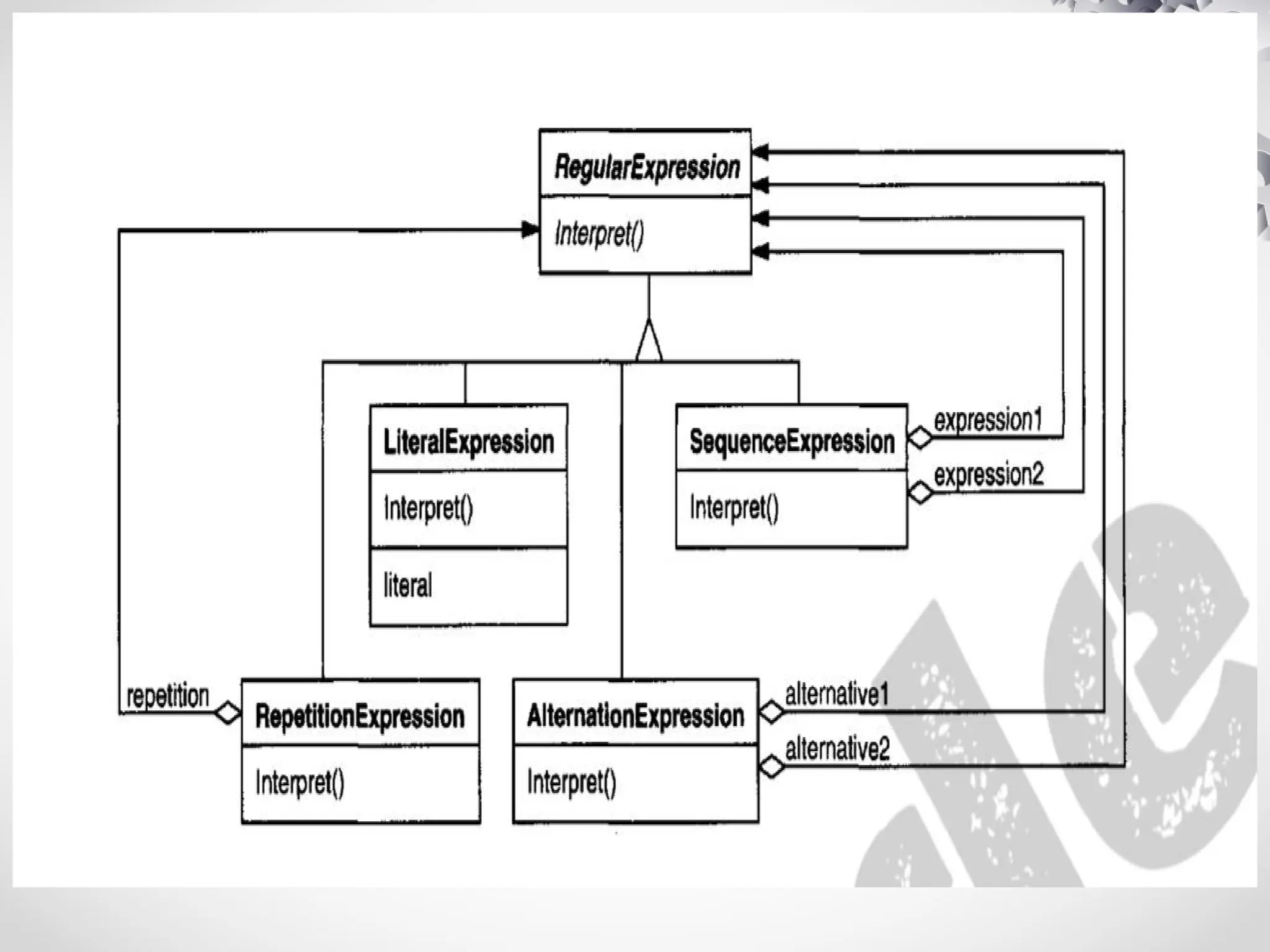
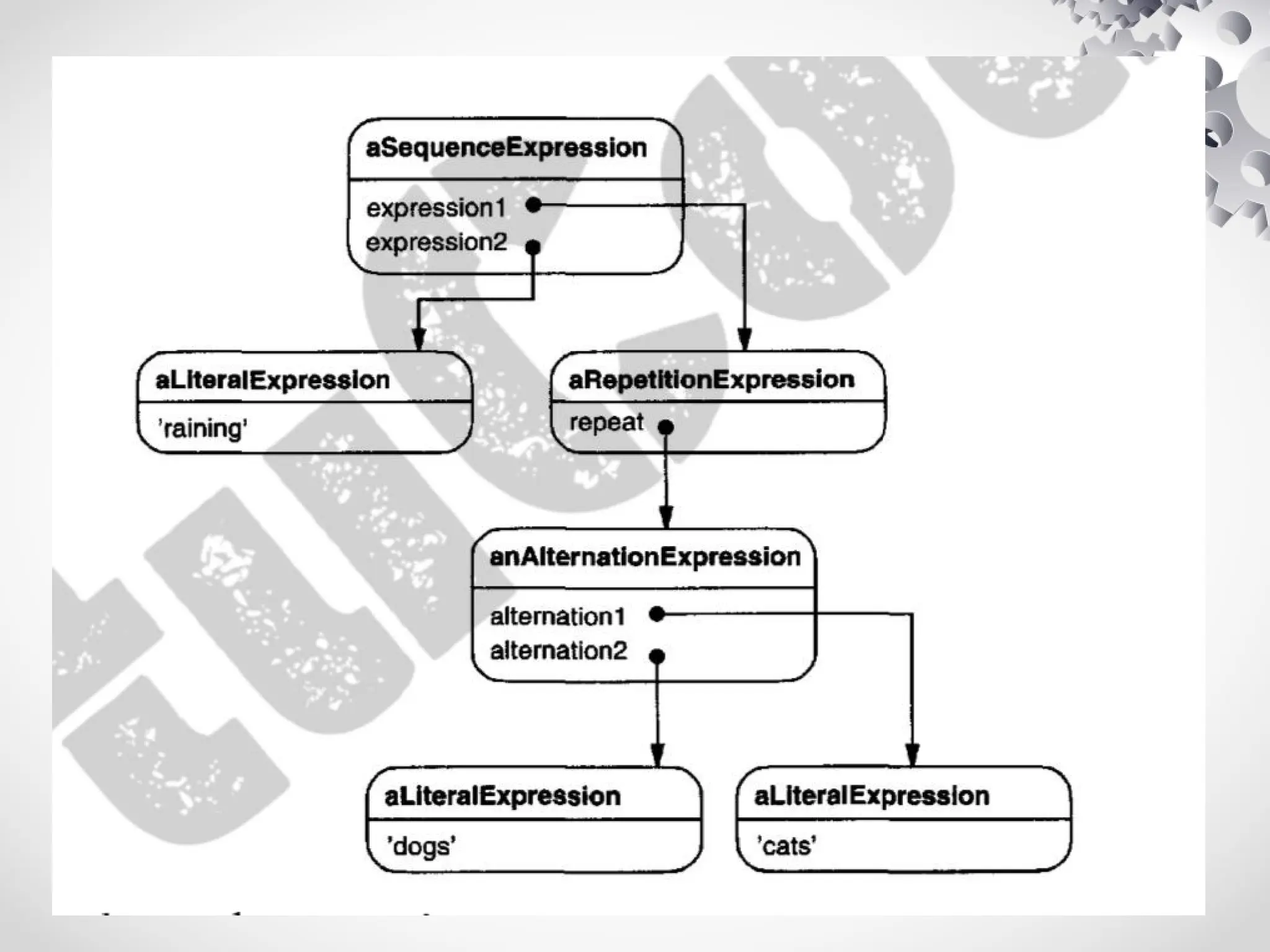
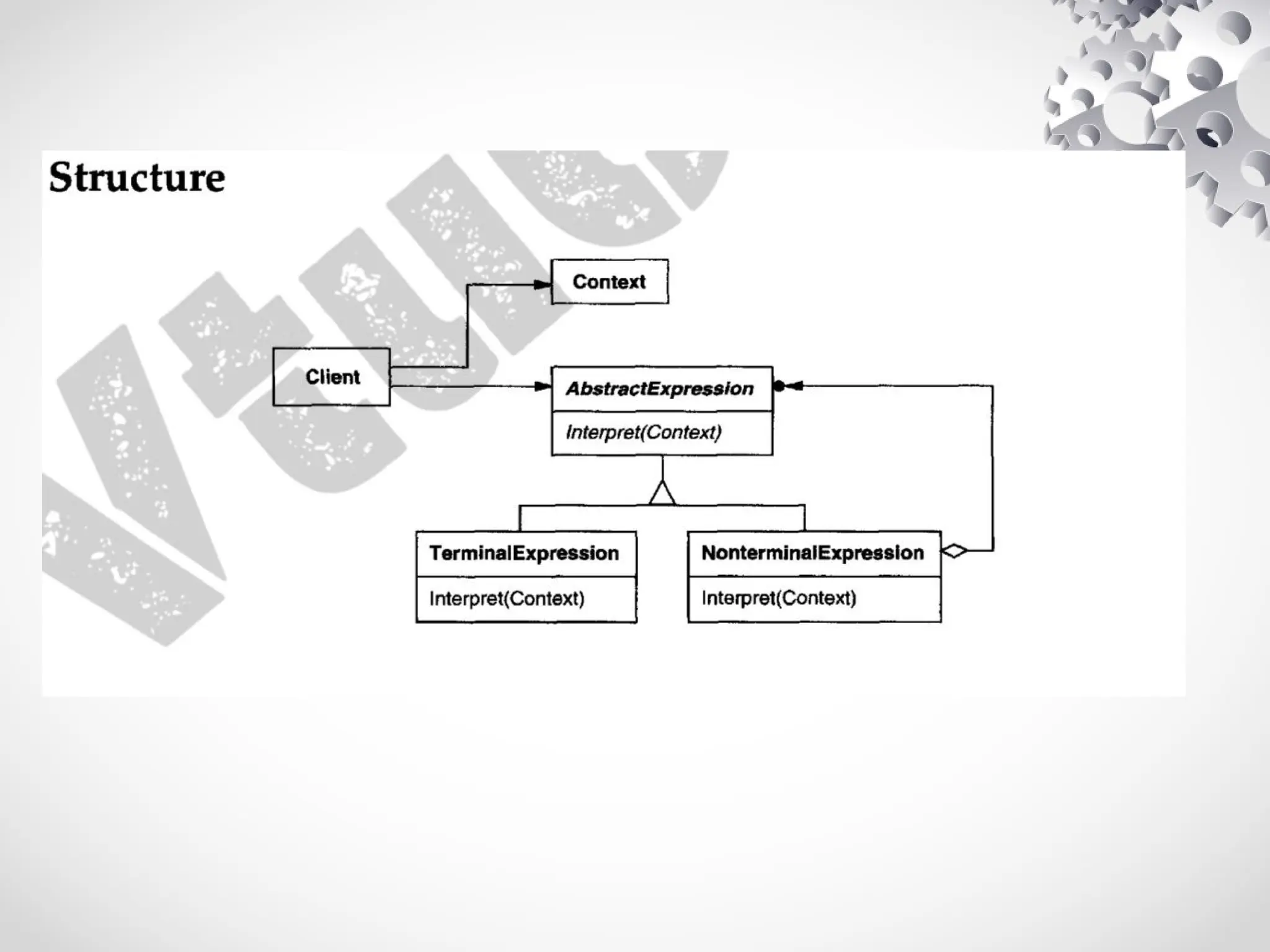
The interpreter design pattern uses classes to represent grammar rules, allowing the construction of abstract syntax trees (ASTs) for interpreting expressions. Key components include abstract expression classes for literals, alternatives, sequences, and repetitions, making it suitable for simple grammars where efficiency is not critical. While it simplifies grammar implementation and extension, it can be complex to maintain for intricate grammars.