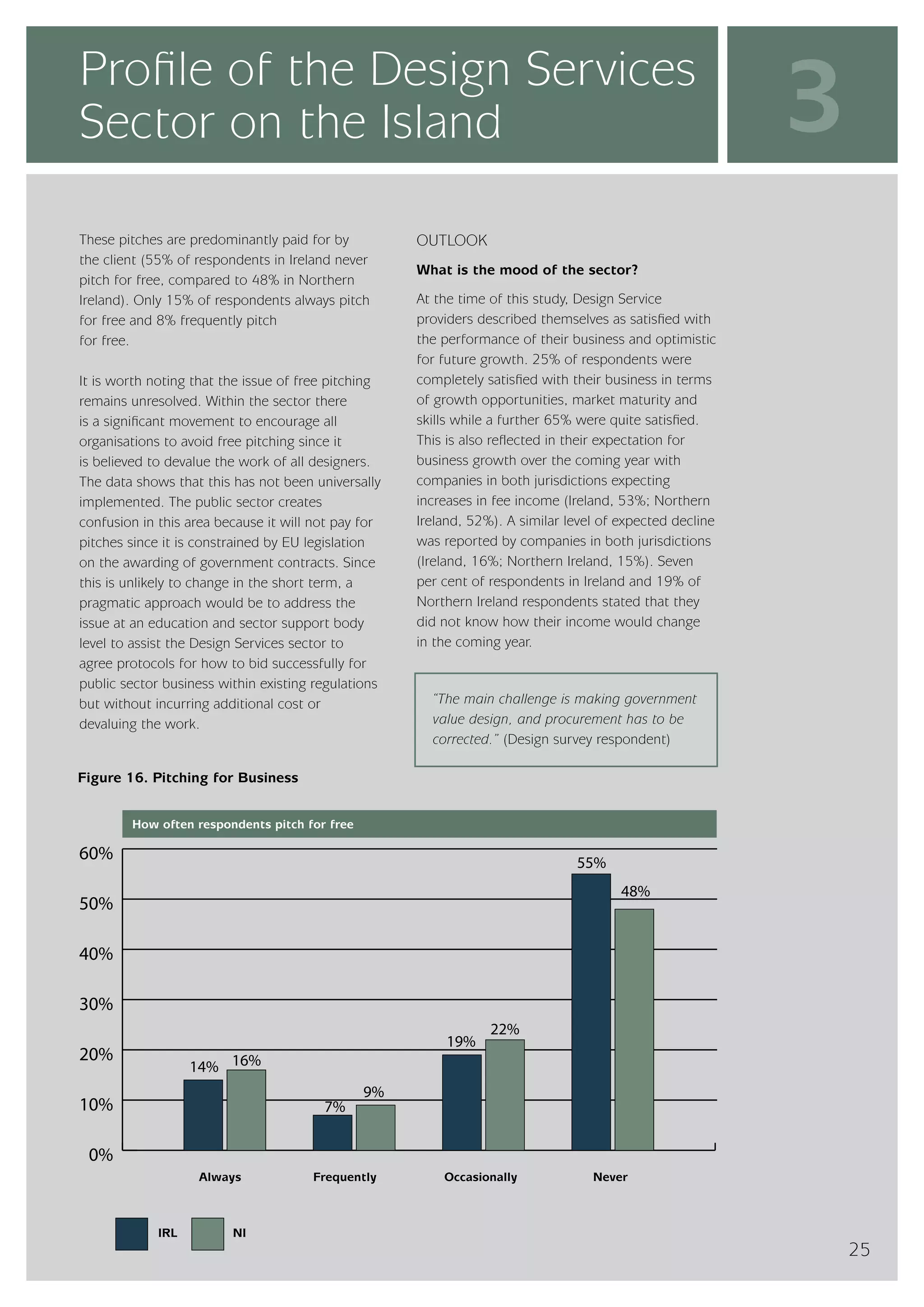










The design services sector on the island of Ireland employs approximately 6,960 people and generates total annual turnover of €545 million. However, the sector is quite small relative to the size of the economy, with design services employment accounting for only 0.24% of the total workforce. In comparison, the design services sector in Great Britain is over 25 times larger based on employment figures. The report finds that while the Irish sector has grown in recent years, the rate of growth has lagged behind that of the broader services economy. This suggests an imbalance between the demand for and supply of design services on the island.


































