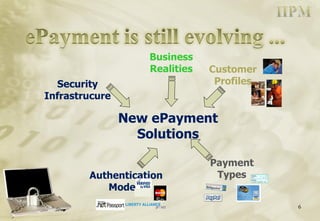
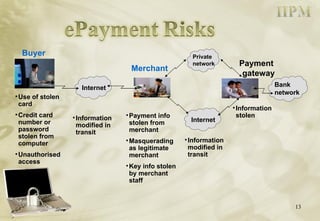
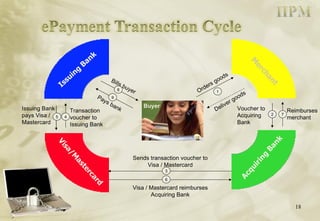
The document discusses electronic payment systems. It defines electronic payments as using an electronic surrogate for financial tender backed by financial institutions. It discusses different types of electronic payment methods including card-based payments, direct account debiting, electronic wallets, digital cheques, and security protocols like SET. It also covers principles for secure electronic payments such as trust, security, identification, authorization, integrity and accountability.